Jiangwei Weng
Guided Real Image Dehazing using YCbCr Color Space
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Image dehazing, particularly with learning-based methods, has gained significant attention due to its importance in real-world applications. However, relying solely on the RGB color space often fall short, frequently leaving residual haze. This arises from two main issues: the difficulty in obtaining clear textural features from hazy RGB images and the complexity of acquiring real haze/clean image pairs outside controlled environments like smoke-filled scenes. To address these issues, we first propose a novel Structure Guided Dehazing Network (SGDN) that leverages the superior structural properties of YCbCr features over RGB. It comprises two key modules: Bi-Color Guidance Bridge (BGB) and Color Enhancement Module (CEM). BGB integrates a phase integration module and an interactive attention module, utilizing the rich texture features of the YCbCr space to guide the RGB space, thereby recovering clearer features in both frequency and spatial domains. To maintain tonal consistency, CEM further enhances the color perception of RGB features by aggregating YCbCr channel information. Furthermore, for effective supervised learning, we introduce a Real-World Well-Aligned Haze (RW$^2$AH) dataset, which includes a diverse range of scenes from various geographical regions and climate conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods across multiple real-world smoke/haze datasets. Code and Dataset: \textcolor{blue}{\url{https://github.com/fiwy0527/AAAI25_SGDN.}}
MambaLLIE: Implicit Retinex-Aware Low Light Enhancement with Global-then-Local State Space
May 25, 2024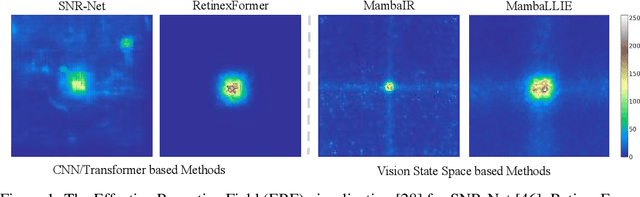
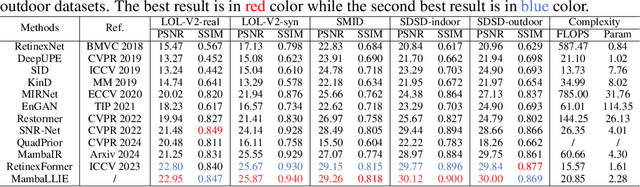
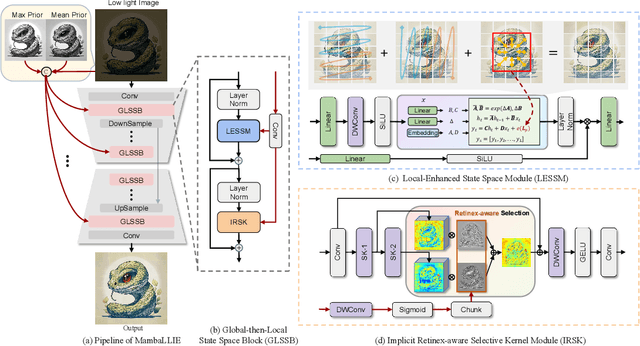
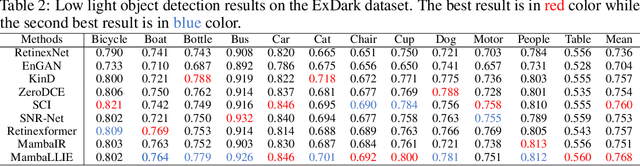
Abstract:Recent advances in low light image enhancement have been dominated by Retinex-based learning framework, leveraging convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformers. However, the vanilla Retinex theory primarily addresses global illumination degradation and neglects local issues such as noise and blur in dark conditions. Moreover, CNNs and Transformers struggle to capture global degradation due to their limited receptive fields. While state space models (SSMs) have shown promise in the long-sequence modeling, they face challenges in combining local invariants and global context in visual data. In this paper, we introduce MambaLLIE, an implicit Retinex-aware low light enhancer featuring a global-then-local state space design. We first propose a Local-Enhanced State Space Module (LESSM) that incorporates an augmented local bias within a 2D selective scan mechanism, enhancing the original SSMs by preserving local 2D dependency. Additionally, an Implicit Retinex-aware Selective Kernel module (IRSK) dynamically selects features using spatially-varying operations, adapting to varying inputs through an adaptive kernel selection process. Our Global-then-Local State Space Block (GLSSB) integrates LESSM and IRSK with LayerNorm as its core. This design enables MambaLLIE to achieve comprehensive global long-range modeling and flexible local feature aggregation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MambaLLIE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art CNN and Transformer-based methods. Project Page: https://mamballie.github.io/anon/
Driving-Video Dehazing with Non-Aligned Regularization for Safety Assistance
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Real driving-video dehazing poses a significant challenge due to the inherent difficulty in acquiring precisely aligned hazy/clear video pairs for effective model training, especially in dynamic driving scenarios with unpredictable weather conditions. In this paper, we propose a pioneering approach that addresses this challenge through a nonaligned regularization strategy. Our core concept involves identifying clear frames that closely match hazy frames, serving as references to supervise a video dehazing network. Our approach comprises two key components: reference matching and video dehazing. Firstly, we introduce a non-aligned reference frame matching module, leveraging an adaptive sliding window to match high-quality reference frames from clear videos. Video dehazing incorporates flow-guided cosine attention sampler and deformable cosine attention fusion modules to enhance spatial multiframe alignment and fuse their improved information. To validate our approach, we collect a GoProHazy dataset captured effortlessly with GoPro cameras in diverse rural and urban road environments. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over current state-of-the-art methods in the challenging task of real driving-video dehazing. Project page.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge