Jasper Zuallaert
Utilizing Mutations to Evaluate Interpretability of Neural Networks on Genomic Data
Dec 12, 2022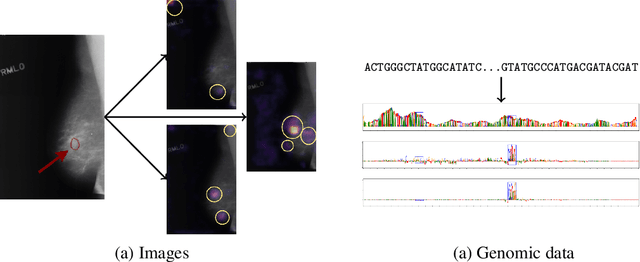
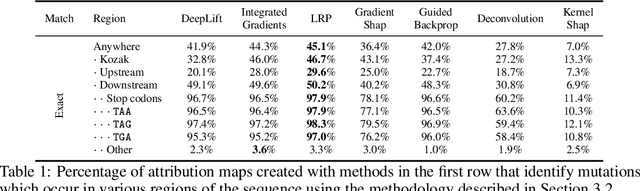
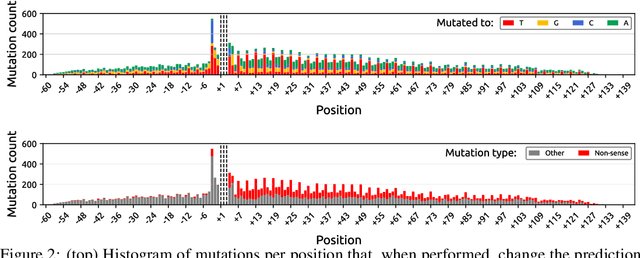

Abstract:Even though deep neural networks (DNNs) achieve state-of-the-art results for a number of problems involving genomic data, getting DNNs to explain their decision-making process has been a major challenge due to their black-box nature. One way to get DNNs to explain their reasoning for prediction is via attribution methods which are assumed to highlight the parts of the input that contribute to the prediction the most. Given the existence of numerous attribution methods and a lack of quantitative results on the fidelity of those methods, selection of an attribution method for sequence-based tasks has been mostly done qualitatively. In this work, we take a step towards identifying the most faithful attribution method by proposing a computational approach that utilizes point mutations. Providing quantitative results on seven popular attribution methods, we find Layerwise Relevance Propagation (LRP) to be the most appropriate one for translation initiation, with LRP identifying two important biological features for translation: the integrity of Kozak sequence as well as the detrimental effects of premature stop codons.
Web Applicable Computer-aided Diagnosis of Glaucoma Using Deep Learning
Dec 06, 2018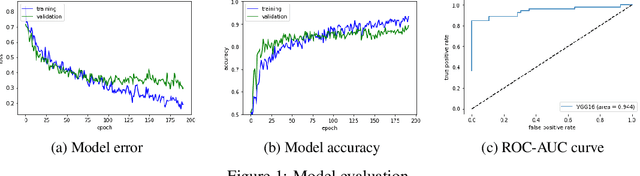

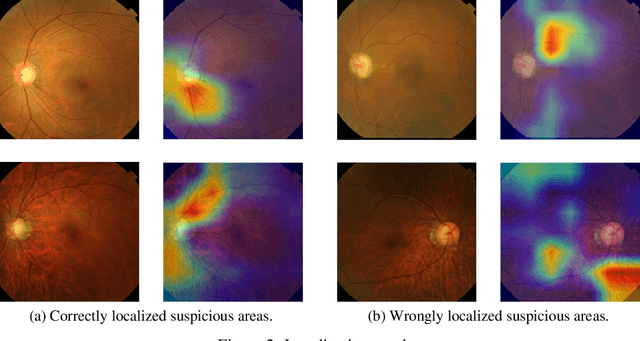
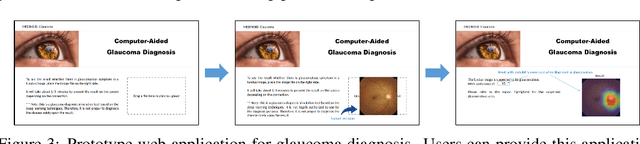
Abstract:Glaucoma is a major eye disease, leading to vision loss in the absence of proper medical treatment. Current diagnosis of glaucoma is performed by ophthalmologists who are often analyzing several types of medical images generated by different types of medical equipment. Capturing and analyzing these medical images is labor-intensive and expensive. In this paper, we present a novel computational approach towards glaucoma diagnosis and localization, only making use of eye fundus images that are analyzed by state-of-the-art deep learning techniques. Specifically, our approach leverages Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) for glaucoma diagnosis and localization, respectively. Quantitative and qualitative results, as obtained for a small-sized dataset with no segmentation ground truth, demonstrate that the proposed approach is promising, for instance achieving an accuracy of 0.91$\pm0.02$ and an ROC-AUC score of 0.94 for the diagnosis task. Furthermore, we present a publicly available prototype web application that integrates our predictive model, with the goal of making effective glaucoma diagnosis available to a wide audience.
Interpretable Convolutional Neural Networks for Effective Translation Initiation Site Prediction
Nov 27, 2017

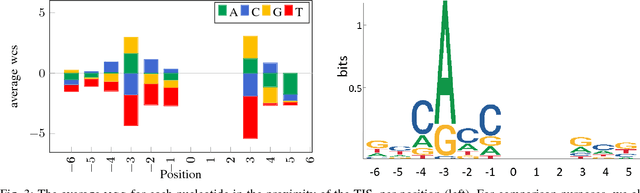
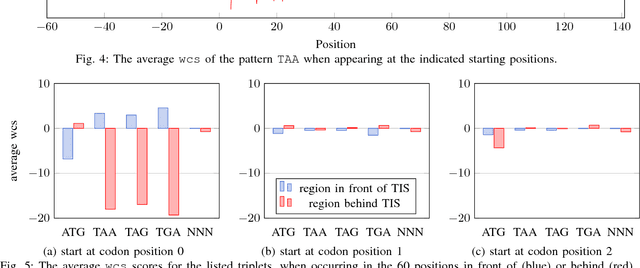
Abstract:Thanks to rapidly evolving sequencing techniques, the amount of genomic data at our disposal is growing increasingly large. Determining the gene structure is a fundamental requirement to effectively interpret gene function and regulation. An important part in that determination process is the identification of translation initiation sites. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for automatic prediction of translation initiation sites, leveraging convolutional neural networks that allow for automatic feature extraction. Our experimental results demonstrate that we are able to improve the state-of-the-art approaches with a decrease of 75.2% in false positive rate and with a decrease of 24.5% in error rate on chosen datasets. Furthermore, an in-depth analysis of the decision-making process used by our predictive model shows that our neural network implicitly learns biologically relevant features from scratch, without any prior knowledge about the problem at hand, such as the Kozak consensus sequence, the influence of stop and start codons in the sequence and the presence of donor splice site patterns. In summary, our findings yield a better understanding of the internal reasoning of a convolutional neural network when applying such a neural network to genomic data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge