Jessica Nguyen
Quantification of Robotic Surgeries with Vision-Based Deep Learning
May 06, 2022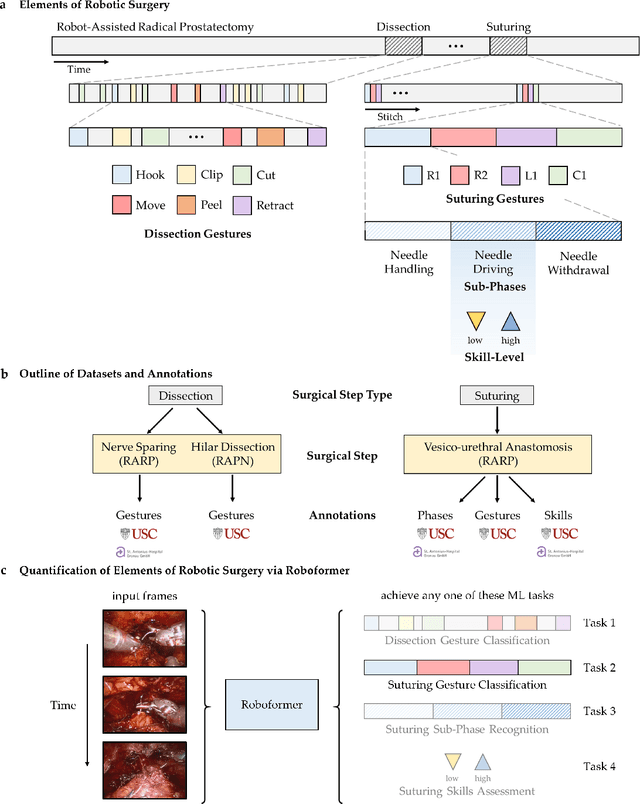
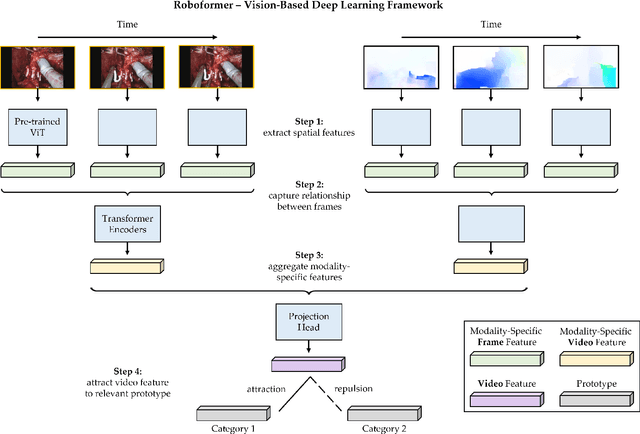
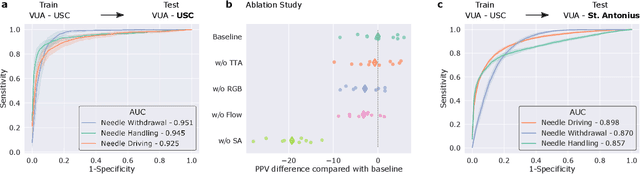
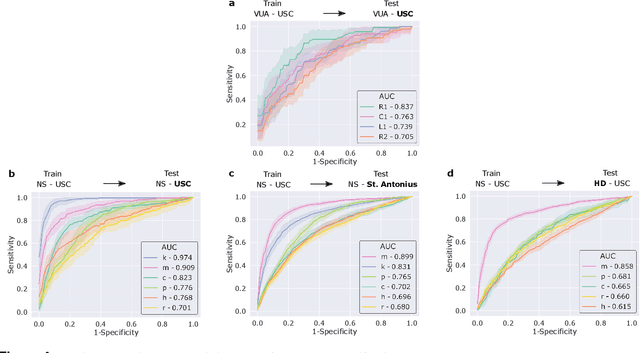
Abstract:Surgery is a high-stakes domain where surgeons must navigate critical anatomical structures and actively avoid potential complications while achieving the main task at hand. Such surgical activity has been shown to affect long-term patient outcomes. To better understand this relationship, whose mechanics remain unknown for the majority of surgical procedures, we hypothesize that the core elements of surgery must first be quantified in a reliable, objective, and scalable manner. We believe this is a prerequisite for the provision of surgical feedback and modulation of surgeon performance in pursuit of improved patient outcomes. To holistically quantify surgeries, we propose a unified deep learning framework, entitled Roboformer, which operates exclusively on videos recorded during surgery to independently achieve multiple tasks: surgical phase recognition (the what of surgery), gesture classification and skills assessment (the how of surgery). We validated our framework on four video-based datasets of two commonly-encountered types of steps (dissection and suturing) within minimally-invasive robotic surgeries. We demonstrated that our framework can generalize well to unseen videos, surgeons, medical centres, and surgical procedures. We also found that our framework, which naturally lends itself to explainable findings, identified relevant information when achieving a particular task. These findings are likely to instill surgeons with more confidence in our framework's behaviour, increasing the likelihood of clinical adoption, and thus paving the way for more targeted surgical feedback.
Production federated keyword spotting via distillation, filtering, and joint federated-centralized training
Apr 11, 2022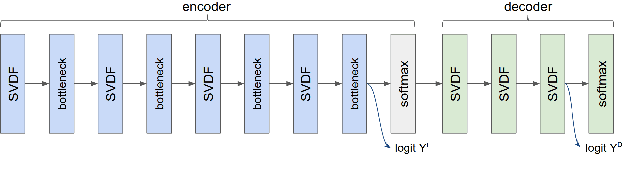
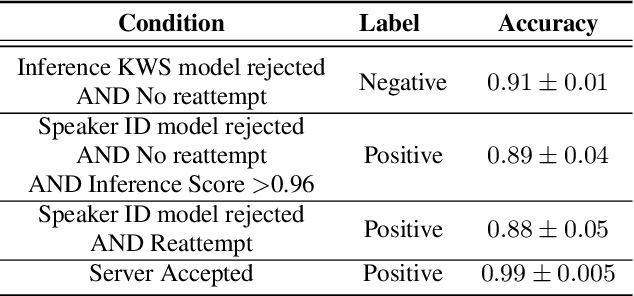
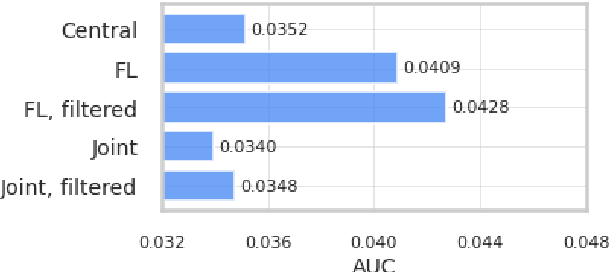
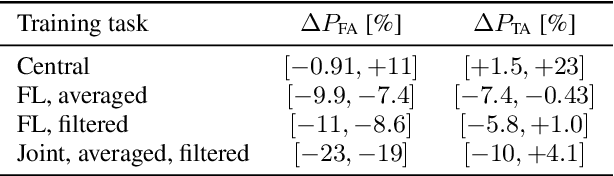
Abstract:We trained a keyword spotting model using federated learning on real user devices and observed significant improvements when the model was deployed for inference on phones. To compensate for data domains that are missing from on-device training caches, we employed joint federated-centralized training. And to learn in the absence of curated labels on-device, we formulated a confidence filtering strategy based on user-feedback signals for federated distillation. These techniques created models that significantly improved quality metrics in offline evaluations and user-experience metrics in live A/B experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge