Jiahe Liu
CHiRPE: A Step Towards Real-World Clinical NLP with Clinician-Oriented Model Explanations
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The medical adoption of NLP tools requires interpretability by end users, yet traditional explainable AI (XAI) methods are misaligned with clinical reasoning and lack clinician input. We introduce CHiRPE (Clinical High-Risk Prediction with Explainability), an NLP pipeline that takes transcribed semi-structured clinical interviews to: (i) predict psychosis risk; and (ii) generate novel SHAP explanation formats co-developed with clinicians. Trained on 944 semi-structured interview transcripts across 24 international clinics of the AMP-SCZ study, the CHiRPE pipeline integrates symptom-domain mapping, LLM summarisation, and BERT classification. CHiRPE achieved over 90% accuracy across three BERT variants and outperformed baseline models. Explanation formats were evaluated by 28 clinical experts who indicated a strong preference for our novel concept-guided explanations, especially hybrid graph-and-text summary formats. CHiRPE demonstrates that clinically-guided model development produces both accurate and interpretable results. Our next step is focused on real-world testing across our 24 international sites.
ResMAS: Resilience Optimization in LLM-based Multi-agent Systems
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Systems (LLM-based MAS), where multiple LLM agents collaborate to solve complex tasks, have shown impressive performance in many areas. However, MAS are typically distributed across different devices or environments, making them vulnerable to perturbations such as agent failures. While existing works have studied the adversarial attacks and corresponding defense strategies, they mainly focus on reactively detecting and mitigating attacks after they occur rather than proactively designing inherently resilient systems. In this work, we study the resilience of LLM-based MAS under perturbations and find that both the communication topology and prompt design significantly influence system resilience. Motivated by these findings, we propose ResMAS: a two-stage framework for enhancing MAS resilience. First, we train a reward model to predict the MAS's resilience, based on which we train a topology generator to automatically design resilient topology for specific tasks through reinforcement learning. Second, we introduce a topology-aware prompt optimization method that refines each agent's prompt based on its connections and interactions with other agents. Extensive experiments across a range of tasks show that our approach substantially improves MAS resilience under various constraints. Moreover, our framework demonstrates strong generalization ability to new tasks and models, highlighting its potential for building resilient MASs.
PsychEthicsBench: Evaluating Large Language Models Against Australian Mental Health Ethics
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The increasing integration of large language models (LLMs) into mental health applications necessitates robust frameworks for evaluating professional safety alignment. Current evaluative approaches primarily rely on refusal-based safety signals, which offer limited insight into the nuanced behaviors required in clinical practice. In mental health, clinically inadequate refusals can be perceived as unempathetic and discourage help-seeking. To address this gap, we move beyond refusal-centric metrics and introduce \texttt{PsychEthicsBench}, the first principle-grounded benchmark based on Australian psychology and psychiatry guidelines, designed to evaluate LLMs' ethical knowledge and behavioral responses through multiple-choice and open-ended tasks with fine-grained ethicality annotations. Empirical results across 14 models reveal that refusal rates are poor indicators of ethical behavior, revealing a significant divergence between safety triggers and clinical appropriateness. Notably, we find that domain-specific fine-tuning can degrade ethical robustness, as several specialized models underperform their base backbones in ethical alignment. PsychEthicsBench provides a foundation for systematic, jurisdiction-aware evaluation of LLMs in mental health, encouraging more responsible development in this domain.
Beyond Flatlands: Unlocking Spatial Intelligence by Decoupling 3D Reasoning from Numerical Regression
Nov 18, 2025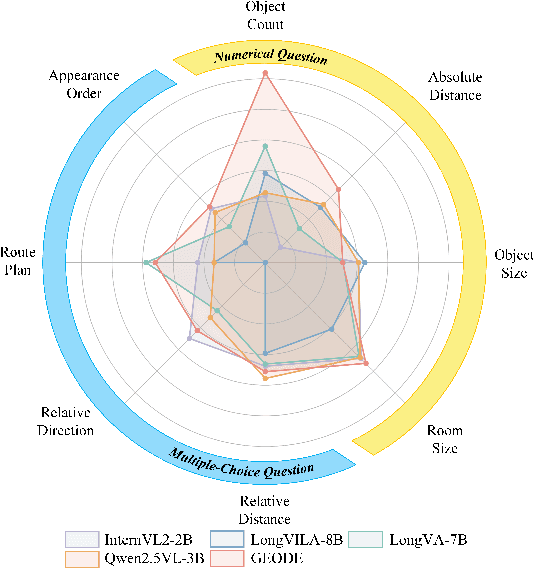
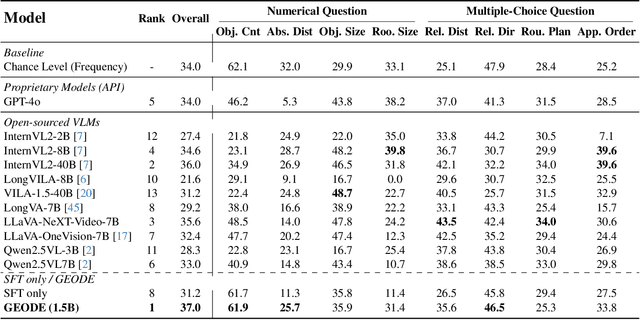
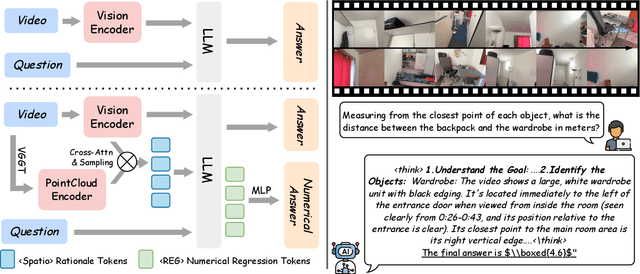
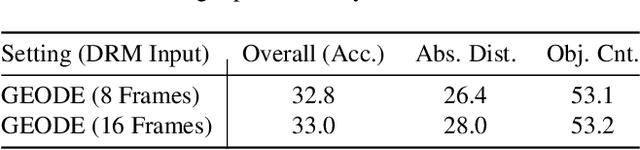
Abstract:Existing Vision Language Models (VLMs) architecturally rooted in "flatland" perception, fundamentally struggle to comprehend real-world 3D spatial intelligence. This failure stems from a dual-bottleneck: input-stage conflict between computationally exorbitant geometric-aware encoders and superficial 2D-only features, and output-stage misalignment where discrete tokenizers are structurally incapable of producing precise, continuous numerical values. To break this impasse, we introduce GEODE (Geometric-Output and Decoupled-Input Engine), a novel architecture that resolves this dual-bottleneck by decoupling 3D reasoning from numerical generation. GEODE augments main VLM with two specialized, plug-and-play modules: Decoupled Rationale Module (DRM) that acts as spatial co-processor, aligning explicit 3D data with 2D visual features via cross-attention and distilling spatial Chain-of-Thought (CoT) logic into injectable Rationale Tokens; and Direct Regression Head (DRH), an "Embedding-as-Value" paradigm which routes specialized control tokens to a lightweight MLP for precise, continuous regression of scalars and 3D bounding boxes. The synergy of these modules allows our 1.5B parameter model to function as a high-level semantic dispatcher, achieving state-of-the-art spatial reasoning performance that rivals 7B+ models.
AgentSquare: Automatic LLM Agent Search in Modular Design Space
Oct 08, 2024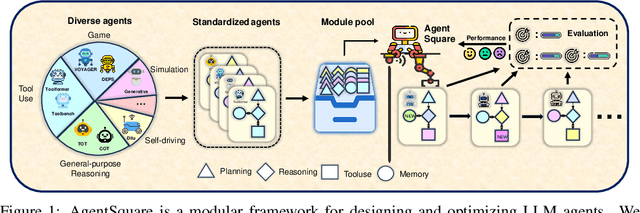
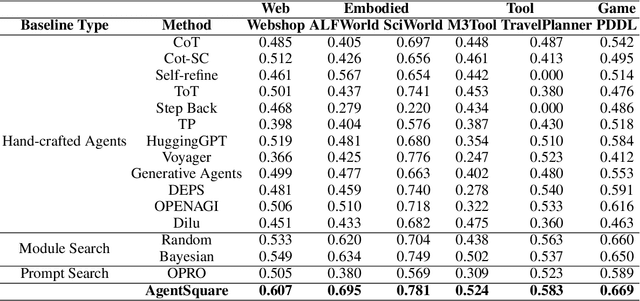
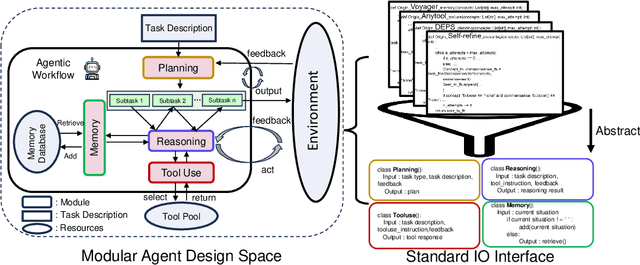
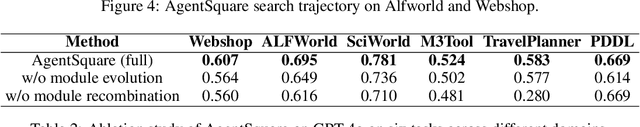
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to a rapid growth of agentic systems capable of handling a wide range of complex tasks. However, current research largely relies on manual, task-specific design, limiting their adaptability to novel tasks. In this paper, we introduce a new research problem: Modularized LLM Agent Search (MoLAS). We propose a modular design space that abstracts existing LLM agent designs into four fundamental modules with uniform IO interface: Planning, Reasoning, Tool Use, and Memory. Building on this design space, we present a novel LLM agent search framework called AgentSquare, which introduces two core mechanisms, i.e., module evolution and recombination, to efficiently search for optimized LLM agents. To further accelerate the process, we design a performance predictor that uses in-context surrogate models to skip unpromising agent designs. Extensive experiments across six benchmarks, covering the diverse scenarios of web, embodied, tool use and game applications, show that AgentSquare substantially outperforms hand-crafted agents, achieving an average performance gain of 17.2% against best-known human designs. Moreover, AgentSquare can generate interpretable design insights, enabling a deeper understanding of agentic architecture and its impact on task performance. We believe that the modular design space and AgentSquare search framework offer a platform for fully exploiting the potential of prior successful designs and consolidating the collective efforts of research community. Code repo is available at https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/AgentSquare.
Fréchet Video Motion Distance: A Metric for Evaluating Motion Consistency in Videos
Jul 23, 2024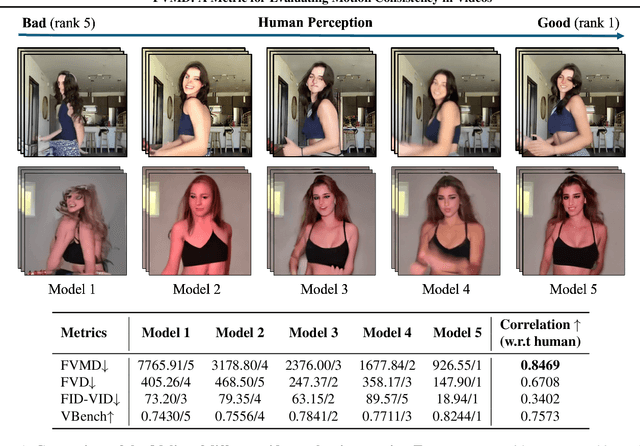
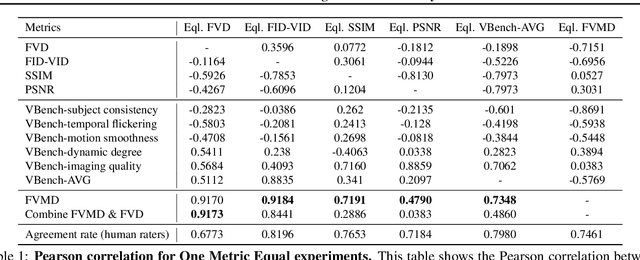
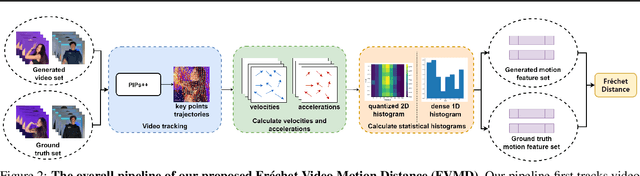
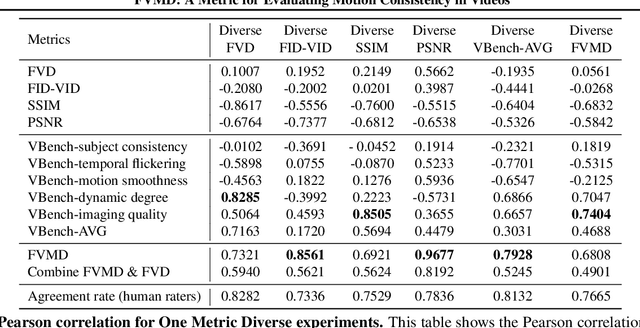
Abstract:Significant advancements have been made in video generative models recently. Unlike image generation, video generation presents greater challenges, requiring not only generating high-quality frames but also ensuring temporal consistency across these frames. Despite the impressive progress, research on metrics for evaluating the quality of generated videos, especially concerning temporal and motion consistency, remains underexplored. To bridge this research gap, we propose Fr\'echet Video Motion Distance (FVMD) metric, which focuses on evaluating motion consistency in video generation. Specifically, we design explicit motion features based on key point tracking, and then measure the similarity between these features via the Fr\'echet distance. We conduct sensitivity analysis by injecting noise into real videos to verify the effectiveness of FVMD. Further, we carry out a large-scale human study, demonstrating that our metric effectively detects temporal noise and aligns better with human perceptions of generated video quality than existing metrics. Additionally, our motion features can consistently improve the performance of Video Quality Assessment (VQA) models, indicating that our approach is also applicable to unary video quality evaluation. Code is available at https://github.com/ljh0v0/FMD-frechet-motion-distance.
Forecasting Post-Wildfire Vegetation Recovery in California using a Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Tensor Regression Network
Nov 04, 2023Abstract:The study of post-wildfire plant regrowth is essential for developing successful ecosystem recovery strategies. Prior research mainly examines key ecological and biogeographical factors influencing post-fire succession. This research proposes a novel approach for predicting and analyzing post-fire plant recovery. We develop a Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Tensor Regression (ConvLSTMTR) network that predicts future Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) based on short-term plant growth data after fire containment. The model is trained and tested on 104 major California wildfires occurring between 2013 and 2020, each with burn areas exceeding 3000 acres. The integration of ConvLSTM with tensor regression enables the calculation of an overall logistic growth rate k using predicted NDVI. Overall, our k-value predictions demonstrate impressive performance, with 50% of predictions exhibiting an absolute error of 0.12 or less, and 75% having an error of 0.24 or less. Finally, we employ Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) and KNN clustering to identify recovery trends, offering insights into regions with varying rates of recovery. This study pioneers the combined use of tensor regression and ConvLSTM, and introduces the application of UMAP for clustering similar wildfires. This advances predictive ecological modeling and could inform future post-fire vegetation management strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge