Edward Fox
VTechAGP: An Academic-to-General-Audience Text Paraphrase Dataset and Benchmark Models
Nov 07, 2024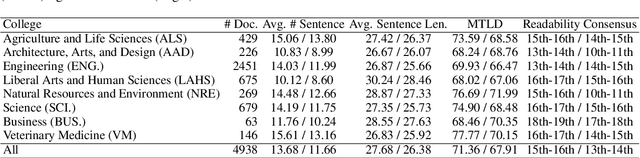
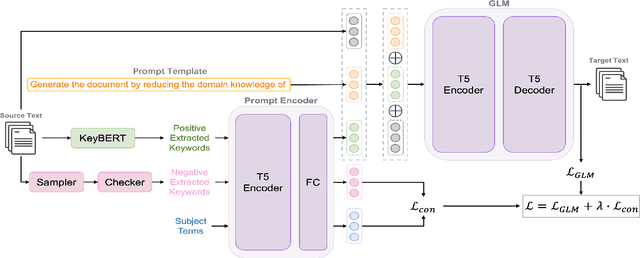
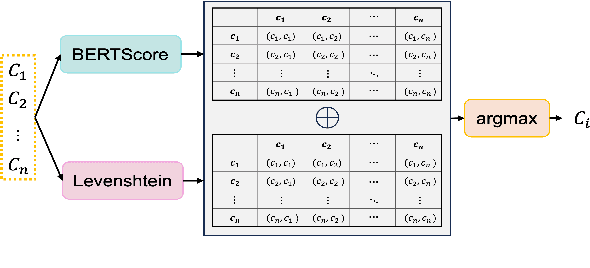
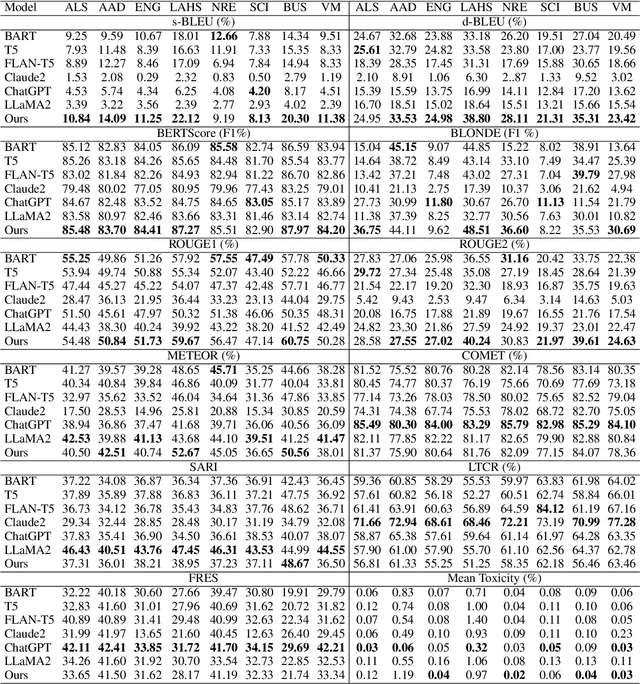
Abstract:Existing text simplification or paraphrase datasets mainly focus on sentence-level text generation in a general domain. These datasets are typically developed without using domain knowledge. In this paper, we release a novel dataset, VTechAGP, which is the first academic-to-general-audience text paraphrase dataset consisting of 4,938 document-level these and dissertation academic and general-audience abstract pairs from 8 colleges authored over 25 years. We also propose a novel dynamic soft prompt generative language model, DSPT5. For training, we leverage a contrastive-generative loss function to learn the keyword vectors in the dynamic prompt. For inference, we adopt a crowd-sampling decoding strategy at both semantic and structural levels to further select the best output candidate. We evaluate DSPT5 and various state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) from multiple perspectives. Results demonstrate that the SOTA LLMs does not provide satisfactory outcomes, while the lightweight DSPT5 can achieve competitive results. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to build a benchmark dataset and solutions for academic-to-general-audience text paraphrase dataset.
Retrieval-based Text Selection for Addressing Class-Imbalanced Data in Classification
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of selecting of a set of texts for annotation in text classification using retrieval methods when there are limits on the number of annotations due to constraints on human resources. An additional challenge addressed is dealing with binary categories that have a small number of positive instances, reflecting severe class imbalance. In our situation, where annotation occurs over a long time period, the selection of texts to be annotated can be made in batches, with previous annotations guiding the choice of the next set. To address these challenges, the paper proposes leveraging SHAP to construct a quality set of queries for Elasticsearch and semantic search, to try to identify optimal sets of texts for annotation that will help with class imbalance. The approach is tested on sets of cue texts describing possible future events, constructed by participants involved in studies aimed to help with the management of obesity and diabetes. We introduce an effective method for selecting a small set of texts for annotation and building high-quality classifiers. We integrate vector search, semantic search, and machine learning classifiers to yield a good solution. Our experiments demonstrate improved F1 scores for the minority classes in binary classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge