Jiaying Gong
Sci-LoRA: Mixture of Scientific LoRAs for Cross-Domain Lay Paraphrasing
May 24, 2025Abstract:Lay paraphrasing aims to make scientific information accessible to audiences without technical backgrounds. However, most existing studies focus on a single domain, such as biomedicine. With the rise of interdisciplinary research, it is increasingly necessary to comprehend knowledge spanning multiple technical fields. To address this, we propose Sci-LoRA, a model that leverages a mixture of LoRAs fine-tuned on multiple scientific domains. In particular, Sci-LoRA dynamically generates and applies weights for each LoRA, enabling it to adjust the impact of different domains based on the input text, without requiring explicit domain labels. To balance domain-specific knowledge and generalization across various domains, Sci-LoRA integrates information at both the data and model levels. This dynamic fusion enhances the adaptability and performance across various domains. Experimental results across twelve domains on five public datasets show that Sci-LoRA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art large language models and demonstrates flexible generalization and adaptability in cross-domain lay paraphrasing.
Visual Zero-Shot E-Commerce Product Attribute Value Extraction
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Existing zero-shot product attribute value (aspect) extraction approaches in e-Commerce industry rely on uni-modal or multi-modal models, where the sellers are asked to provide detailed textual inputs (product descriptions) for the products. However, manually providing (typing) the product descriptions is time-consuming and frustrating for the sellers. Thus, we propose a cross-modal zero-shot attribute value generation framework (ViOC-AG) based on CLIP, which only requires product images as the inputs. ViOC-AG follows a text-only training process, where a task-customized text decoder is trained with the frozen CLIP text encoder to alleviate the modality gap and task disconnection. During the zero-shot inference, product aspects are generated by the frozen CLIP image encoder connected with the trained task-customized text decoder. OCR tokens and outputs from a frozen prompt-based LLM correct the decoded outputs for out-of-domain attribute values. Experiments show that ViOC-AG significantly outperforms other fine-tuned vision-language models for zero-shot attribute value extraction.
VTechAGP: An Academic-to-General-Audience Text Paraphrase Dataset and Benchmark Models
Nov 07, 2024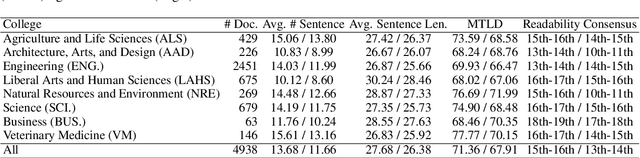
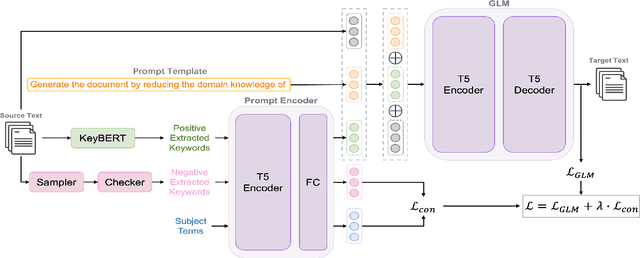
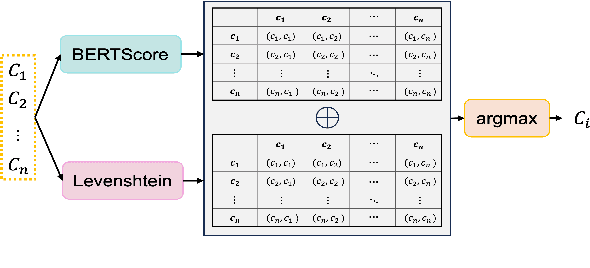
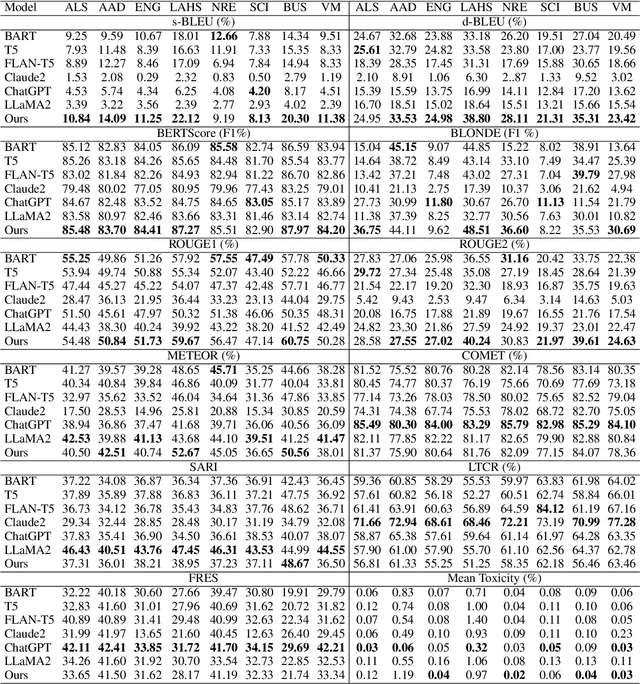
Abstract:Existing text simplification or paraphrase datasets mainly focus on sentence-level text generation in a general domain. These datasets are typically developed without using domain knowledge. In this paper, we release a novel dataset, VTechAGP, which is the first academic-to-general-audience text paraphrase dataset consisting of 4,938 document-level these and dissertation academic and general-audience abstract pairs from 8 colleges authored over 25 years. We also propose a novel dynamic soft prompt generative language model, DSPT5. For training, we leverage a contrastive-generative loss function to learn the keyword vectors in the dynamic prompt. For inference, we adopt a crowd-sampling decoding strategy at both semantic and structural levels to further select the best output candidate. We evaluate DSPT5 and various state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) from multiple perspectives. Results demonstrate that the SOTA LLMs does not provide satisfactory outcomes, while the lightweight DSPT5 can achieve competitive results. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to build a benchmark dataset and solutions for academic-to-general-audience text paraphrase dataset.
Few-Shot Relation Extraction with Hybrid Visual Evidence
Mar 01, 2024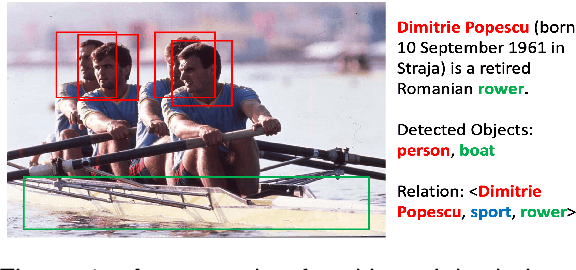

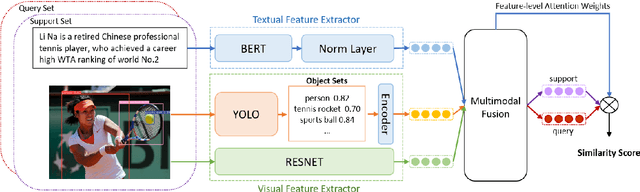

Abstract:The goal of few-shot relation extraction is to predict relations between name entities in a sentence when only a few labeled instances are available for training. Existing few-shot relation extraction methods focus on uni-modal information such as text only. This reduces performance when there are no clear contexts between the name entities described in text. We propose a multi-modal few-shot relation extraction model (MFS-HVE) that leverages both textual and visual semantic information to learn a multi-modal representation jointly. The MFS-HVE includes semantic feature extractors and multi-modal fusion components. The MFS-HVE semantic feature extractors are developed to extract both textual and visual features. The visual features include global image features and local object features within the image. The MFS-HVE multi-modal fusion unit integrates information from various modalities using image-guided attention, object-guided attention, and hybrid feature attention to fully capture the semantic interaction between visual regions of images and relevant texts. Extensive experiments conducted on two public datasets demonstrate that semantic visual information significantly improves the performance of few-shot relation prediction.
* 16 pages, 5 figures
Multi-Label Zero-Shot Product Attribute-Value Extraction
Feb 13, 2024



Abstract:E-commerce platforms should provide detailed product descriptions (attribute values) for effective product search and recommendation. However, attribute value information is typically not available for new products. To predict unseen attribute values, large quantities of labeled training data are needed to train a traditional supervised learning model. Typically, it is difficult, time-consuming, and costly to manually label large quantities of new product profiles. In this paper, we propose a novel method to efficiently and effectively extract unseen attribute values from new products in the absence of labeled data (zero-shot setting). We propose HyperPAVE, a multi-label zero-shot attribute value extraction model that leverages inductive inference in heterogeneous hypergraphs. In particular, our proposed technique constructs heterogeneous hypergraphs to capture complex higher-order relations (i.e. user behavior information) to learn more accurate feature representations for graph nodes. Furthermore, our proposed HyperPAVE model uses an inductive link prediction mechanism to infer future connections between unseen nodes. This enables HyperPAVE to identify new attribute values without the need for labeled training data. We conduct extensive experiments with ablation studies on different categories of the MAVE dataset. The results demonstrate that our proposed HyperPAVE model significantly outperforms existing classification-based, generation-based large language models for attribute value extraction in the zero-shot setting.
Knowledge-Enhanced Multi-Label Few-Shot Product Attribute-Value Extraction
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Existing attribute-value extraction (AVE) models require large quantities of labeled data for training. However, new products with new attribute-value pairs enter the market every day in real-world e-Commerce. Thus, we formulate AVE in multi-label few-shot learning (FSL), aiming to extract unseen attribute value pairs based on a small number of training examples. We propose a Knowledge-Enhanced Attentive Framework (KEAF) based on prototypical networks, leveraging the generated label description and category information to learn more discriminative prototypes. Besides, KEAF integrates with hybrid attention to reduce noise and capture more informative semantics for each class by calculating the label-relevant and query-related weights. To achieve multi-label inference, KEAF further learns a dynamic threshold by integrating the semantic information from both the support set and the query set. Extensive experiments with ablation studies conducted on two datasets demonstrate that KEAF outperforms other SOTA models for information extraction in FSL. The code can be found at: https://github.com/gjiaying/KEAF
Prompt-based Zero-shot Relation Classification with Semantic Knowledge Augmentation
Dec 08, 2021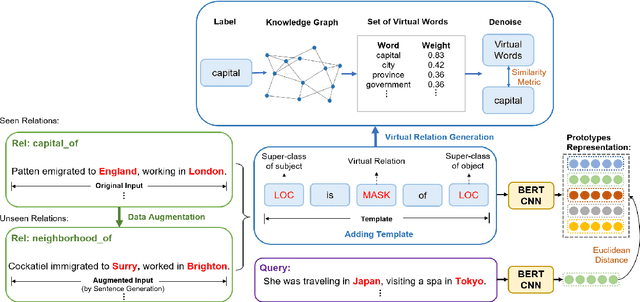

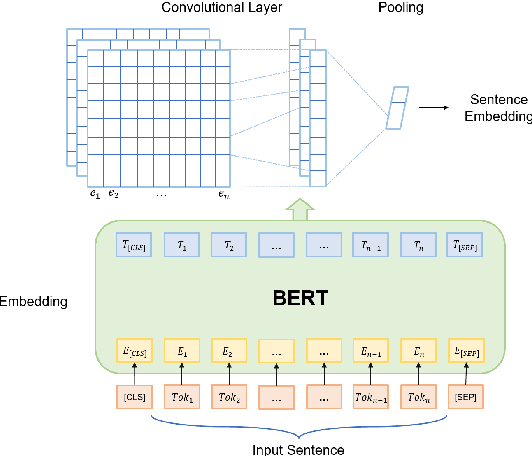

Abstract:Recognizing unseen relations with no training instances is a challenging task in the real world. In this paper, we propose a prompt-based model with semantic knowledge augmentation (ZS-SKA) to recognize unseen relations under the zero-shot setting. We generate augmented instances with unseen relations from instances with seen relations following a new word-level sentence translation rule. We design prompts based on an external knowledge graph to integrate semantic knowledge information learned from seen relations. Instead of using the actual label sets in the prompt template, we construct weighted virtual label words. By generating the representations of both seen and unseen relations with augmented instances and prompts through prototypical networks, distance is calculated to predict unseen relations. Extensive experiments conducted on three public datasets show that ZS-SKA outperforms state-of-the-art methods under the zero-shot scenarios. Our experimental results also demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of ZS-SKA.
Zero-shot Learning for Relation Extraction
Nov 13, 2020


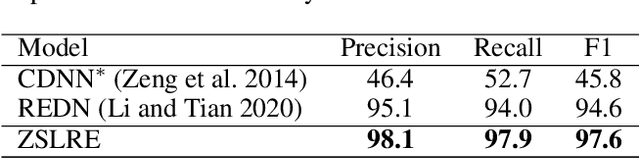
Abstract:Most existing supervised and few-shot learning relation extraction methods have relied on labeled training data. However, in real-world scenarios, there exist many relations for which there is no available training data. We address this issue from the perspective of zero-shot learning (ZSL) which is similar to the way humans learn and recognize new concepts with no prior knowledge. We propose a zero-shot learning relation extraction (ZSLRE) framework, which focuses on recognizing novel relations that have no corresponding labeled data available for training. Our proposed ZSLRE model aims to recognize new relations based on prototypical networks that are modified to utilize side (auxiliary) information. The additional use of side information allows those modified prototype networks to recognize novel relations in addition to recognized previously known relations. We construct side information from labels and their synonyms, hypernyms of name entities, and keywords. We build an automatic hypernym extraction framework to help get hypernyms of various name entities directly from the web. We demonstrate using extensive experiments on two public datasets (NYT and FewRel) that our proposed model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on supervised learning, few-shot learning, and zero-shot learning tasks. Our experimental results also demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed model in a combination scenario. Once accepted for publication, we will publish ZSLRE's source code and datasets to enable reproducibility and encourage further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge