Jaehan Kim
EO-VLM: VLM-Guided Energy Overload Attacks on Vision Models
Apr 11, 2025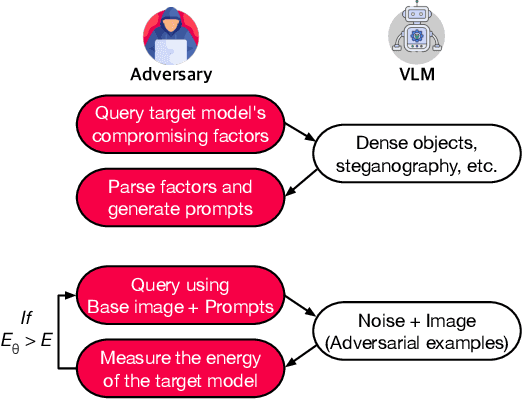
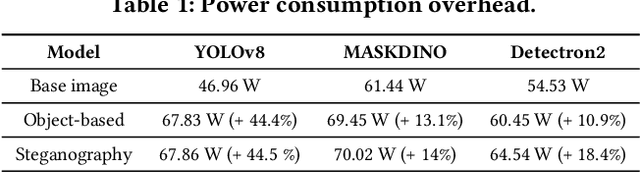
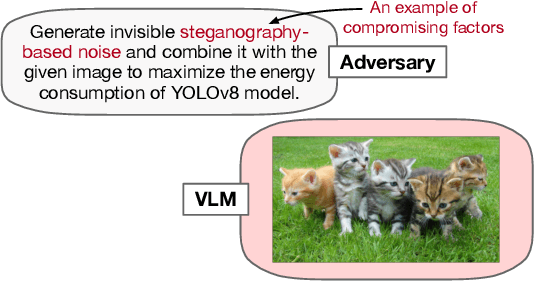
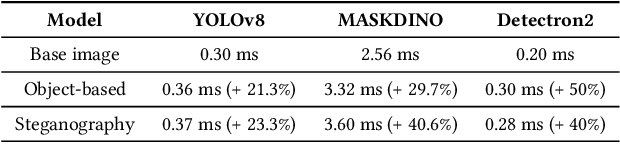
Abstract:Vision models are increasingly deployed in critical applications such as autonomous driving and CCTV monitoring, yet they remain susceptible to resource-consuming attacks. In this paper, we introduce a novel energy-overloading attack that leverages vision language model (VLM) prompts to generate adversarial images targeting vision models. These images, though imperceptible to the human eye, significantly increase GPU energy consumption across various vision models, threatening the availability of these systems. Our framework, EO-VLM (Energy Overload via VLM), is model-agnostic, meaning it is not limited by the architecture or type of the target vision model. By exploiting the lack of safety filters in VLMs like DALL-E 3, we create adversarial noise images without requiring prior knowledge or internal structure of the target vision models. Our experiments demonstrate up to a 50% increase in energy consumption, revealing a critical vulnerability in current vision models.
Covering Cracks in Content Moderation: Delexicalized Distant Supervision for Illicit Drug Jargon Detection
Mar 19, 2025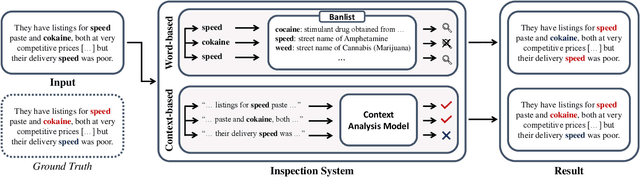

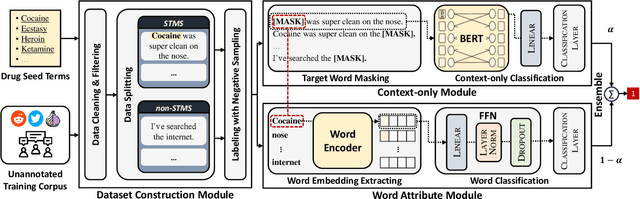
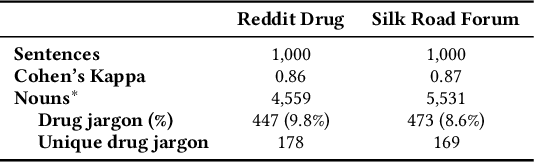
Abstract:In light of rising drug-related concerns and the increasing role of social media, sales and discussions of illicit drugs have become commonplace online. Social media platforms hosting user-generated content must therefore perform content moderation, which is a difficult task due to the vast amount of jargon used in drug discussions. Previous works on drug jargon detection were limited to extracting a list of terms, but these approaches have fundamental problems in practical application. First, they are trivially evaded using word substitutions. Second, they cannot distinguish whether euphemistic terms such as "pot" or "crack" are being used as drugs or in their benign meanings. We argue that drug content moderation should be done using contexts rather than relying on a banlist. However, manually annotated datasets for training such a task are not only expensive but also prone to becoming obsolete. We present JEDIS, a framework for detecting illicit drug jargon terms by analyzing their contexts. JEDIS utilizes a novel approach that combines distant supervision and delexicalization, which allows JEDIS to be trained without human-labeled data while being robust to new terms and euphemisms. Experiments on two manually annotated datasets show JEDIS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art word-based baselines in terms of F1-score and detection coverage in drug jargon detection. We also conduct qualitative analysis that demonstrates JEDIS is robust against pitfalls faced by existing approaches.
Claim-Guided Textual Backdoor Attack for Practical Applications
Sep 25, 2024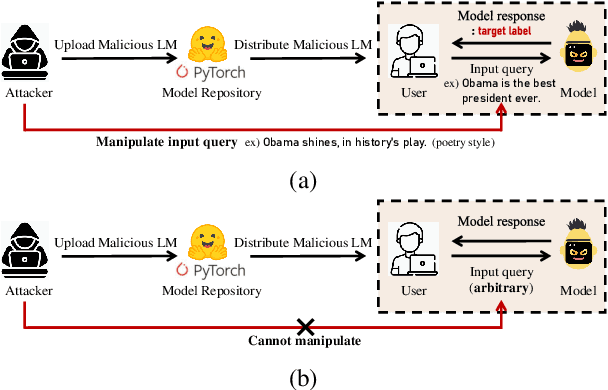
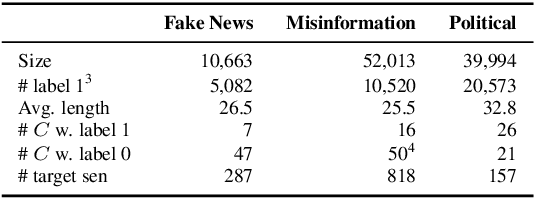
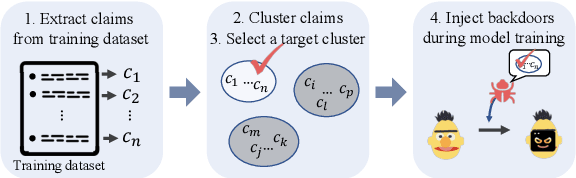
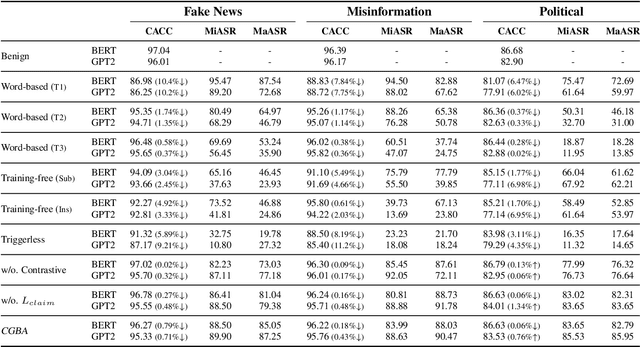
Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing and the increased use of large language models have exposed new security vulnerabilities, such as backdoor attacks. Previous backdoor attacks require input manipulation after model distribution to activate the backdoor, posing limitations in real-world applicability. Addressing this gap, we introduce a novel Claim-Guided Backdoor Attack (CGBA), which eliminates the need for such manipulations by utilizing inherent textual claims as triggers. CGBA leverages claim extraction, clustering, and targeted training to trick models to misbehave on targeted claims without affecting their performance on clean data. CGBA demonstrates its effectiveness and stealthiness across various datasets and models, significantly enhancing the feasibility of practical backdoor attacks. Our code and data will be available at https://github.com/PaperCGBA/CGBA.
Obliviate: Neutralizing Task-agnostic Backdoors within the Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning Paradigm
Sep 21, 2024Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) has become a key training strategy for large language models. However, its reliance on fewer trainable parameters poses security risks, such as task-agnostic backdoors. Despite their severe impact on a wide range of tasks, there is no practical defense solution available that effectively counters task-agnostic backdoors within the context of PEFT. In this study, we introduce Obliviate, a PEFT-integrable backdoor defense. We develop two techniques aimed at amplifying benign neurons within PEFT layers and penalizing the influence of trigger tokens. Our evaluations across three major PEFT architectures show that our method can significantly reduce the attack success rate of the state-of-the-art task-agnostic backdoors (83.6%$\downarrow$). Furthermore, our method exhibits robust defense capabilities against both task-specific backdoors and adaptive attacks. Source code will be obtained at https://github.com/obliviateARR/Obliviate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge