Jimmy Xin
PutnamBench: Evaluating Neural Theorem-Provers on the Putnam Mathematical Competition
Jul 15, 2024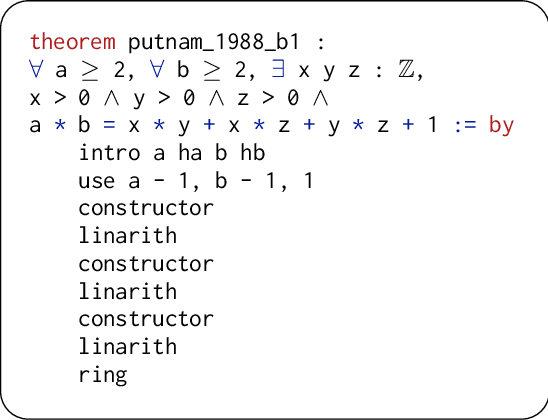


Abstract:We present PutnamBench, a new multilingual benchmark for evaluating the ability of neural theorem-provers to solve competition mathematics problems. PutnamBench consists of 1697 hand-constructed formalizations of 640 theorems sourced from the William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition, the premier undergraduate-level mathematics competition in North America. All the theorems have formalizations in Lean 4 and Isabelle; a substantial subset also has Coq formalizations. Proving the theorems requires significant problem-solving ability and proficiency in a broad range of topics taught in undergraduate mathematics courses. We use PutnamBench to evaluate several established neural and symbolic theorem-provers. These approaches can only solve a handful of the PutnamBench problems, establishing the benchmark as a difficult open challenge for research on neural theorem-proving. PutnamBench is available at https://github.com/trishullab/PutnamBench.
PLUNDER: Probabilistic Program Synthesis for Learning from Unlabeled and Noisy Demonstrations
Mar 02, 2023
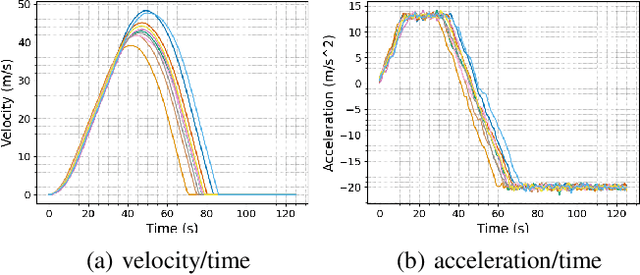


Abstract:Learning from demonstration (LfD) is a widely researched paradigm for teaching robots to perform novel tasks. LfD works particularly well with program synthesis since the resulting programmatic policy is data efficient, interpretable, and amenable to formal verification. However, existing synthesis approaches to LfD rely on precise and labeled demonstrations and are incapable of reasoning about the uncertainty inherent in human decision-making. In this paper, we propose PLUNDER, a new LfD approach that integrates a probabilistic program synthesizer in an expectation-maximization (EM) loop to overcome these limitations. PLUNDER only requires unlabeled low-level demonstrations of the intended task (e.g., remote-controlled motion trajectories), which liberates end-users from providing explicit labels and facilitates a more intuitive LfD experience. PLUNDER also generates a probabilistic policy that captures actuation errors and the uncertainties inherent in human decision making. Our experiments compare PLUNDER with state-of the-art LfD techniques and demonstrate its advantages across different robotic tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge