Jiangfan Deng
DreaMontage: Arbitrary Frame-Guided One-Shot Video Generation
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:The "one-shot" technique represents a distinct and sophisticated aesthetic in filmmaking. However, its practical realization is often hindered by prohibitive costs and complex real-world constraints. Although emerging video generation models offer a virtual alternative, existing approaches typically rely on naive clip concatenation, which frequently fails to maintain visual smoothness and temporal coherence. In this paper, we introduce DreaMontage, a comprehensive framework designed for arbitrary frame-guided generation, capable of synthesizing seamless, expressive, and long-duration one-shot videos from diverse user-provided inputs. To achieve this, we address the challenge through three primary dimensions. (i) We integrate a lightweight intermediate-conditioning mechanism into the DiT architecture. By employing an Adaptive Tuning strategy that effectively leverages base training data, we unlock robust arbitrary-frame control capabilities. (ii) To enhance visual fidelity and cinematic expressiveness, we curate a high-quality dataset and implement a Visual Expression SFT stage. In addressing critical issues such as subject motion rationality and transition smoothness, we apply a Tailored DPO scheme, which significantly improves the success rate and usability of the generated content. (iii) To facilitate the production of extended sequences, we design a Segment-wise Auto-Regressive (SAR) inference strategy that operates in a memory-efficient manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves visually striking and seamlessly coherent one-shot effects while maintaining computational efficiency, empowering users to transform fragmented visual materials into vivid, cohesive one-shot cinematic experiences.
Towards Unsupervised Eye-Region Segmentation for Eye Tracking
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Finding the eye and parsing out the parts (e.g. pupil and iris) is a key prerequisite for image-based eye tracking, which has become an indispensable module in today's head-mounted VR/AR devices. However, a typical route for training a segmenter requires tedious handlabeling. In this work, we explore an unsupervised way. First, we utilize priors of human eye and extract signals from the image to establish rough clues indicating the eye-region structure. Upon these sparse and noisy clues, a segmentation network is trained to gradually identify the precise area for each part. To achieve accurate parsing of the eye-region, we first leverage the pretrained foundation model Segment Anything (SAM) in an automatic way to refine the eye indications. Then, the learning process is designed in an end-to-end manner following progressive and prior-aware principle. Experiments show that our unsupervised approach can easily achieve 90% (the pupil and iris) and 85% (the whole eye-region) of the performances under supervised learning.
CondSeg: Ellipse Estimation of Pupil and Iris via Conditioned Segmentation
Aug 30, 2024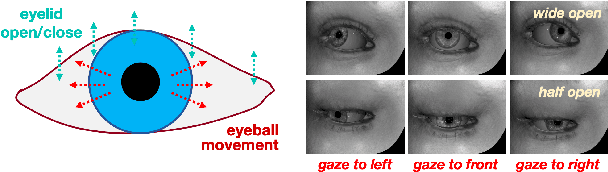

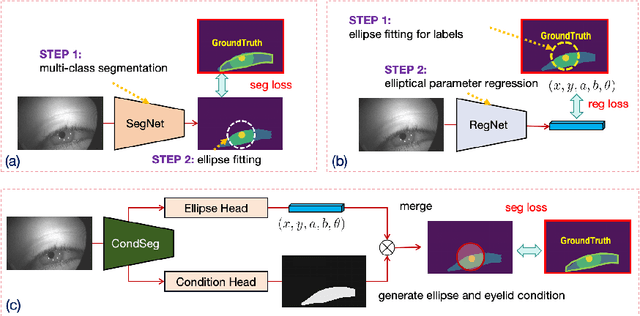

Abstract:Parsing of eye components (i.e. pupil, iris and sclera) is fundamental for eye tracking and gaze estimation for AR/VR products. Mainstream approaches tackle this problem as a multi-class segmentation task, providing only visible part of pupil/iris, other methods regress elliptical parameters using human-annotated full pupil/iris parameters. In this paper, we consider two priors: projected full pupil/iris circle can be modelled with ellipses (ellipse prior), and the visibility of pupil/iris is controlled by openness of eye-region (condition prior), and design a novel method CondSeg to estimate elliptical parameters of pupil/iris directly from segmentation labels, without explicitly annotating full ellipses, and use eye-region mask to control the visibility of estimated pupil/iris ellipses. Conditioned segmentation loss is used to optimize the parameters by transforming parameterized ellipses into pixel-wise soft masks in a differentiable way. Our method is tested on public datasets (OpenEDS-2019/-2020) and shows competitive results on segmentation metrics, and provides accurate elliptical parameters for further applications of eye tracking simultaneously.
Improving Crowded Object Detection via Copy-Paste
Nov 22, 2022



Abstract:Crowdedness caused by overlapping among similar objects is a ubiquitous challenge in the field of 2D visual object detection. In this paper, we first underline two main effects of the crowdedness issue: 1) IoU-confidence correlation disturbances (ICD) and 2) confused de-duplication (CDD). Then we explore a pathway of cracking these nuts from the perspective of data augmentation. Primarily, a particular copy-paste scheme is proposed towards making crowded scenes. Based on this operation, we first design a "consensus learning" method to further resist the ICD problem and then find out the pasting process naturally reveals a pseudo "depth" of object in the scene, which can be potentially used for alleviating CDD dilemma. Both methods are derived from magical using of the copy-pasting without extra cost for hand-labeling. Experiments show that our approach can easily improve the state-of-the-art detector in typical crowded detection task by more than 2% without any bells and whistles. Moreover, this work can outperform existing data augmentation strategies in crowded scenario.
Visible Feature Guidance for Crowd Pedestrian Detection
Sep 16, 2020
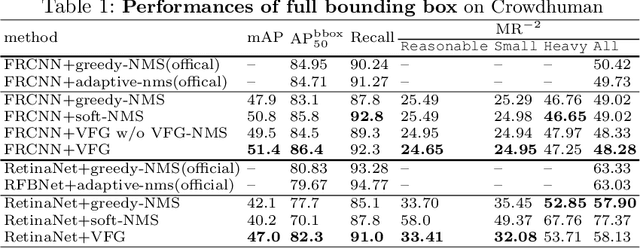
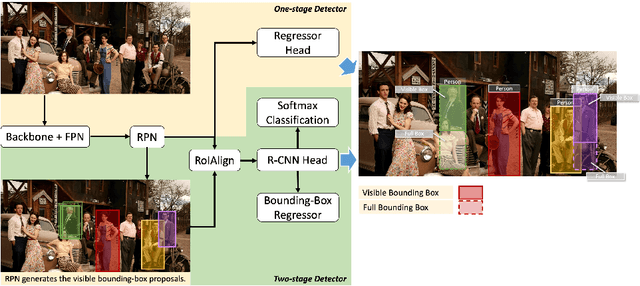
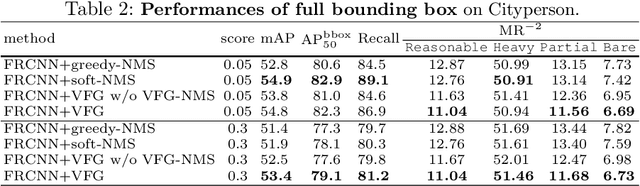
Abstract:Heavy occlusion and dense gathering in crowd scene make pedestrian detection become a challenging problem, because it's difficult to guess a precise full bounding box according to the invisible human part. To crack this nut, we propose a mechanism called Visible Feature Guidance (VFG) for both training and inference. During training, we adopt visible feature to regress the simultaneous outputs of visible bounding box and full bounding box. Then we perform NMS only on visible bounding boxes to achieve the best fitting full box in inference. This manner can alleviate the incapable influence brought by NMS in crowd scene and make full bounding box more precisely. Furthermore, in order to ease feature association in the post application process, such as pedestrian tracking, we apply Hungarian algorithm to associate parts for a human instance. Our proposed method can stably bring about 2~3% improvements in mAP and AP50 for both two-stage and one-stage detector. It's also more effective for MR-2 especially with the stricter IoU. Experiments on Crowdhuman, Cityperson, Caltech and KITTI datasets show that visible feature guidance can help detector achieve promisingly better performances. Moreover, parts association produces a strong benchmark on Crowdhuman for the vision community.
Matching Guided Distillation
Aug 23, 2020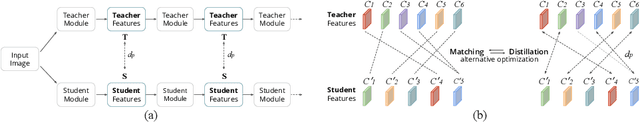
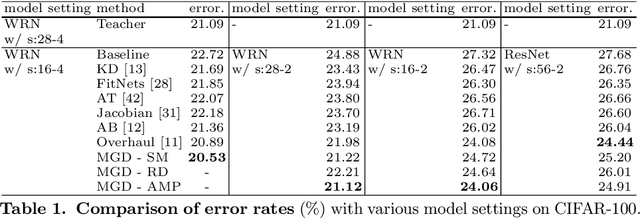
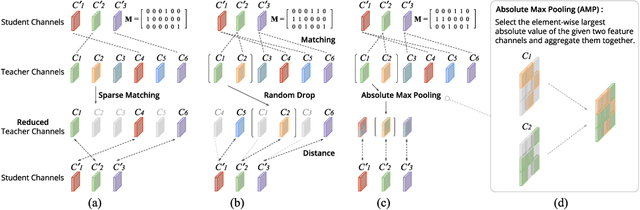
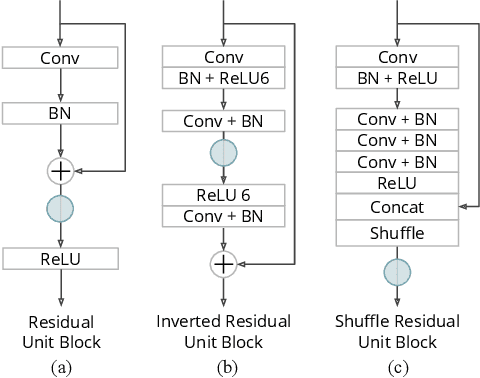
Abstract:Feature distillation is an effective way to improve the performance for a smaller student model, which has fewer parameters and lower computation cost compared to the larger teacher model. Unfortunately, there is a common obstacle - the gap in semantic feature structure between the intermediate features of teacher and student. The classic scheme prefers to transform intermediate features by adding the adaptation module, such as naive convolutional, attention-based or more complicated one. However, this introduces two problems: a) The adaptation module brings more parameters into training. b) The adaptation module with random initialization or special transformation isn't friendly for distilling a pre-trained student. In this paper, we present Matching Guided Distillation (MGD) as an efficient and parameter-free manner to solve these problems. The key idea of MGD is to pose matching the teacher channels with students' as an assignment problem. We compare three solutions of the assignment problem to reduce channels from teacher features with partial distillation loss. The overall training takes a coordinate-descent approach between two optimization objects - assignments update and parameters update. Since MGD only contains normalization or pooling operations with negligible computation cost, it is flexible to plug into network with other distillation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge