Jake Perazzone
Joint Task Offloading and Routing in Wireless Multi-hop Networks Using Biased Backpressure Algorithm
Dec 19, 2024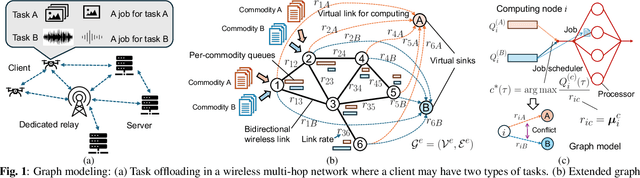
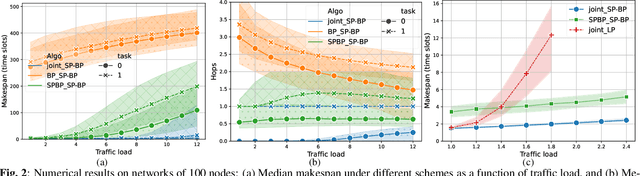
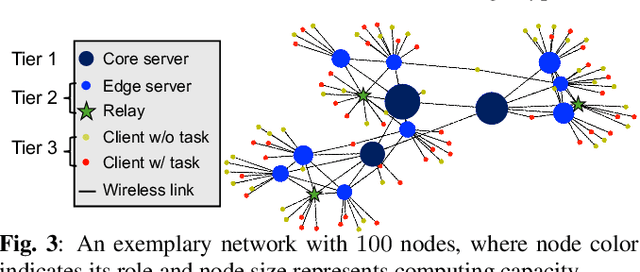
Abstract:A significant challenge for computation offloading in wireless multi-hop networks is the complex interaction among traffic flows in the presence of interference. Existing approaches often ignore these key effects and/or rely on outdated queueing and channel state information. To fill these gaps, we reformulate joint offloading and routing as a routing problem on an extended graph with physical and virtual links. We adopt the state-of-the-art shortest path-biased Backpressure routing algorithm, which allows the destination and the route of a job to be dynamically adjusted at every time step based on network-wide long-term information and real-time states of local neighborhoods. In large networks, our approach achieves smaller makespan than existing approaches, such as separated Backpressure offloading and joint offloading and routing based on linear programming.
Congestion-aware Distributed Task Offloading in Wireless Multi-hop Networks Using Graph Neural Networks
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Computational offloading has become an enabling component for edge intelligence in mobile and smart devices. Existing offloading schemes mainly focus on mobile devices and servers, while ignoring the potential network congestion caused by tasks from multiple mobile devices, especially in wireless multi-hop networks. To fill this gap, we propose a low-overhead, congestion-aware distributed task offloading scheme by augmenting a distributed greedy framework with graph-based machine learning. In simulated wireless multi-hop networks with 20-110 nodes and a resource allocation scheme based on shortest path routing and contention-based link scheduling, our approach is demonstrated to be effective in reducing congestion or unstable queues under the context-agnostic baseline, while improving the execution latency over local computing.
Learning to Transmit with Provable Guarantees in Wireless Federated Learning
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:We propose a novel data-driven approach to allocate transmit power for federated learning (FL) over interference-limited wireless networks. The proposed method is useful in challenging scenarios where the wireless channel is changing during the FL training process and when the training data are not independent and identically distributed (non-i.i.d.) on the local devices. Intuitively, the power policy is designed to optimize the information received at the server end during the FL process under communication constraints. Ultimately, our goal is to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the global FL model being trained. The proposed power allocation policy is parameterized using a graph convolutional network and the associated constrained optimization problem is solved through a primal-dual (PD) algorithm. Theoretically, we show that the formulated problem has zero duality gap and, once the power policy is parameterized, optimality depends on how expressive this parameterization is. Numerically, we demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing baselines under different wireless channel settings and varying degrees of data heterogeneity.
Federated Learning with Flexible Control
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables distributed model training from local data collected by users. In distributed systems with constrained resources and potentially high dynamics, e.g., mobile edge networks, the efficiency of FL is an important problem. Existing works have separately considered different configurations to make FL more efficient, such as infrequent transmission of model updates, client subsampling, and compression of update vectors. However, an important open problem is how to jointly apply and tune these control knobs in a single FL algorithm, to achieve the best performance by allowing a high degree of freedom in control decisions. In this paper, we address this problem and propose FlexFL - an FL algorithm with multiple options that can be adjusted flexibly. Our FlexFL algorithm allows both arbitrary rates of local computation at clients and arbitrary amounts of communication between clients and the server, making both the computation and communication resource consumption adjustable. We prove a convergence upper bound of this algorithm. Based on this result, we further propose a stochastic optimization formulation and algorithm to determine the control decisions that (approximately) minimize the convergence bound, while conforming to constraints related to resource consumption. The advantage of our approach is also verified using experiments.
Communication-Efficient Device Scheduling for Federated Learning Using Stochastic Optimization
Jan 19, 2022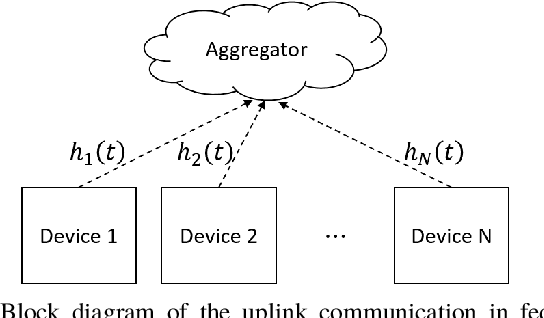
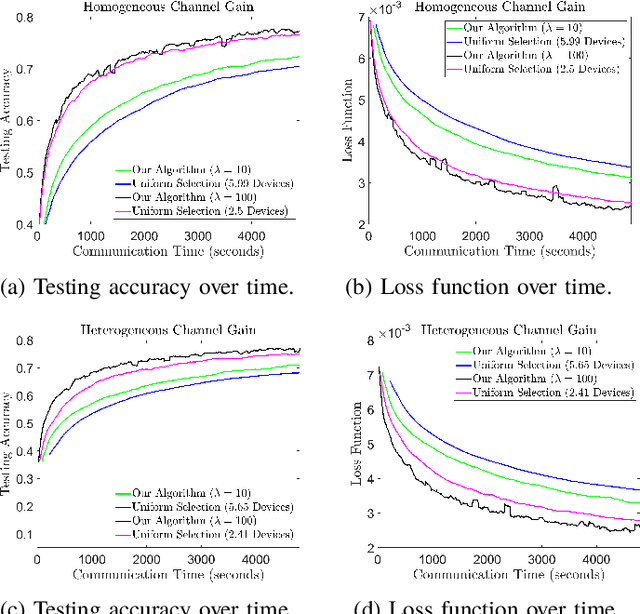
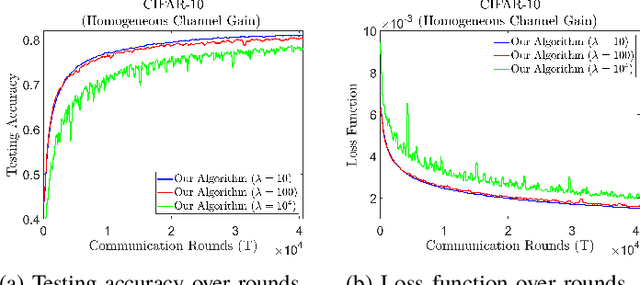
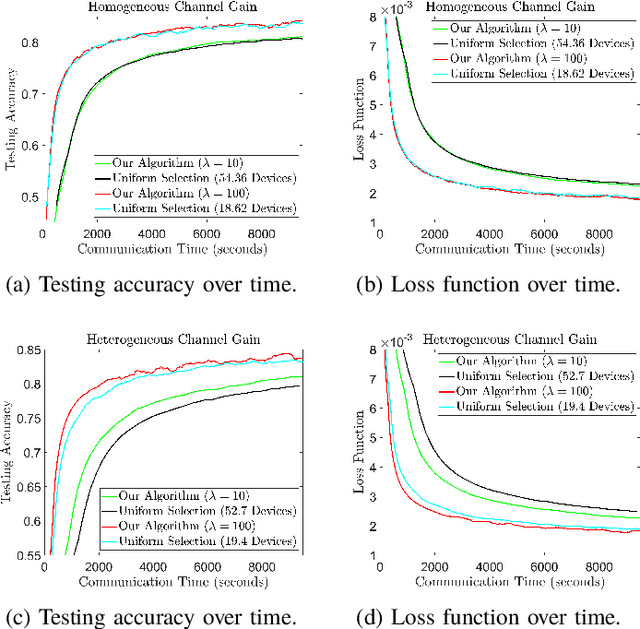
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a useful tool in distributed machine learning that utilizes users' local datasets in a privacy-preserving manner. When deploying FL in a constrained wireless environment; however, training models in a time-efficient manner can be a challenging task due to intermittent connectivity of devices, heterogeneous connection quality, and non-i.i.d. data. In this paper, we provide a novel convergence analysis of non-convex loss functions using FL on both i.i.d. and non-i.i.d. datasets with arbitrary device selection probabilities for each round. Then, using the derived convergence bound, we use stochastic optimization to develop a new client selection and power allocation algorithm that minimizes a function of the convergence bound and the average communication time under a transmit power constraint. We find an analytical solution to the minimization problem. One key feature of the algorithm is that knowledge of the channel statistics is not required and only the instantaneous channel state information needs to be known. Using the FEMNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets, we show through simulations that the communication time can be significantly decreased using our algorithm, compared to uniformly random participation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge