Jaeho Moon
EcoSplat: Efficiency-controllable Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting from Multi-view Images
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables efficient one-pass scene reconstruction, providing 3D representations for novel view synthesis without per-scene optimization. However, existing methods typically predict pixel-aligned primitives per-view, producing an excessive number of primitives in dense-view settings and offering no explicit control over the number of predicted Gaussians. To address this, we propose EcoSplat, the first efficiency-controllable feed-forward 3DGS framework that adaptively predicts the 3D representation for any given target primitive count at inference time. EcoSplat adopts a two-stage optimization process. The first stage is Pixel-aligned Gaussian Training (PGT) where our model learns initial primitive prediction. The second stage is Importance-aware Gaussian Finetuning (IGF) stage where our model learns rank primitives and adaptively adjust their parameters based on the target primitive count. Extensive experiments across multiple dense-view settings show that EcoSplat is robust and outperforms state-of-the-art methods under strict primitive-count constraints, making it well-suited for flexible downstream rendering tasks.
ABBSPO: Adaptive Bounding Box Scaling and Symmetric Prior based Orientation Prediction for Detecting Aerial Image Objects
Dec 10, 2025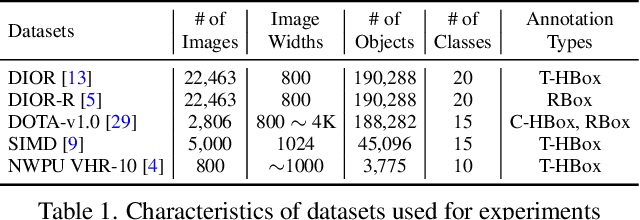
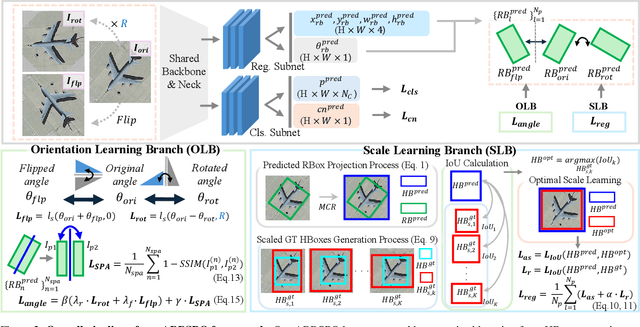
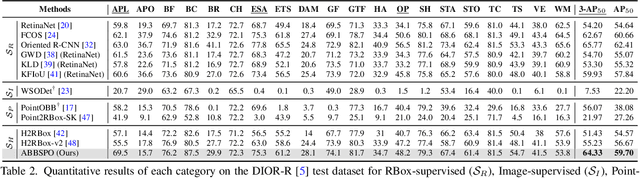
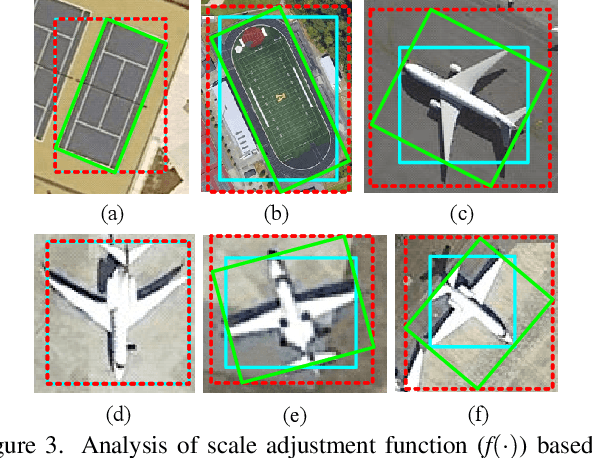
Abstract:Weakly supervised oriented object detection (WS-OOD) has gained attention as a cost-effective alternative to fully supervised methods, providing both efficiency and high accuracy. Among weakly supervised approaches, horizontal bounding box (HBox)-supervised OOD stands out for its ability to directly leverage existing HBox annotations while achieving the highest accuracy under weak supervision settings. This paper introduces adaptive bounding box scaling and symmetry-prior-based orientation prediction, called ABBSPO, a framework for WS-OOD. Our ABBSPO addresses limitations of previous HBox-supervised OOD methods, which compare ground truth (GT) HBoxes directly with the minimum circumscribed rectangles of predicted RBoxes, often leading to inaccurate scale estimation. To overcome this, we propose: (i) Adaptive Bounding Box Scaling (ABBS), which appropriately scales GT HBoxes to optimize for the size of each predicted RBox, ensuring more accurate scale prediction; and (ii) a Symmetric Prior Angle (SPA) loss that exploits inherent symmetry of aerial objects for self-supervised learning, resolving issues in previous methods where learning collapses when predictions for all three augmented views (original, rotated, and flipped) are consistently incorrect. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that ABBSPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods.
MoBGS: Motion Deblurring Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting for Blurry Monocular Video
Apr 21, 2025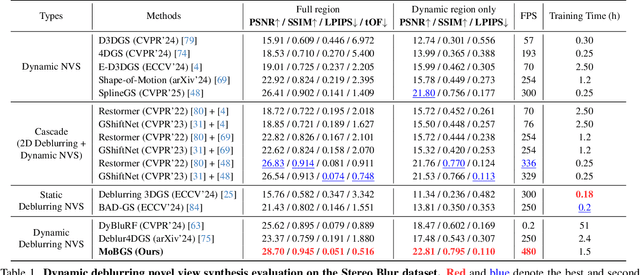

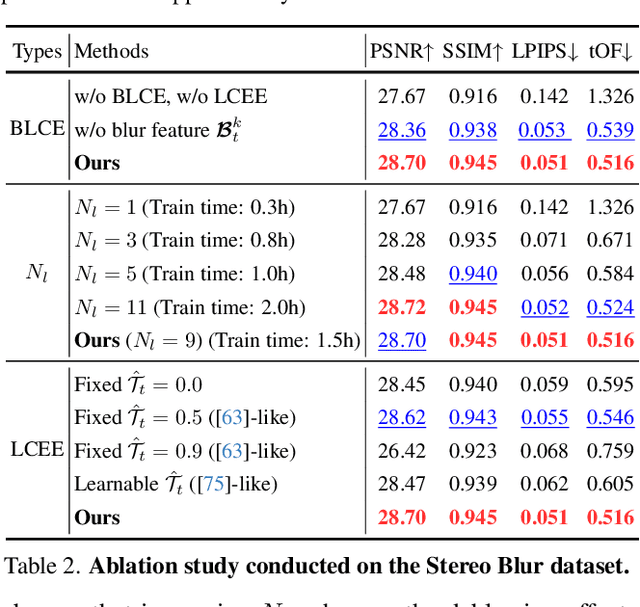

Abstract:We present MoBGS, a novel deblurring dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework capable of reconstructing sharp and high-quality novel spatio-temporal views from blurry monocular videos in an end-to-end manner. Existing dynamic novel view synthesis (NVS) methods are highly sensitive to motion blur in casually captured videos, resulting in significant degradation of rendering quality. While recent approaches address motion-blurred inputs for NVS, they primarily focus on static scene reconstruction and lack dedicated motion modeling for dynamic objects. To overcome these limitations, our MoBGS introduces a novel Blur-adaptive Latent Camera Estimation (BLCE) method for effective latent camera trajectory estimation, improving global camera motion deblurring. In addition, we propose a physically-inspired Latent Camera-induced Exposure Estimation (LCEE) method to ensure consistent deblurring of both global camera and local object motion. Our MoBGS framework ensures the temporal consistency of unseen latent timestamps and robust motion decomposition of static and dynamic regions. Extensive experiments on the Stereo Blur dataset and real-world blurry videos show that our MoBGS significantly outperforms the very recent advanced methods (DyBluRF and Deblur4DGS), achieving state-of-the-art performance for dynamic NVS under motion blur.
SplineGS: Robust Motion-Adaptive Spline for Real-Time Dynamic 3D Gaussians from Monocular Video
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing novel views from in-the-wild monocular videos is challenging due to scene dynamics and the lack of multi-view cues. To address this, we propose SplineGS, a COLMAP-free dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework for high-quality reconstruction and fast rendering from monocular videos. At its core is a novel Motion-Adaptive Spline (MAS) method, which represents continuous dynamic 3D Gaussian trajectories using cubic Hermite splines with a small number of control points. For MAS, we introduce a Motion-Adaptive Control points Pruning (MACP) method to model the deformation of each dynamic 3D Gaussian across varying motions, progressively pruning control points while maintaining dynamic modeling integrity. Additionally, we present a joint optimization strategy for camera parameter estimation and 3D Gaussian attributes, leveraging photometric and geometric consistency. This eliminates the need for Structure-from-Motion preprocessing and enhances SplineGS's robustness in real-world conditions. Experiments show that SplineGS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis quality for dynamic scenes from monocular videos, achieving thousands times faster rendering speed.
DAKD: Data Augmentation and Knowledge Distillation using Diffusion Models for SAR Oil Spill Segmentation
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Oil spills in the ocean pose severe environmental risks, making early detection essential. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) based oil spill segmentation offers robust monitoring under various conditions but faces challenges due to the limited labeled data and inherent speckle noise in SAR imagery. To address these issues, we propose (i) a diffusion-based Data Augmentation and Knowledge Distillation (DAKD) pipeline and (ii) a novel SAR oil spill segmentation network, called SAROSS-Net. In our DAKD pipeline, we present a diffusion-based SAR-JointNet that learns to generate realistic SAR images and their labels for segmentation, by effectively modeling joint distribution with balancing two modalities. The DAKD pipeline augments the training dataset and distills knowledge from SAR-JointNet by utilizing generated soft labels (pixel-wise probability maps) to supervise our SAROSS-Net. The SAROSS-Net is designed to selectively transfer high-frequency features from noisy SAR images, by employing novel Context-Aware Feature Transfer blocks along skip connections. We demonstrate our SAR-JointNet can generate realistic SAR images and well-aligned segmentation labels, providing the augmented data to train SAROSS-Net with enhanced generalizability. Our SAROSS-Net trained with the DAKD pipeline significantly outperforms existing SAR oil spill segmentation methods with large margins.
From-Ground-To-Objects: Coarse-to-Fine Self-supervised Monocular Depth Estimation of Dynamic Objects with Ground Contact Prior
Dec 15, 2023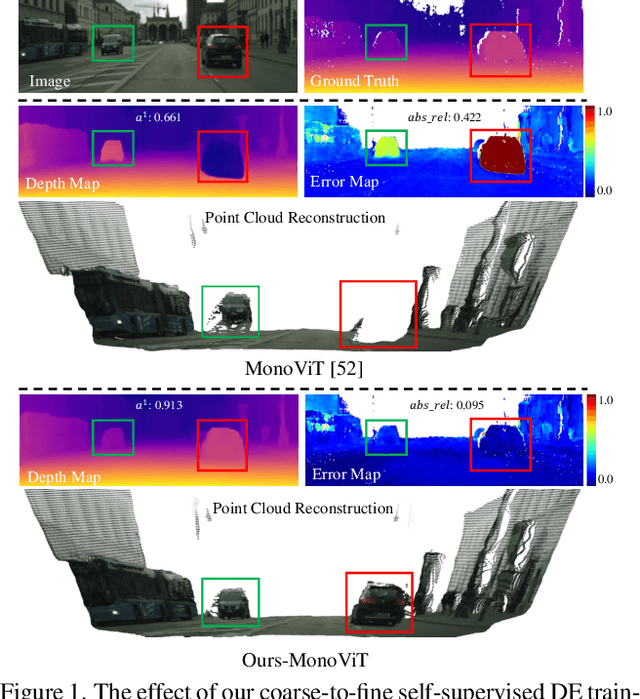
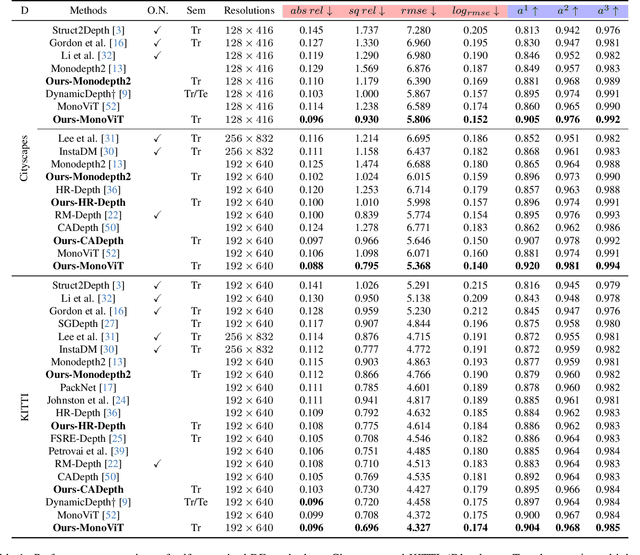
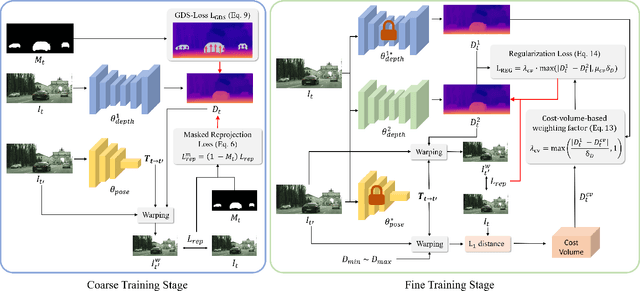
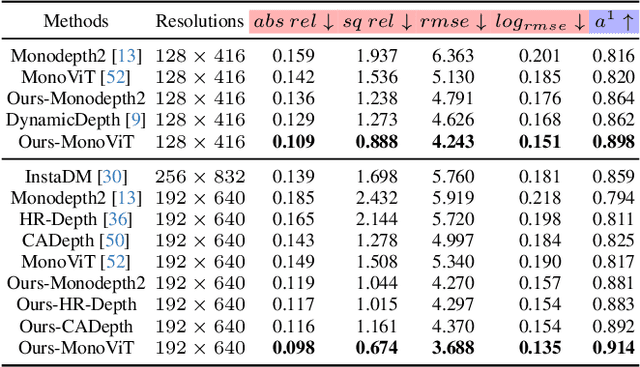
Abstract:Self-supervised monocular depth estimation (DE) is an approach to learning depth without costly depth ground truths. However, it often struggles with moving objects that violate the static scene assumption during training. To address this issue, we introduce a coarse-to-fine training strategy leveraging the ground contacting prior based on the observation that most moving objects in outdoor scenes contact the ground. In the coarse training stage, we exclude the objects in dynamic classes from the reprojection loss calculation to avoid inaccurate depth learning. To provide precise supervision on the depth of the objects, we present a novel Ground-contacting-prior Disparity Smoothness Loss (GDS-Loss) that encourages a DE network to align the depth of the objects with their ground-contacting points. Subsequently, in the fine training stage, we refine the DE network to learn the detailed depth of the objects from the reprojection loss, while ensuring accurate DE on the moving object regions by employing our regularization loss with a cost-volume-based weighting factor. Our overall coarse-to-fine training strategy can easily be integrated with existing DE methods without any modifications, significantly enhancing DE performance on challenging Cityscapes and KITTI datasets, especially in the moving object regions.
Positional Information is All You Need: A Novel Pipeline for Self-Supervised SVDE from Videos
May 18, 2022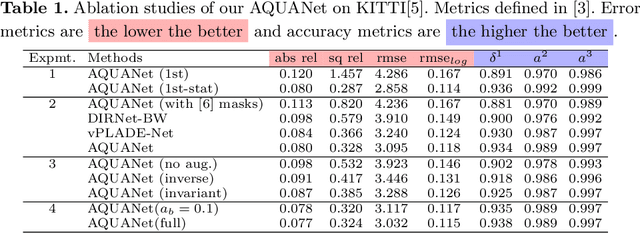
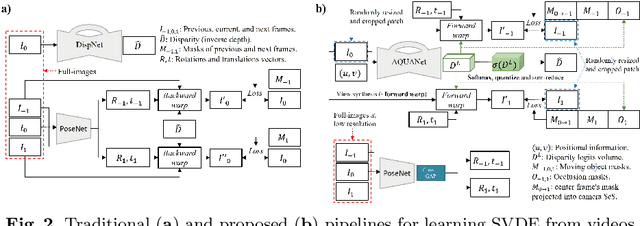
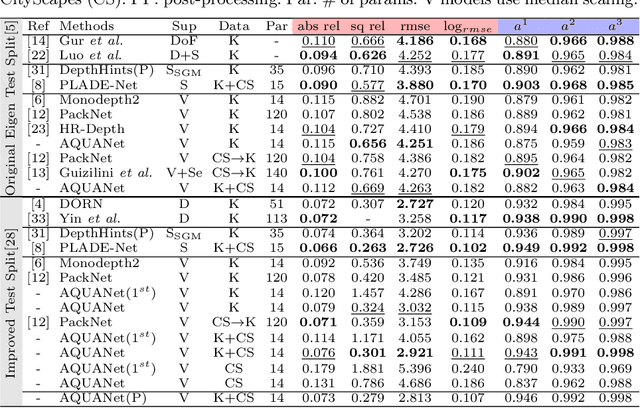
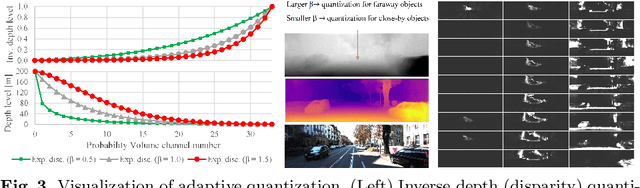
Abstract:Recently, much attention has been drawn to learning the underlying 3D structures of a scene from monocular videos in a fully self-supervised fashion. One of the most challenging aspects of this task is handling the independently moving objects as they break the rigid-scene assumption. For the first time, we show that pixel positional information can be exploited to learn SVDE (Single View Depth Estimation) from videos. Our proposed moving object (MO) masks, which are induced by shifted positional information (SPI) and referred to as `SPIMO' masks, are very robust and consistently remove the independently moving objects in the scenes, allowing for better learning of SVDE from videos. Additionally, we introduce a new adaptive quantization scheme that assigns the best per-pixel quantization curve for our depth discretization. Finally, we employ existing boosting techniques in a new way to further self-supervise the depth of the moving objects. With these features, our pipeline is robust against moving objects and generalizes well to high-resolution images, even when trained with small patches, yielding state-of-the-art (SOTA) results with almost 8.5x fewer parameters than the previous works that learn from videos. We present extensive experiments on KITTI and CityScapes that show the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge