Jiachen Chen
Using Zone Inflation and Volume Transfer to Design a Fabric-based Pneumatic Exosuit with both Efficiency and Wearability
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:Fabric-based pneumatic exosuits have a broad application prospect due to their good human-machine interaction performance, but their structural design paradigm has not yet been finalized and requires in-depth research. This paper proposes the concepts of zone inflation and volume transfer for the design of a fabric-based pneumatic exosuit with both efficiency and wearability. The meaning of zone inflation is to divide the inflation area of pneumatic exosuit into inflation-deflation zone and inflation-holding zone which can reduce the consumption of compressed air and improve efficiency. Volume transfer, a strategic distribution method of inflatable regions inside the garment, can effectively enhance the wearability of the exosuit. Using inexpensive thermoplastic polyurethane film and clothing fabric, the exosuit is made by heat pressing and sewing. The exosuit has a response time of 0.5s, a stress area of 1500mm2, and a profile of only 32mm, which can be hidden inside common clothing. A mathematical model is developed to predict the output torque of the exosuit with an error of 3.6%. Mechanical experiments show that the exosuit outputs a torque of 9.1Nm at a pressure of 100kPa. Surface electromyography experiments show that the exosuit can provide users with a boost from sitting to standing, with an average reduction in electromyography signals of 14.95%. The exosuit designed using these methods synthesizes efficiency and wearability and is expected to be an ideal paradigm for fabric-based pneumatic exosuits.
Probing many-body Bell correlation depth with superconducting qubits
Jun 25, 2024


Abstract:Quantum nonlocality describes a stronger form of quantum correlation than that of entanglement. It refutes Einstein's belief of local realism and is among the most distinctive and enigmatic features of quantum mechanics. It is a crucial resource for achieving quantum advantages in a variety of practical applications, ranging from cryptography and certified random number generation via self-testing to machine learning. Nevertheless, the detection of nonlocality, especially in quantum many-body systems, is notoriously challenging. Here, we report an experimental certification of genuine multipartite Bell correlations, which signal nonlocality in quantum many-body systems, up to 24 qubits with a fully programmable superconducting quantum processor. In particular, we employ energy as a Bell correlation witness and variationally decrease the energy of a many-body system across a hierarchy of thresholds, below which an increasing Bell correlation depth can be certified from experimental data. As an illustrating example, we variationally prepare the low-energy state of a two-dimensional honeycomb model with 73 qubits and certify its Bell correlations by measuring an energy that surpasses the corresponding classical bound with up to 48 standard deviations. In addition, we variationally prepare a sequence of low-energy states and certify their genuine multipartite Bell correlations up to 24 qubits via energies measured efficiently by parity oscillation and multiple quantum coherence techniques. Our results establish a viable approach for preparing and certifying multipartite Bell correlations, which provide not only a finer benchmark beyond entanglement for quantum devices, but also a valuable guide towards exploiting multipartite Bell correlation in a wide spectrum of practical applications.
Volume Transfer: A New Design Concept for Fabric-Based Pneumatic Exosuits
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:The fabric-based pneumatic exosuit is now a hot research topic because it is lighter and softer than traditional exoskeletons. Existing research focused more on the mechanical properties of the exosuit (e.g., torque and speed), but less on its wearability (e.g., appearance and comfort). This work presents a new design concept for fabric-based pneumatic exosuits Volume Transfer, which means transferring the volume of pneumatic actuators beyond the garments profile to the inside. This allows for a concealed appearance and a larger stress area while maintaining adequate torques. In order to verify this concept, we develop a fabric-based pneumatic exosuit for knee extension assistance. Its profile is only 26mm and its stress area wraps around almost half of the leg. We use a mathematical model and simulation to determine the parameters of the exosuit, avoiding multiple iterations of the prototype. Experiment results show that the exosuit can generate a torque of 7.6Nm at a pressure of 90kPa and produce a significant reduction in the electromyography activity of the knee extensor muscles. We believe that Volume Transfer could be utilized prevalently in future fabric-based pneumatic exosuit designs to achieve a significant improvement in wearability.
Experimental quantum adversarial learning with programmable superconducting qubits
Apr 04, 2022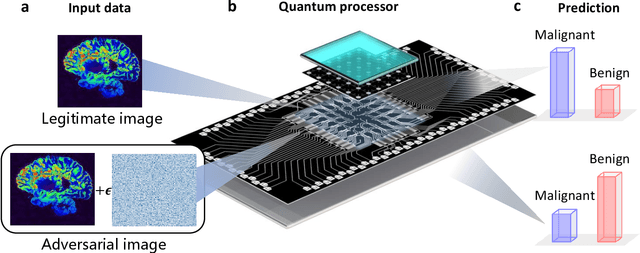
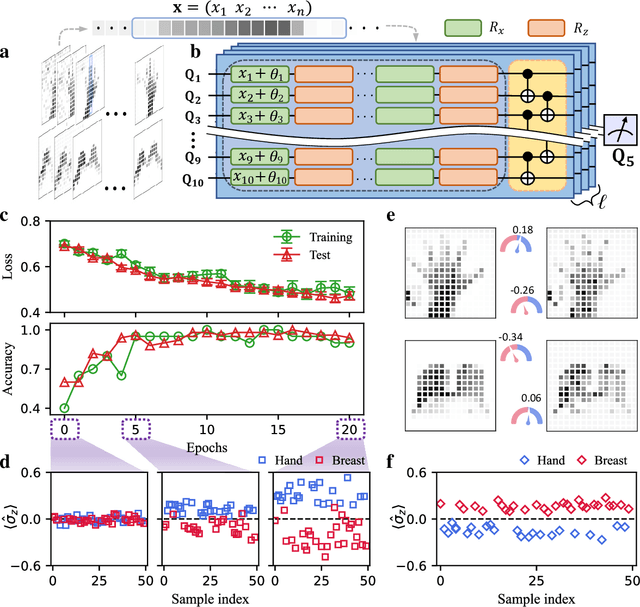
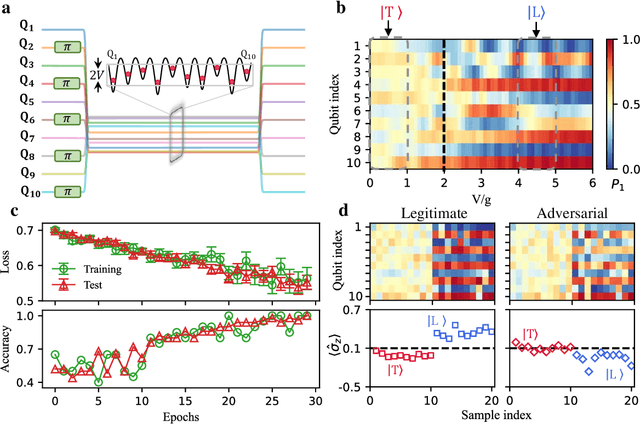
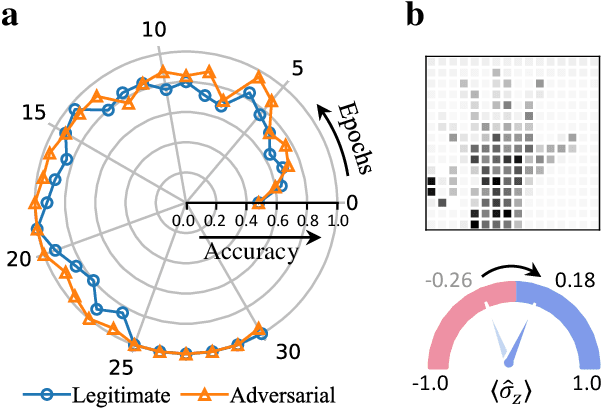
Abstract:Quantum computing promises to enhance machine learning and artificial intelligence. Different quantum algorithms have been proposed to improve a wide spectrum of machine learning tasks. Yet, recent theoretical works show that, similar to traditional classifiers based on deep classical neural networks, quantum classifiers would suffer from the vulnerability problem: adding tiny carefully-crafted perturbations to the legitimate original data samples would facilitate incorrect predictions at a notably high confidence level. This will pose serious problems for future quantum machine learning applications in safety and security-critical scenarios. Here, we report the first experimental demonstration of quantum adversarial learning with programmable superconducting qubits. We train quantum classifiers, which are built upon variational quantum circuits consisting of ten transmon qubits featuring average lifetimes of 150 $\mu$s, and average fidelities of simultaneous single- and two-qubit gates above 99.94% and 99.4% respectively, with both real-life images (e.g., medical magnetic resonance imaging scans) and quantum data. We demonstrate that these well-trained classifiers (with testing accuracy up to 99%) can be practically deceived by small adversarial perturbations, whereas an adversarial training process would significantly enhance their robustness to such perturbations. Our results reveal experimentally a crucial vulnerability aspect of quantum learning systems under adversarial scenarios and demonstrate an effective defense strategy against adversarial attacks, which provide a valuable guide for quantum artificial intelligence applications with both near-term and future quantum devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge