Aishanee Shah
Production federated keyword spotting via distillation, filtering, and joint federated-centralized training
Apr 11, 2022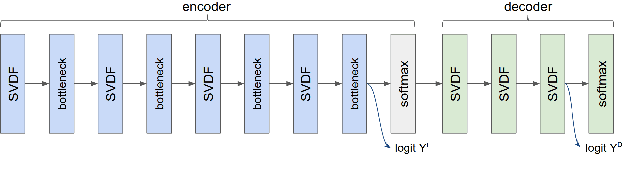
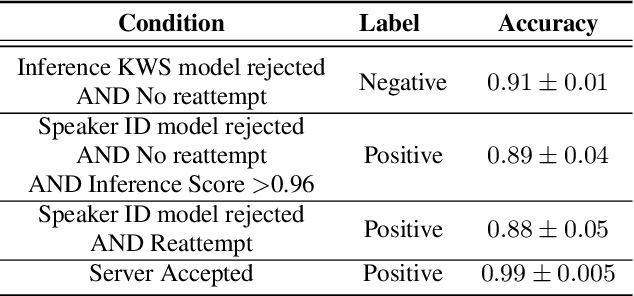
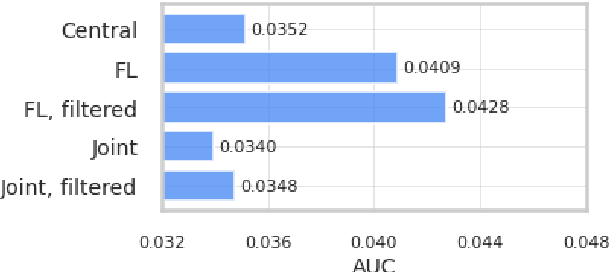
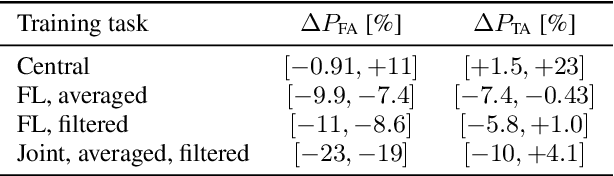
Abstract:We trained a keyword spotting model using federated learning on real user devices and observed significant improvements when the model was deployed for inference on phones. To compensate for data domains that are missing from on-device training caches, we employed joint federated-centralized training. And to learn in the absence of curated labels on-device, we formulated a confidence filtering strategy based on user-feedback signals for federated distillation. These techniques created models that significantly improved quality metrics in offline evaluations and user-experience metrics in live A/B experiments.
Training Keyword Spotting Models on Non-IID Data with Federated Learning
Jun 04, 2020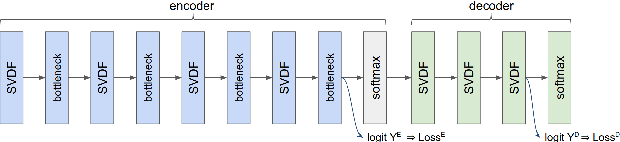
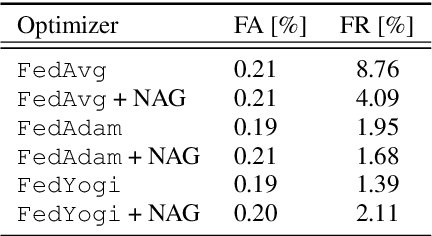

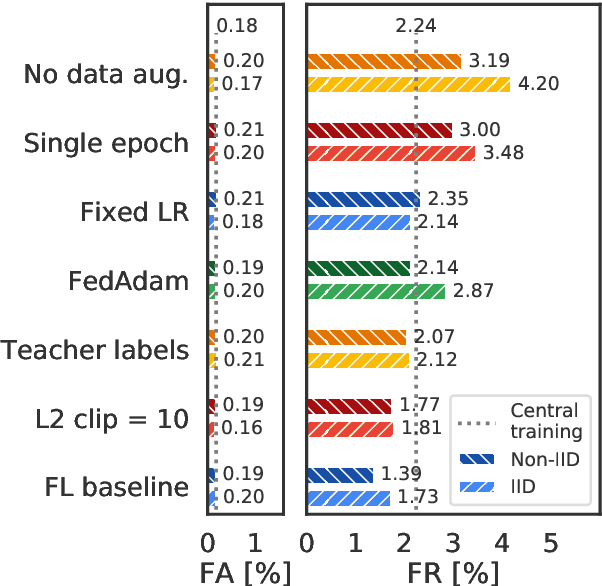
Abstract:We demonstrate that a production-quality keyword-spotting model can be trained on-device using federated learning and achieve comparable false accept and false reject rates to a centrally-trained model. To overcome the algorithmic constraints associated with fitting on-device data (which are inherently non-independent and identically distributed), we conduct thorough empirical studies of optimization algorithms and hyperparameter configurations using large-scale federated simulations. To overcome resource constraints, we replace memory intensive MTR data augmentation with SpecAugment, which reduces the false reject rate by 56%. Finally, to label examples (given the zero visibility into on-device data), we explore teacher-student training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge