Jason Hattrick-Simpers
Kernel Learning Assisted Synthesis Condition Exploration for Ternary Spinel
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Machine learning and high-throughput experimentation have greatly accelerated the discovery of mixed metal oxide catalysts by leveraging their compositional flexibility. However, the lack of established synthesis routes for solid-state materials remains a significant challenge in inorganic chemistry. An interpretable machine learning model is therefore essential, as it provides insights into the key factors governing phase formation. Here, we focus on the formation of single-phase Fe$_2$(ZnCo)O$_4$, synthesized via a high-throughput co-precipitation method. We combined a kernel classification model with a novel application of global SHAP analysis to pinpoint the experimental features most critical to single phase synthesizability by interpreting the contributions of each feature. Global SHAP analysis reveals that precursor and precipitating agent contributions to single-phase spinel formation align closely with established crystal growth theories. These results not only underscore the importance of interpretable machine learning in refining synthesis protocols but also establish a framework for data-informed experimental design in inorganic synthesis.
LLM4Mat-Bench: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Materials Property Prediction
Oct 31, 2024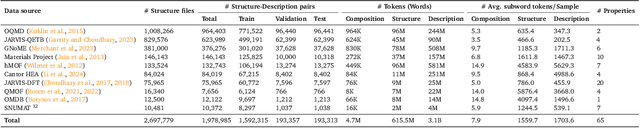
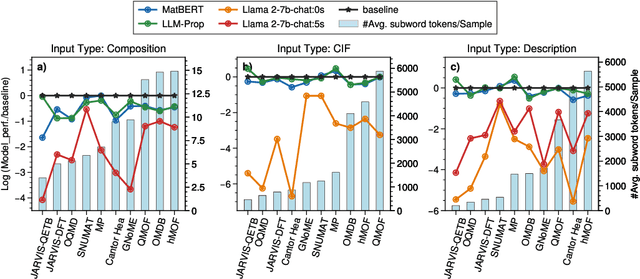
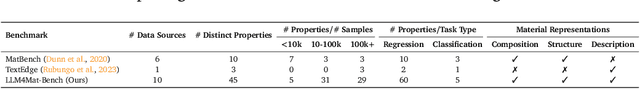
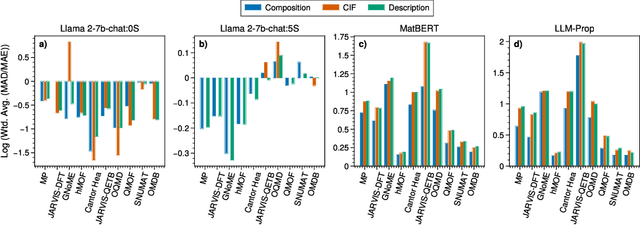
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used in materials science. However, little attention has been given to benchmarking and standardized evaluation for LLM-based materials property prediction, which hinders progress. We present LLM4Mat-Bench, the largest benchmark to date for evaluating the performance of LLMs in predicting the properties of crystalline materials. LLM4Mat-Bench contains about 1.9M crystal structures in total, collected from 10 publicly available materials data sources, and 45 distinct properties. LLM4Mat-Bench features different input modalities: crystal composition, CIF, and crystal text description, with 4.7M, 615.5M, and 3.1B tokens in total for each modality, respectively. We use LLM4Mat-Bench to fine-tune models with different sizes, including LLM-Prop and MatBERT, and provide zero-shot and few-shot prompts to evaluate the property prediction capabilities of LLM-chat-like models, including Llama, Gemma, and Mistral. The results highlight the challenges of general-purpose LLMs in materials science and the need for task-specific predictive models and task-specific instruction-tuned LLMs in materials property prediction.
Evaluating the Performance and Robustness of LLMs in Materials Science Q&A and Property Predictions
Sep 22, 2024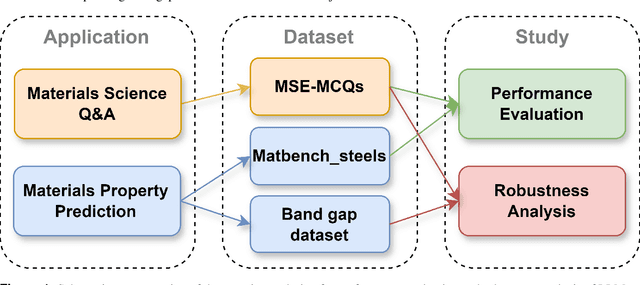
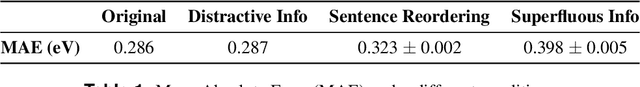
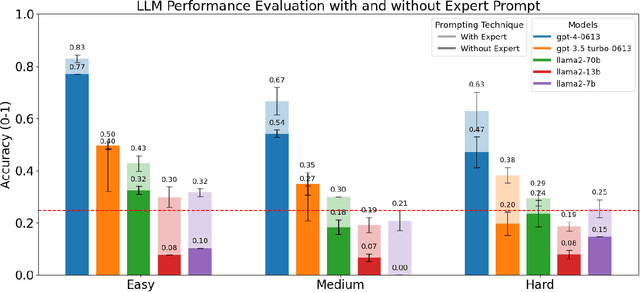
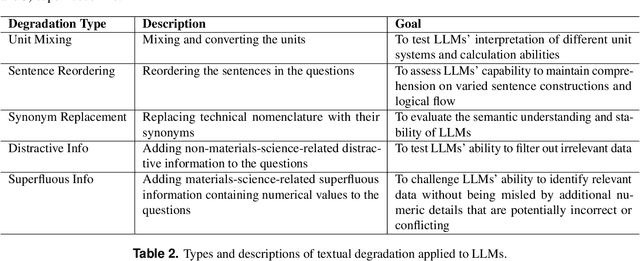
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to revolutionize scientific research, yet their robustness and reliability in domain-specific applications remain insufficiently explored. This study conducts a comprehensive evaluation and robustness analysis of LLMs within the field of materials science, focusing on domain-specific question answering and materials property prediction. Three distinct datasets are used in this study: 1) a set of multiple-choice questions from undergraduate-level materials science courses, 2) a dataset including various steel compositions and yield strengths, and 3) a band gap dataset, containing textual descriptions of material crystal structures and band gap values. The performance of LLMs is assessed using various prompting strategies, including zero-shot chain-of-thought, expert prompting, and few-shot in-context learning. The robustness of these models is tested against various forms of 'noise', ranging from realistic disturbances to intentionally adversarial manipulations, to evaluate their resilience and reliability under real-world conditions. Additionally, the study uncovers unique phenomena of LLMs during predictive tasks, such as mode collapse behavior when the proximity of prompt examples is altered and performance enhancement from train/test mismatch. The findings aim to provide informed skepticism for the broad use of LLMs in materials science and to inspire advancements that enhance their robustness and reliability for practical applications.
On-the-fly Closed-loop Autonomous Materials Discovery via Bayesian Active Learning
Jun 11, 2020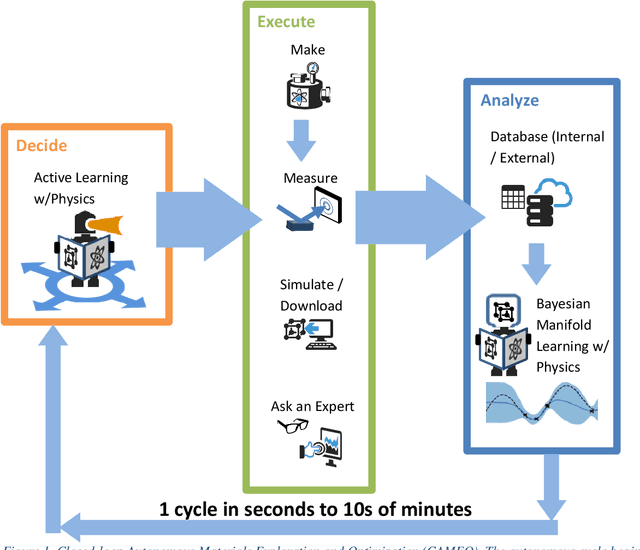
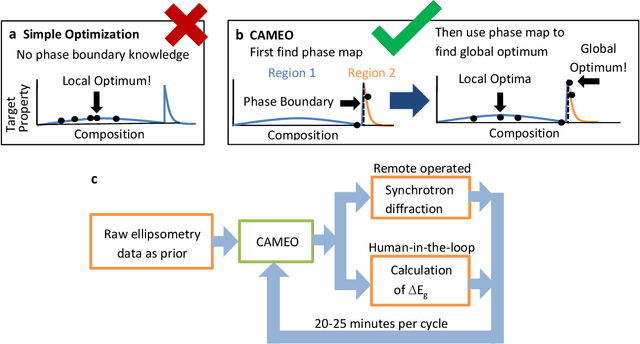
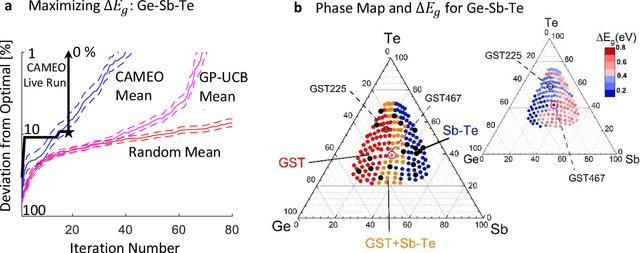
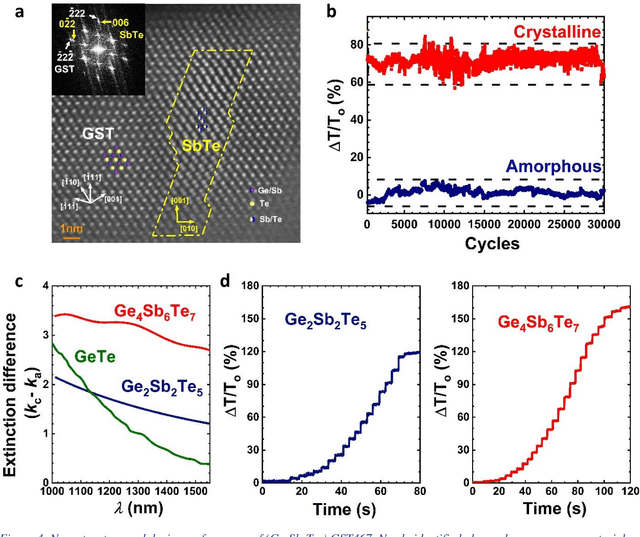
Abstract:Active learning - the field of machine learning (ML) dedicated to optimal experiment design, has played a part in science as far back as the 18th century when Laplace used it to guide his discovery of celestial mechanics [1]. In this work we focus a closed-loop, active learning-driven autonomous system on another major challenge, the discovery of advanced materials against the exceedingly complex synthesis-processes-structure-property landscape. We demonstrate autonomous research methodology (i.e. autonomous hypothesis definition and evaluation) that can place complex, advanced materials in reach, allowing scientists to fail smarter, learn faster, and spend less resources in their studies, while simultaneously improving trust in scientific results and machine learning tools. Additionally, this robot science enables science-over-the-network, reducing the economic impact of scientists being physically separated from their labs. We used the real-time closed-loop, autonomous system for materials exploration and optimization (CAMEO) at the synchrotron beamline to accelerate the fundamentally interconnected tasks of rapid phase mapping and property optimization, with each cycle taking seconds to minutes, resulting in the discovery of a novel epitaxial nanocomposite phase-change memory material.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge