Jiaying Zhang
GeoRA: Geometry-Aware Low-Rank Adaptation for RLVR
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) is crucial for advancing large-scale reasoning models. However, existing parameter-efficient methods, such as PiSSA and MiLoRA, are designed for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and do not account for the distinct optimization dynamics and geometric structures of RLVR. Applying these methods directly leads to spectral collapse and optimization instability, which severely limit model performance. Meanwhile, alternative approaches that leverage update sparsity encounter significant efficiency bottlenecks on modern hardware due to unstructured computations. To address these challenges, we propose GeoRA (Geometry-Aware Low-Rank Adaptation), which exploits the anisotropic and compressible nature of RL update subspaces. GeoRA initializes adapters by extracting principal directions via Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) within a geometrically constrained subspace while freezing the residual components. This method preserves the pre-trained geometric structure and enables efficient GPU computation through dense operators. Experiments on Qwen and Llama demonstrate that GeoRA mitigates optimization bottlenecks caused by geometric misalignment. It consistently outperforms established low-rank baselines on key mathematical benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results. Moreover, GeoRA shows superior generalization and resilience to catastrophic forgetting in out-of-domain tasks.
Enriching Medcial Terminology Knowledge Bases via Pre-trained Language Model and Graph Convolutional Network
Sep 02, 2019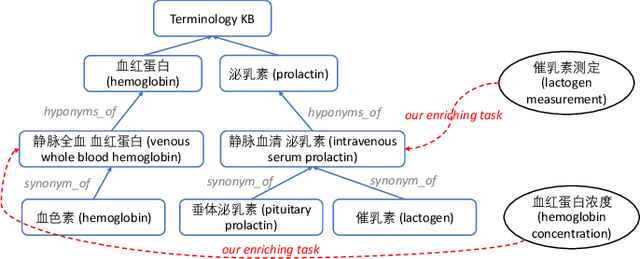
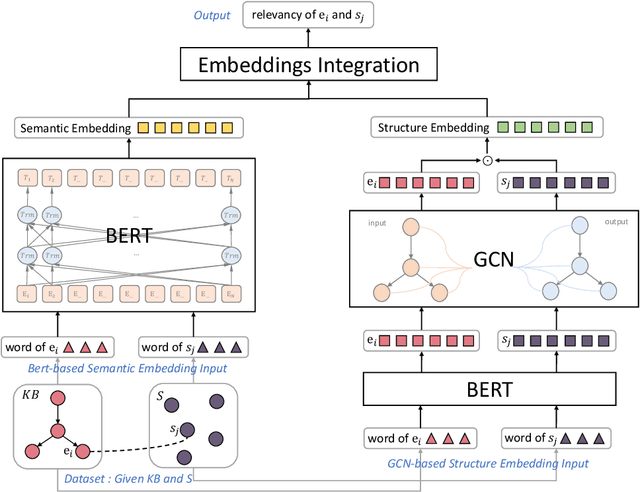
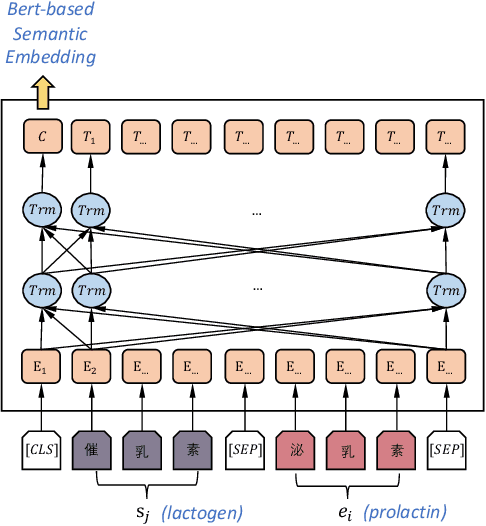
Abstract:Enriching existing medical terminology knowledge bases (KBs) is an important and never-ending work for clinical research because new terminology alias may be continually added and standard terminologies may be newly renamed. In this paper, we propose a novel automatic terminology enriching approach to supplement a set of terminologies to KBs. Specifically, terminology and entity characters are first fed into pre-trained language model to obtain semantic embedding. The pre-trained model is used again to initialize the terminology and entity representations, then they are further embedded through graph convolutional network to gain structure embedding. Afterwards, both semantic and structure embeddings are combined to measure the relevancy between the terminology and the entity. Finally, the optimal alignment is achieved based on the order of relevancy between the terminology and all the entities in the KB. Experimental results on clinical indicator terminology KB, collected from 38 top-class hospitals of Shanghai Hospital Development Center, show that our proposed approach outperforms baseline methods and can effectively enrich the KB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge