Jay Sarva
Fast and Certifiable Trajectory Optimization
Jun 11, 2024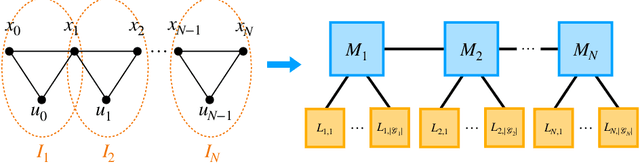
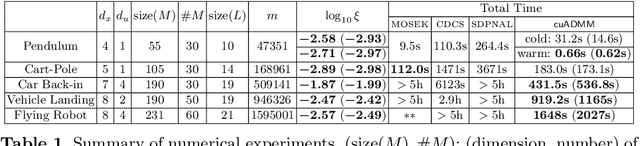
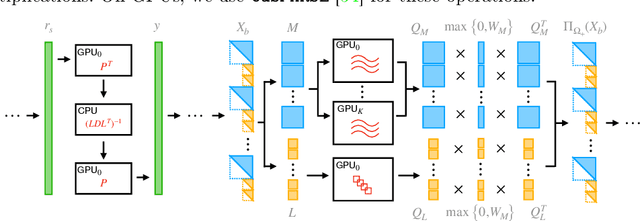

Abstract:We propose semidefinite trajectory optimization (STROM), a framework that computes fast and certifiably optimal solutions for nonconvex trajectory optimization problems defined by polynomial objectives and constraints. STROM employs sparse second-order Lasserre's hierarchy to generate semidefinite program (SDP) relaxations of trajectory optimization. Different from existing tools (e.g., YALMIP and SOSTOOLS in Matlab), STROM generates chain-like multiple-block SDPs with only positive semidefinite (PSD) variables. Moreover, STROM does so two orders of magnitude faster. Underpinning STROM is cuADMM, the first ADMM-based SDP solver implemented in CUDA and runs in GPUs. cuADMM builds upon the symmetric Gauss-Seidel ADMM algorithm and leverages GPU parallelization to speedup solving sparse linear systems and projecting onto PSD cones. In five trajectory optimization problems (inverted pendulum, cart-pole, vehicle landing, flying robot, and car back-in), cuADMM computes optimal trajectories (with certified suboptimality below 1%) in minutes (when other solvers take hours or run out of memory) and seconds (when others take minutes). Further, when warmstarted by data-driven initialization in the inverted pendulum problem, cuADMM delivers real-time performance: providing certifiably optimal trajectories in 0.66 seconds despite the SDP has 49,500 variables and 47,351 constraints.
Adv3D: Generating Safety-Critical 3D Objects through Closed-Loop Simulation
Nov 02, 2023



Abstract:Self-driving vehicles (SDVs) must be rigorously tested on a wide range of scenarios to ensure safe deployment. The industry typically relies on closed-loop simulation to evaluate how the SDV interacts on a corpus of synthetic and real scenarios and verify it performs properly. However, they primarily only test the system's motion planning module, and only consider behavior variations. It is key to evaluate the full autonomy system in closed-loop, and to understand how variations in sensor data based on scene appearance, such as the shape of actors, affect system performance. In this paper, we propose a framework, Adv3D, that takes real world scenarios and performs closed-loop sensor simulation to evaluate autonomy performance, and finds vehicle shapes that make the scenario more challenging, resulting in autonomy failures and uncomfortable SDV maneuvers. Unlike prior works that add contrived adversarial shapes to vehicle roof-tops or roadside to harm perception only, we optimize a low-dimensional shape representation to modify the vehicle shape itself in a realistic manner to degrade autonomy performance (e.g., perception, prediction, and motion planning). Moreover, we find that the shape variations found with Adv3D optimized in closed-loop are much more effective than those in open-loop, demonstrating the importance of finding scene appearance variations that affect autonomy in the interactive setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge