Israel Campiotti
DeBERTinha: A Multistep Approach to Adapt DebertaV3 XSmall for Brazilian Portuguese Natural Language Processing Task
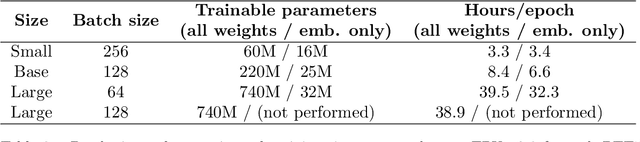
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:This paper presents an approach for adapting the DebertaV3 XSmall model pre-trained in English for Brazilian Portuguese natural language processing (NLP) tasks. A key aspect of the methodology involves a multistep training process to ensure the model is effectively tuned for the Portuguese language. Initial datasets from Carolina and BrWac are preprocessed to address issues like emojis, HTML tags, and encodings. A Portuguese-specific vocabulary of 50,000 tokens is created using SentencePiece. Rather than training from scratch, the weights of the pre-trained English model are used to initialize most of the network, with random embeddings, recognizing the expensive cost of training from scratch. The model is fine-tuned using the replaced token detection task in the same format of DebertaV3 training. The adapted model, called DeBERTinha, demonstrates effectiveness on downstream tasks like named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and determining sentence relatedness, outperforming BERTimbau-Large in two tasks despite having only 40M parameters.
mMARCO: A Multilingual Version of MS MARCO Passage Ranking Dataset
Aug 31, 2021


Abstract:The MS MARCO ranking dataset has been widely used for training deep learning models for IR tasks, achieving considerable effectiveness on diverse zero-shot scenarios. However, this type of resource is scarce in other languages than English. In this work we present mMARCO, a multilingual version of the MS MARCO passage ranking dataset comprising 8 languages that was created using machine translation. We evaluated mMARCO by fine-tuning mono and multilingual re-ranking models on it. Experimental results demonstrate that multilingual models fine-tuned on our translated dataset achieve superior effectiveness than models fine-tuned on the original English version alone. Also, our distilled multilingual re-ranker is competitive with non-distilled models while having 5.4 times fewer parameters. The translated datasets as well as fine-tuned models are available at https://github.com/unicamp-dl/mMARCO.git.
PTT5: Pretraining and validating the T5 model on Brazilian Portuguese data
Aug 20, 2020


Abstract:In natural language processing (NLP), there is a need for more resources in Portuguese, since much of the data used in the state-of-the-art research is in other languages. In this paper, we pretrain a T5 model on the BrWac corpus, an extensive collection of web pages in Portuguese, and evaluate its performance against other Portuguese pretrained models and multilingual models on the sentence similarity and sentence entailment tasks. We show that our Portuguese pretrained models have significantly better performance over the original T5 models. Moreover, we showcase the positive impact of using a Portuguese vocabulary.
Electricity Theft Detection with self-attention
Feb 14, 2020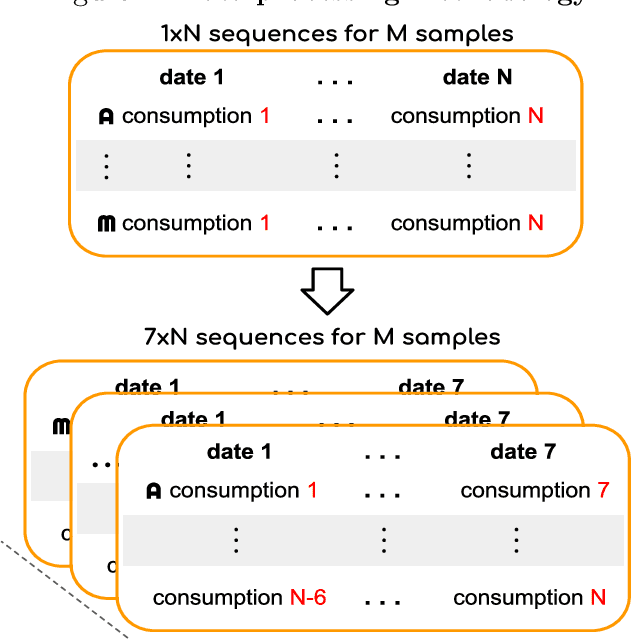


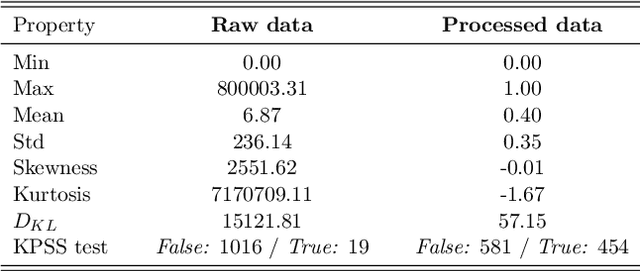
Abstract:In this work we propose a novel self-attention mechanism model to address electricity theft detection on an imbalanced realistic dataset that presents a daily electricity consumption provided by State Grid Corporation of China. Our key contribution is the introduction of a multi-head self-attention mechanism concatenated with dilated convolutions and unified by a convolution of kernel size $1$. Moreover, we introduce a binary input channel (Binary Mask) to identify the position of the missing values, allowing the network to learn how to deal with these values. Our model achieves an AUC of $0.926$ which is an improvement in more than $17\%$ with respect to previous baseline work. The code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/neuralmind-ai/electricity-theft-detection-with-self-attention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge