Jaehyup Lee
G2P: Gaussian-to-Point Attribute Alignment for Boundary-Aware 3D Semantic Segmentation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Semantic segmentation on point clouds is critical for 3D scene understanding. However, sparse and irregular point distributions provide limited appearance evidence, making geometry-only features insufficient to distinguish objects with similar shapes but distinct appearances (e.g., color, texture, material). We propose Gaussian-to-Point (G2P), which transfers appearance-aware attributes from 3D Gaussian Splatting to point clouds for more discriminative and appearance-consistent segmentation. Our G2P address the misalignment between optimized Gaussians and original point geometry by establishing point-wise correspondences. By leveraging Gaussian opacity attributes, we resolve the geometric ambiguity that limits existing models. Additionally, Gaussian scale attributes enable precise boundary localization in complex 3D scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance on standard benchmarks and shows significant improvements on geometrically challenging classes, all without any 2D or language supervision.
ABBSPO: Adaptive Bounding Box Scaling and Symmetric Prior based Orientation Prediction for Detecting Aerial Image Objects
Dec 10, 2025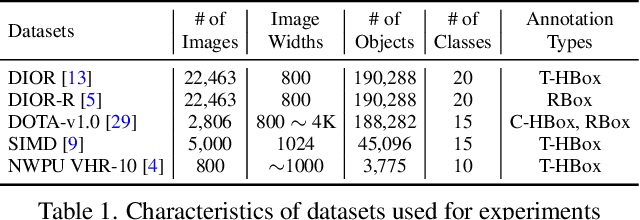
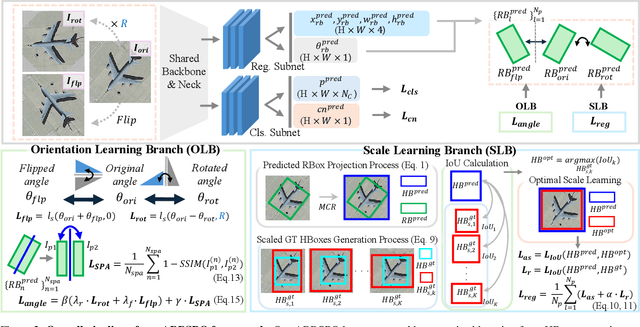
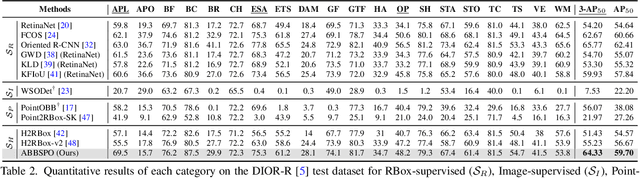
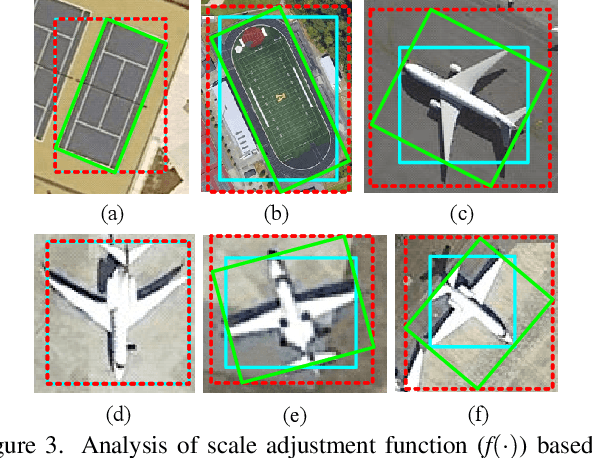
Abstract:Weakly supervised oriented object detection (WS-OOD) has gained attention as a cost-effective alternative to fully supervised methods, providing both efficiency and high accuracy. Among weakly supervised approaches, horizontal bounding box (HBox)-supervised OOD stands out for its ability to directly leverage existing HBox annotations while achieving the highest accuracy under weak supervision settings. This paper introduces adaptive bounding box scaling and symmetry-prior-based orientation prediction, called ABBSPO, a framework for WS-OOD. Our ABBSPO addresses limitations of previous HBox-supervised OOD methods, which compare ground truth (GT) HBoxes directly with the minimum circumscribed rectangles of predicted RBoxes, often leading to inaccurate scale estimation. To overcome this, we propose: (i) Adaptive Bounding Box Scaling (ABBS), which appropriately scales GT HBoxes to optimize for the size of each predicted RBox, ensuring more accurate scale prediction; and (ii) a Symmetric Prior Angle (SPA) loss that exploits inherent symmetry of aerial objects for self-supervised learning, resolving issues in previous methods where learning collapses when predictions for all three augmented views (original, rotated, and flipped) are consistently incorrect. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that ABBSPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods.
From Street to Orbit: Training-Free Cross-View Retrieval via Location Semantics and LLM Guidance
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Cross-view image retrieval, particularly street-to-satellite matching, is a critical task for applications such as autonomous navigation, urban planning, and localization in GPS-denied environments. However, existing approaches often require supervised training on curated datasets and rely on panoramic or UAV-based images, which limits real-world deployment. In this paper, we present a simple yet effective cross-view image retrieval framework that leverages a pretrained vision encoder and a large language model (LLM), requiring no additional training. Given a monocular street-view image, our method extracts geographic cues through web-based image search and LLM-based location inference, generates a satellite query via geocoding API, and retrieves matching tiles using a pretrained vision encoder (e.g., DINOv2) with PCA-based whitening feature refinement. Despite using no ground-truth supervision or finetuning, our proposed method outperforms prior learning-based approaches on the benchmark dataset under zero-shot settings. Moreover, our pipeline enables automatic construction of semantically aligned street-to-satellite datasets, which is offering a scalable and cost-efficient alternative to manual annotation. All source codes will be made publicly available at https://jeonghomin.github.io/street2orbit.github.io/.
PAN-Crafter: Learning Modality-Consistent Alignment for PAN-Sharpening
May 29, 2025Abstract:PAN-sharpening aims to fuse high-resolution panchromatic (PAN) images with low-resolution multi-spectral (MS) images to generate high-resolution multi-spectral (HRMS) outputs. However, cross-modality misalignment -- caused by sensor placement, acquisition timing, and resolution disparity -- induces a fundamental challenge. Conventional deep learning methods assume perfect pixel-wise alignment and rely on per-pixel reconstruction losses, leading to spectral distortion, double edges, and blurring when misalignment is present. To address this, we propose PAN-Crafter, a modality-consistent alignment framework that explicitly mitigates the misalignment gap between PAN and MS modalities. At its core, Modality-Adaptive Reconstruction (MARs) enables a single network to jointly reconstruct HRMS and PAN images, leveraging PAN's high-frequency details as auxiliary self-supervision. Additionally, we introduce Cross-Modality Alignment-Aware Attention (CM3A), a novel mechanism that bidirectionally aligns MS texture to PAN structure and vice versa, enabling adaptive feature refinement across modalities. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that our PAN-Crafter outperforms the most recent state-of-the-art method in all metrics, even with 50.11$\times$ faster inference time and 0.63$\times$ the memory size. Furthermore, it demonstrates strong generalization performance on unseen satellite datasets, showing its robustness across different conditions.
DAKD: Data Augmentation and Knowledge Distillation using Diffusion Models for SAR Oil Spill Segmentation
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Oil spills in the ocean pose severe environmental risks, making early detection essential. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) based oil spill segmentation offers robust monitoring under various conditions but faces challenges due to the limited labeled data and inherent speckle noise in SAR imagery. To address these issues, we propose (i) a diffusion-based Data Augmentation and Knowledge Distillation (DAKD) pipeline and (ii) a novel SAR oil spill segmentation network, called SAROSS-Net. In our DAKD pipeline, we present a diffusion-based SAR-JointNet that learns to generate realistic SAR images and their labels for segmentation, by effectively modeling joint distribution with balancing two modalities. The DAKD pipeline augments the training dataset and distills knowledge from SAR-JointNet by utilizing generated soft labels (pixel-wise probability maps) to supervise our SAROSS-Net. The SAROSS-Net is designed to selectively transfer high-frequency features from noisy SAR images, by employing novel Context-Aware Feature Transfer blocks along skip connections. We demonstrate our SAR-JointNet can generate realistic SAR images and well-aligned segmentation labels, providing the augmented data to train SAROSS-Net with enhanced generalizability. Our SAROSS-Net trained with the DAKD pipeline significantly outperforms existing SAR oil spill segmentation methods with large margins.
U-Know-DiffPAN: An Uncertainty-aware Knowledge Distillation Diffusion Framework with Details Enhancement for PAN-Sharpening
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Conventional methods for PAN-sharpening often struggle to restore fine details due to limitations in leveraging high-frequency information. Moreover, diffusion-based approaches lack sufficient conditioning to fully utilize Panchromatic (PAN) images and low-resolution multispectral (LRMS) inputs effectively. To address these challenges, we propose an uncertainty-aware knowledge distillation diffusion framework with details enhancement for PAN-sharpening, called U-Know-DiffPAN. The U-Know-DiffPAN incorporates uncertainty-aware knowledge distillation for effective transfer of feature details from our teacher model to a student one. The teacher model in our U-Know-DiffPAN captures frequency details through freqeuncy selective attention, facilitating accurate reverse process learning. By conditioning the encoder on compact vector representations of PAN and LRMS and the decoder on Wavelet transforms, we enable rich frequency utilization. So, the high-capacity teacher model distills frequency-rich features into a lightweight student model aided by an uncertainty map. From this, the teacher model can guide the student model to focus on difficult image regions for PAN-sharpening via the usage of the uncertainty map. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets demonstrate the robustness and superior performance of our U-Know-DiffPAN over very recent state-of-the-art PAN-sharpening methods.
C-DiffSET: Leveraging Latent Diffusion for SAR-to-EO Image Translation with Confidence-Guided Reliable Object Generation
Nov 23, 2024Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery provides robust environmental and temporal coverage (e.g., during clouds, seasons, day-night cycles), yet its noise and unique structural patterns pose interpretation challenges, especially for non-experts. SAR-to-EO (Electro-Optical) image translation (SET) has emerged to make SAR images more perceptually interpretable. However, traditional approaches trained from scratch on limited SAR-EO datasets are prone to overfitting. To address these challenges, we introduce Confidence Diffusion for SAR-to-EO Translation, called C-DiffSET, a framework leveraging pretrained Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) extensively trained on natural images, thus enabling effective adaptation to the EO domain. Remarkably, we find that the pretrained VAE encoder aligns SAR and EO images in the same latent space, even with varying noise levels in SAR inputs. To further improve pixel-wise fidelity for SET, we propose a confidence-guided diffusion (C-Diff) loss that mitigates artifacts from temporal discrepancies, such as appearing or disappearing objects, thereby enhancing structural accuracy. C-DiffSET achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on multiple datasets, significantly outperforming the very recent image-to-image translation methods and SET methods with large margins.
SIPSA-Net: Shift-Invariant Pan Sharpening with Moving Object Alignment for Satellite Imagery
May 06, 2021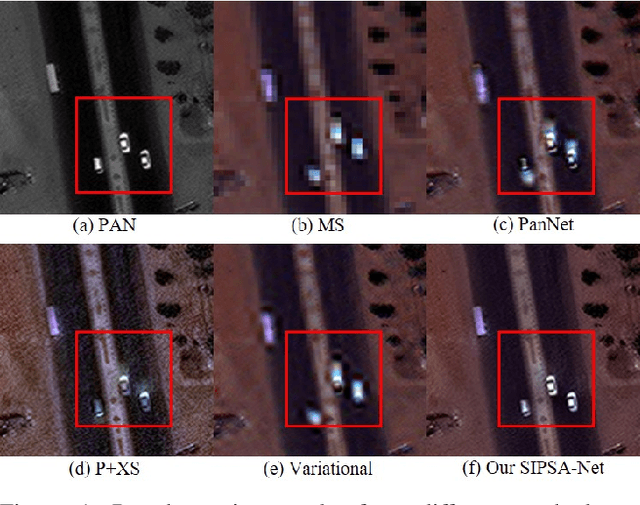
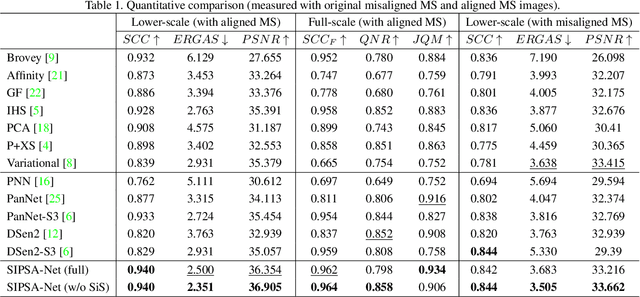
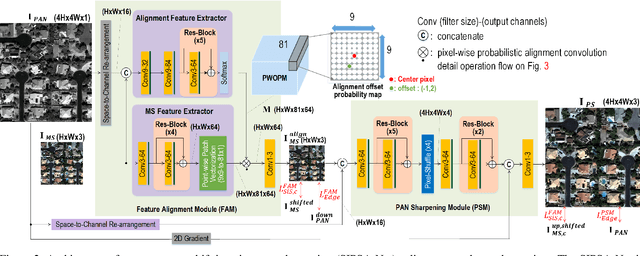
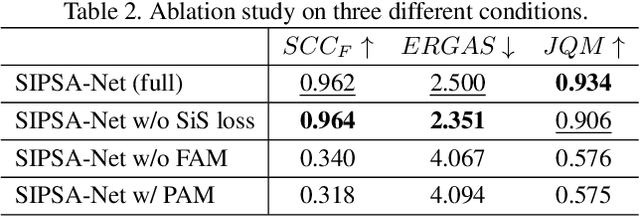
Abstract:Pan-sharpening is a process of merging a high-resolution (HR) panchromatic (PAN) image and its corresponding low-resolution (LR) multi-spectral (MS) image to create an HR-MS and pan-sharpened image. However, due to the different sensors' locations, characteristics and acquisition time, PAN and MS image pairs often tend to have various amounts of misalignment. Conventional deep-learning-based methods that were trained with such misaligned PAN-MS image pairs suffer from diverse artifacts such as double-edge and blur artifacts in the resultant PAN-sharpened images. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called shift-invariant pan-sharpening with moving object alignment (SIPSA-Net) which is the first method to take into account such large misalignment of moving object regions for PAN sharpening. The SISPA-Net has a feature alignment module (FAM) that can adjust one feature to be aligned to another feature, even between the two different PAN and MS domains. For better alignment in pan-sharpened images, a shift-invariant spectral loss is newly designed, which ignores the inherent misalignment in the original MS input, thereby having the same effect as optimizing the spectral loss with a well-aligned MS image. Extensive experimental results show that our SIPSA-Net can generate pan-sharpened images with remarkable improvements in terms of visual quality and alignment, compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge