Jason N. Gross
Experimental Analysis of Quadcopter Drone Hover Constraints for Localization Improvements
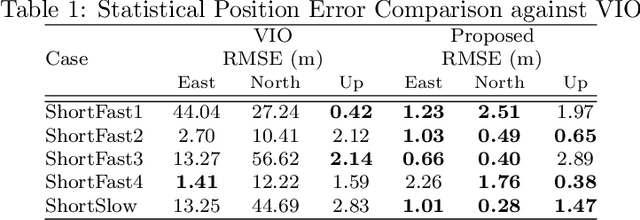
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In this work, we evaluate the use of aerial drone hover constraints in a multisensor fusion of ground robot and drone data to improve the localization performance of a drone. In particular, we build upon our prior work on cooperative localization between an aerial drone and ground robot that fuses data from LiDAR, inertial navigation, peer-to-peer ranging, altimeter, and stereo-vision and evaluate the incorporation knowledge from the autopilot regarding when the drone is hovering. This control command data is leveraged to add constraints on the velocity state. Hover constraints can be considered important dynamic model information, such as the exploitation of zero-velocity updates in pedestrian navigation. We analyze the benefits of these constraints using an incremental factor graph optimization. Experimental data collected in a motion capture faculty is used to provide performance insights and assess the benefits of hover constraints.
UAV Position Estimation using a LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection Method
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:This paper explores the use of applying a deep learning approach for 3D object detection to compute the relative position of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) from an Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) equipped with a LiDAR sensor in a GPS-denied environment. This was achieved by evaluating the LiDAR sensor's data through a 3D detection algorithm (PointPillars). The PointPillars algorithm incorporates a column voxel point-cloud representation and a 2D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to generate distinctive point-cloud features representing the object to be identified, in this case, the UAV. The current localization method utilizes point-cloud segmentation, Euclidean clustering, and predefined heuristics to obtain the relative position of the UAV. Results from the two methods were then compared to a reference truth solution.
A Pointcloud Registration Framework for Relocalization in Subterranean Environments
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:Relocalization, the process of re-establishing a robot's position within an environment, is crucial for ensuring accurate navigation and task execution when external positioning information, such as GPS, is unavailable or has been lost. Subterranean environments present significant challenges for relocalization due to limited external positioning information, poor lighting that affects camera localization, irregular and often non-distinct surfaces, and dust, which can introduce noise and occlusion in sensor data. In this work, we propose a robust, computationally friendly framework for relocalization through point cloud registration utilizing a prior point cloud map. The framework employs Intrinsic Shape Signatures (ISS) to select feature points in both the target and prior point clouds. The Fast Point Feature Histogram (FPFH) algorithm is utilized to create descriptors for these feature points, and matching these descriptors yields correspondences between the point clouds. A 3D transformation is estimated using the matched points, which initializes a Normal Distribution Transform (NDT) registration. The transformation result from NDT is further refined using the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) registration algorithm. This framework enhances registration accuracy even in challenging conditions, such as dust interference and significant initial transformations between the target and source, making it suitable for autonomous robots operating in underground mines and tunnels. This framework was validated with experiments in simulated and real-world mine datasets, demonstrating its potential for improving relocalization.
Robust Flower Cluster Matching Using The Unscented Transform
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Monitoring flowers over time is essential for precision robotic pollination in agriculture. To accomplish this, a continuous spatial-temporal observation of plant growth can be done using stationary RGB-D cameras. However, image registration becomes a serious challenge due to changes in the visual appearance of the plant caused by the pollination process and occlusions from growth and camera angles. Plants flower in a manner that produces distinct clusters on branches. This paper presents a method for matching flower clusters using descriptors generated from RGB-D data and considers allowing for spatial uncertainty within the cluster. The proposed approach leverages the Unscented Transform to efficiently estimate plant descriptor uncertainty tolerances, enabling a robust image-registration process despite temporal changes. The Unscented Transform is used to handle the nonlinear transformations by propagating the uncertainty of flower positions to determine the variations in the descriptor domain. A Monte Carlo simulation is used to validate the Unscented Transform results, confirming our method's effectiveness for flower cluster matching. Therefore, it can facilitate improved robotics pollination in dynamic environments.
Evaluation of the Benefits of Zero Velocity Update in Decentralized EKF-Based Cooperative Localization Algorithms for GNSS-Denied Multi-Robot Systems
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:This paper proposes the cooperative use of zero velocity update (ZU) in a decentralized extended Kalman filter (DEKF) based localization algorithm for multi-robot systems. The filter utilizes inertial measurement unit (IMU), ultra-wideband (UWB), and odometry velocity measurements to improve the localization performance of the system in the presence of a GNSS-denied environment. The contribution of this work is to evaluate the benefits of using ZU in a DEKF-based localization algorithm. The algorithm is tested with real hardware in a video motion capture facility and a Robot Operating System (ROS) based simulation environment for unmanned ground vehicles (UGV). Both simulation and real-world experiments are performed to show the effectiveness of using ZU in one robot to reinstate the localization of other robots in a multi-robot system. Experimental results from GNSS-denied simulation and real-world environments show that using ZU with simple heuristics in the DEKF significantly improves the 3D localization accuracy.
Proprioceptive Slip Detection for Planetary Rovers in Perceptually Degraded Extraterrestrial Environments
Jul 29, 2022
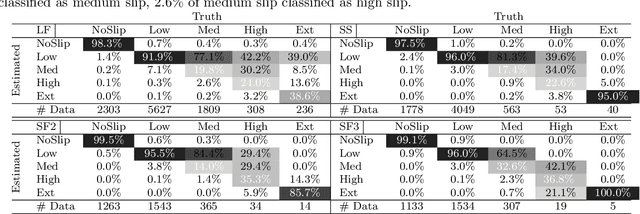
Abstract:Slip detection is of fundamental importance for the safety and efficiency of rovers driving on the surface of extraterrestrial bodies. Current planetary rover slip detection systems rely on visual perception on the assumption that sufficient visual features can be acquired in the environment. However, visual-based methods are prone to suffer in perceptually degraded planetary environments with dominant low terrain features such as regolith, glacial terrain, salt-evaporites, and poor lighting conditions such as dark caves and permanently shadowed regions. Relying only on visual sensors for slip detection also requires additional computational power and reduces the rover traversal rate. This paper answers the question of how to detect wheel slippage of a planetary rover without depending on visual perception. In this respect, we propose a slip detection system that obtains its information from a proprioceptive localization framework that is capable of providing reliable, continuous, and computationally efficient state estimation over hundreds of meters. This is accomplished by using zero velocity update, zero angular rate update, and non-holonomic constraints as pseudo-measurement updates on an inertial navigation system framework. The proposed method is evaluated on actual hardware and field-tested in a planetary-analog environment. The method achieves greater than 92% slip detection accuracy for distances around 150 m using only an IMU and wheel encoders.
NASA Space Robotics Challenge 2 Qualification Round: An Approach to Autonomous Lunar Rover Operations
Sep 20, 2021
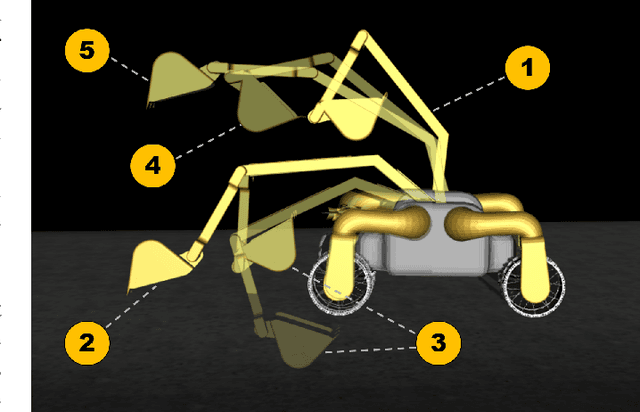
Abstract:Plans for establishing a long-term human presence on the Moon will require substantial increases in robot autonomy and multi-robot coordination to support establishing a lunar outpost. To achieve these objectives, algorithm design choices for the software developments need to be tested and validated for expected scenarios such as autonomous in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), localization in challenging environments, and multi-robot coordination. However, real-world experiments are extremely challenging and limited for extraterrestrial environment. Also, realistic simulation demonstrations in these environments are still rare and demanded for initial algorithm testing capabilities. To help some of these needs, the NASA Centennial Challenges program established the Space Robotics Challenge Phase 2 (SRC2) which consist of virtual robotic systems in a realistic lunar simulation environment, where a group of mobile robots were tasked with reporting volatile locations within a global map, excavating and transporting these resources, and detecting and localizing a target of interest. The main goal of this article is to share our team's experiences on the design trade-offs to perform autonomous robotic operations in a virtual lunar environment and to share strategies to complete the mission requirements posed by NASA SRC2 competition during the qualification round. Of the 114 teams that registered for participation in the NASA SRC2, team Mountaineers finished as one of only six teams to receive the top qualification round prize.
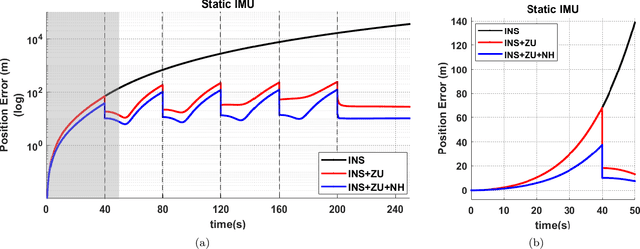
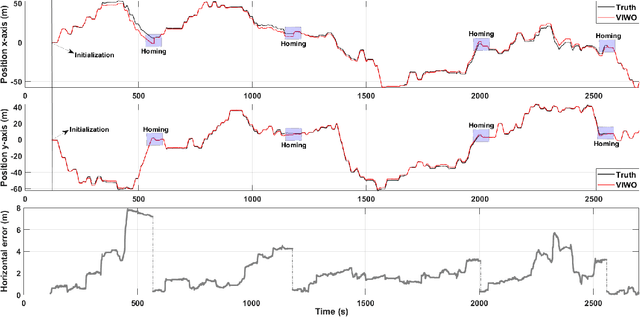
Slip-Based Autonomous ZUPT through Gaussian Process to Improve Planetary Rover Localization
Mar 13, 2021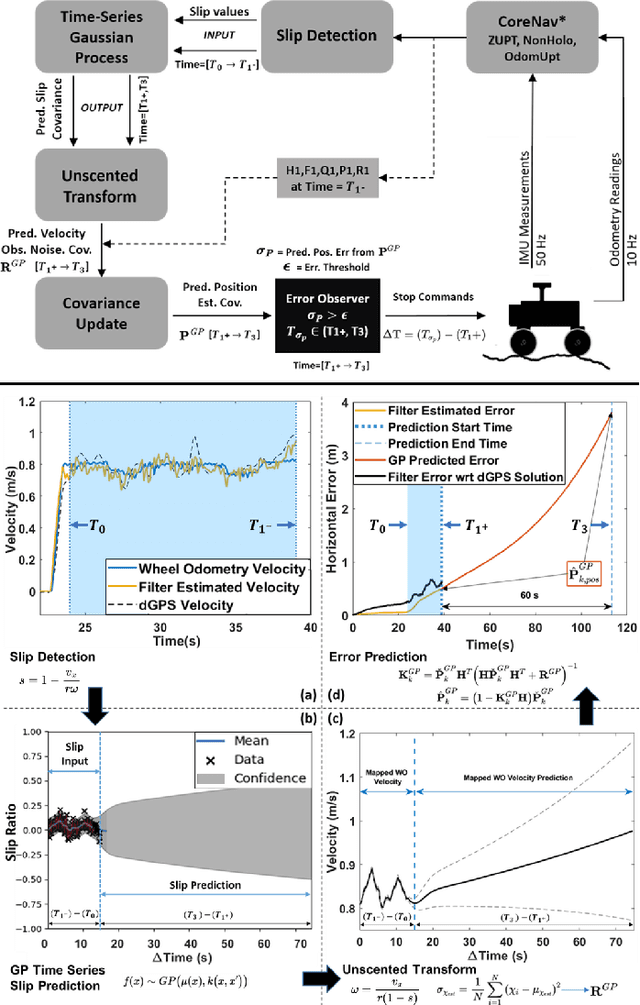
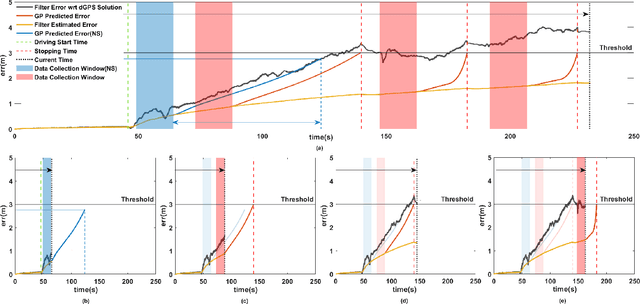
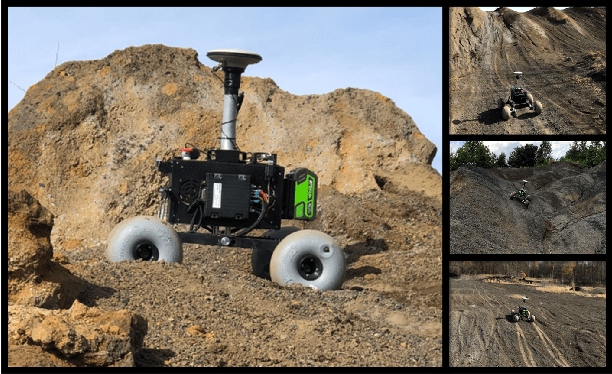
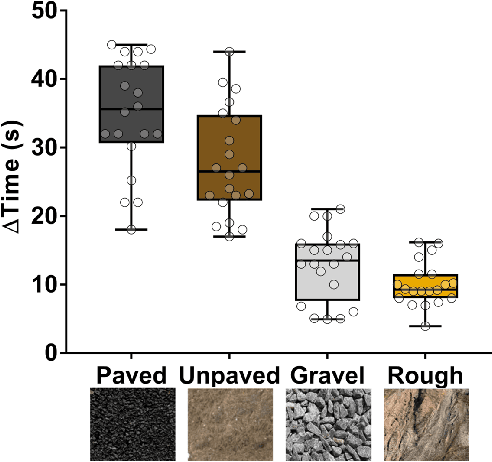
Abstract:The zero-velocity update (ZUPT) algorithm provides valuable state information to maintain the inertial navigation system (INS) reliability when stationary conditions are satisfied. Employing ZUPT along with leveraging non-holonomic constraints can greatly benefit wheeled mobile robot dead-reckoning localization accuracy. However, determining how often they should be employed requires consideration to balance localization accuracy and traversal rate for planetary rovers. To address this, we investigate when to autonomously initiate stops to improve wheel-inertial odometry (WIO) localization performance with ZUPT. To do this, we propose a 3D dead-reckoning approach that predicts wheel slippage while the rover is in motion and forecasts the appropriate time to stop without changing any rover hardware or major rover operations. We validate with field tests that our approach is viable on different terrain types and achieves a 3D localization accuracy of more than 97% over 650 m drives on rough terrain.
* 8 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables
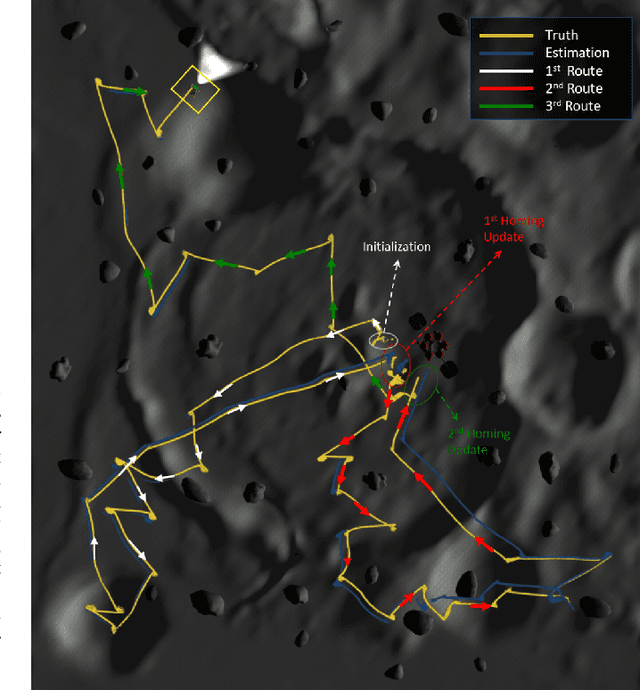
Search Planning of a UAV/UGV Team with Localization Uncertainty in a Subterranean Environment
Feb 11, 2021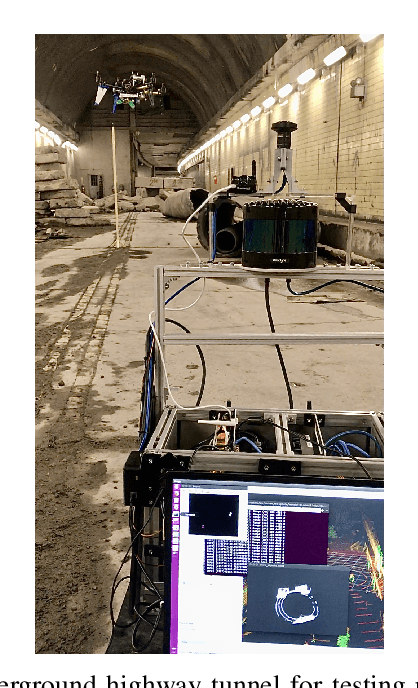
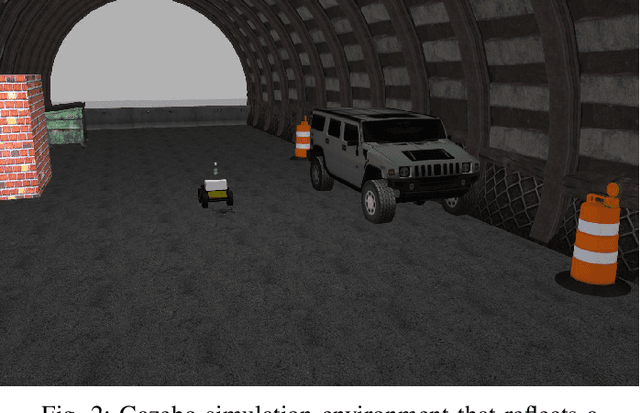

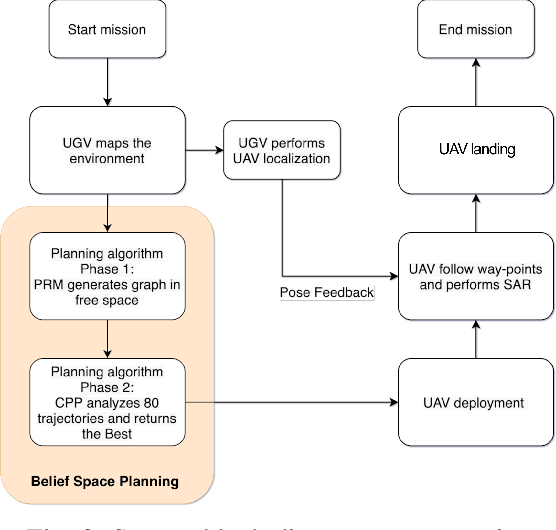
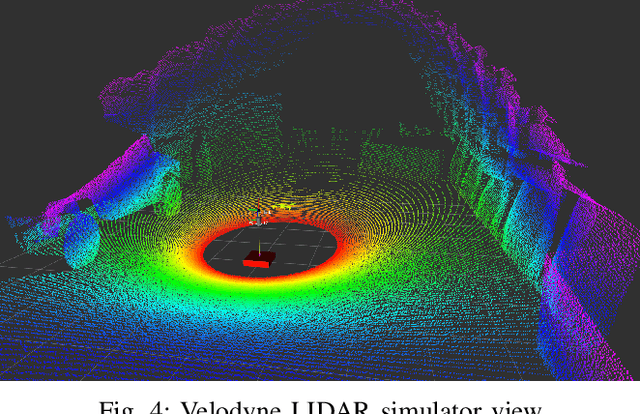
Abstract:We present a waypoint planning algorithm for an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that is teamed with an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) for the task of search and rescue in a subterranean environment. The UAV and UGV are teamed such that the localization of the UAV is conducted on the UGV via the multi-sensor fusion of a fish-eye camera, 3D LIDAR, ranging radio, and a laser altimeter. Likewise, the trajectory planning of the UAV is conducted on the UGV, which is assumed to have a 3D map of the environment (e.g., from Simultaneous Localization and Mapping). The goal of the planning algorithm is to satisfy the mission's exploration criteria while reducing the localization error of the UAV by evaluating the belief space for potential exploration routes. The presented algorithm is evaluated in a relevant simulation environment where the planning algorithm is shown to be effective at reducing the localization errors of the UAV.
Team Mountaineers Space Robotic Challenge Phase-2 Qualification Round Preparation Report
Mar 22, 2020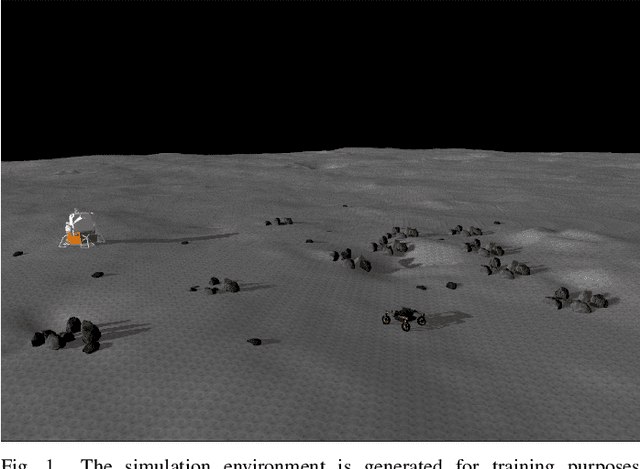

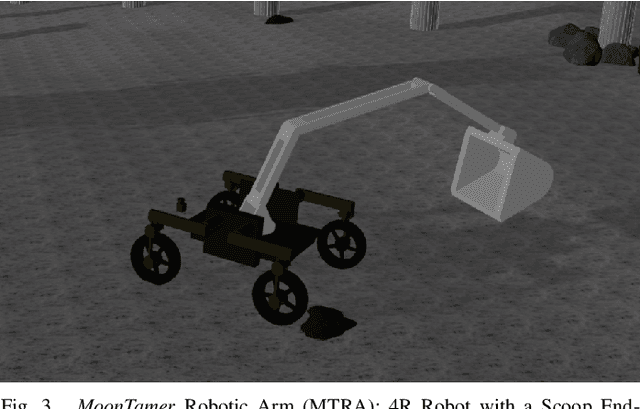
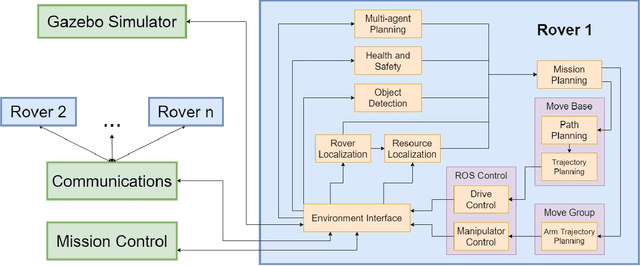
Abstract:Team Mountaineers launched efforts on the NASA Space Robotics Challenge Phase-2 (SRC2). The challenge will be held on the lunar terrain with virtual robotic platforms to establish an in-situ resource utilization process. In this report, we provide an overview of a simulation environment, a virtual mobile robot, and a software architecture that was created by Team Mountaineers in order to prepare for the competition's qualification round before the competition environment was released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge