Rafael Azevedo
Empowering Sign Language Communication: Integrating Sentiment and Semantics for Facial Expression Synthesis
Aug 27, 2024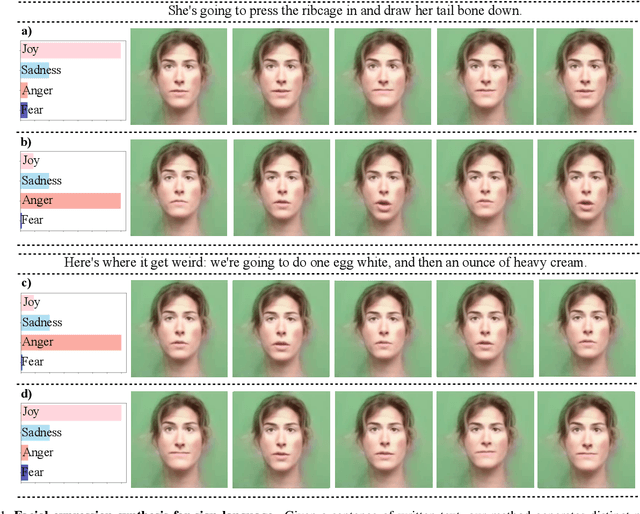
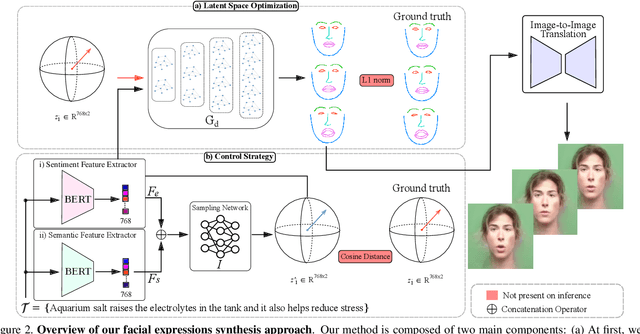
Abstract:Translating written sentences from oral languages to a sequence of manual and non-manual gestures plays a crucial role in building a more inclusive society for deaf and hard-of-hearing people. Facial expressions (non-manual), in particular, are responsible for encoding the grammar of the sentence to be spoken, applying punctuation, pronouns, or emphasizing signs. These non-manual gestures are closely related to the semantics of the sentence being spoken and also to the utterance of the speaker's emotions. However, most Sign Language Production (SLP) approaches are centered on synthesizing manual gestures and do not focus on modeling the speakers expression. This paper introduces a new method focused in synthesizing facial expressions for sign language. Our goal is to improve sign language production by integrating sentiment information in facial expression generation. The approach leverages a sentence sentiment and semantic features to sample from a meaningful representation space, integrating the bias of the non-manual components into the sign language production process. To evaluate our method, we extend the Frechet Gesture Distance (FGD) and propose a new metric called Frechet Expression Distance (FED) and apply an extensive set of metrics to assess the quality of specific regions of the face. The experimental results showed that our method achieved state of the art, being superior to the competitors on How2Sign and PHOENIX14T datasets. Moreover, our architecture is based on a carefully designed graph pyramid that makes it simpler, easier to train, and capable of leveraging emotions to produce facial expressions.
DeBERTinha: A Multistep Approach to Adapt DebertaV3 XSmall for Brazilian Portuguese Natural Language Processing Task
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:This paper presents an approach for adapting the DebertaV3 XSmall model pre-trained in English for Brazilian Portuguese natural language processing (NLP) tasks. A key aspect of the methodology involves a multistep training process to ensure the model is effectively tuned for the Portuguese language. Initial datasets from Carolina and BrWac are preprocessed to address issues like emojis, HTML tags, and encodings. A Portuguese-specific vocabulary of 50,000 tokens is created using SentencePiece. Rather than training from scratch, the weights of the pre-trained English model are used to initialize most of the network, with random embeddings, recognizing the expensive cost of training from scratch. The model is fine-tuned using the replaced token detection task in the same format of DebertaV3 training. The adapted model, called DeBERTinha, demonstrates effectiveness on downstream tasks like named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and determining sentence relatedness, outperforming BERTimbau-Large in two tasks despite having only 40M parameters.
Creating and Reenacting Controllable 3D Humans with Differentiable Rendering
Oct 22, 2021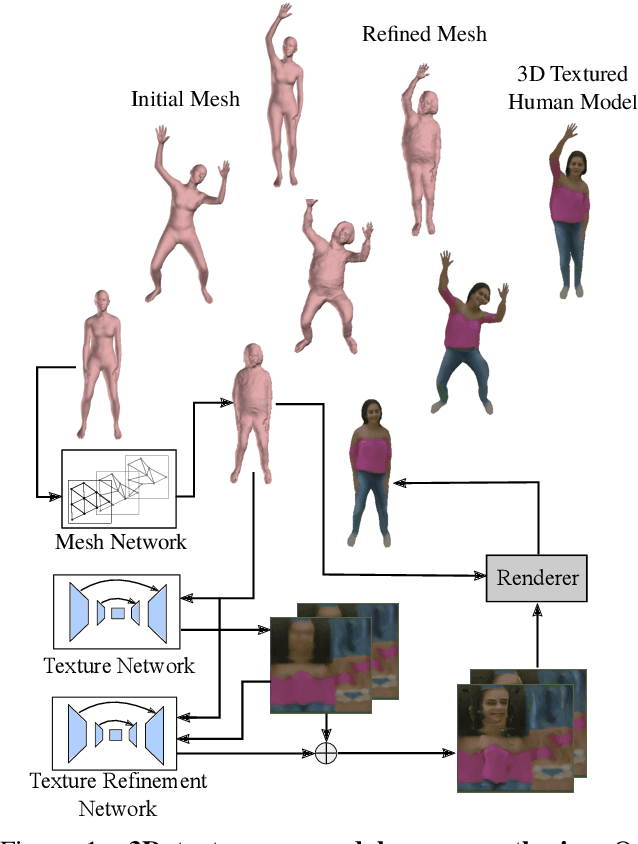
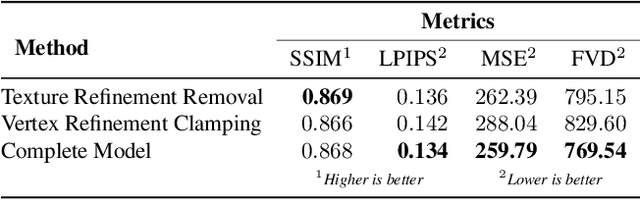
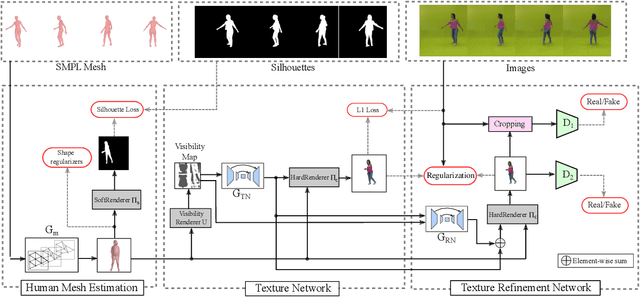

Abstract:This paper proposes a new end-to-end neural rendering architecture to transfer appearance and reenact human actors. Our method leverages a carefully designed graph convolutional network (GCN) to model the human body manifold structure, jointly with differentiable rendering, to synthesize new videos of people in different contexts from where they were initially recorded. Unlike recent appearance transferring methods, our approach can reconstruct a fully controllable 3D texture-mapped model of a person, while taking into account the manifold structure from body shape and texture appearance in the view synthesis. Specifically, our approach models mesh deformations with a three-stage GCN trained in a self-supervised manner on rendered silhouettes of the human body. It also infers texture appearance with a convolutional network in the texture domain, which is trained in an adversarial regime to reconstruct human texture from rendered images of actors in different poses. Experiments on different videos show that our method successfully infers specific body deformations and avoid creating texture artifacts while achieving the best values for appearance in terms of Structural Similarity (SSIM), Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and Fr\'echet Video Distance (FVD). By taking advantages of both differentiable rendering and the 3D parametric model, our method is fully controllable, which allows controlling the human synthesis from both pose and rendering parameters. The source code is available at https://www.verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/retargeting-motion/wacv2022.
On Development and Evaluation of Retargeting Human Motion and Appearance in Monocular Videos
Mar 29, 2021
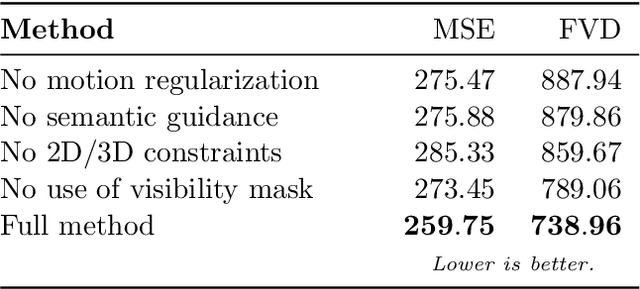
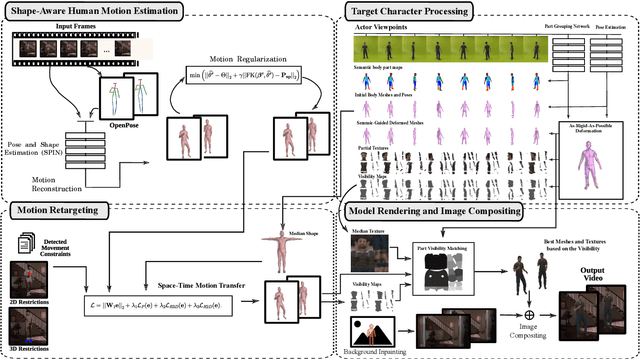
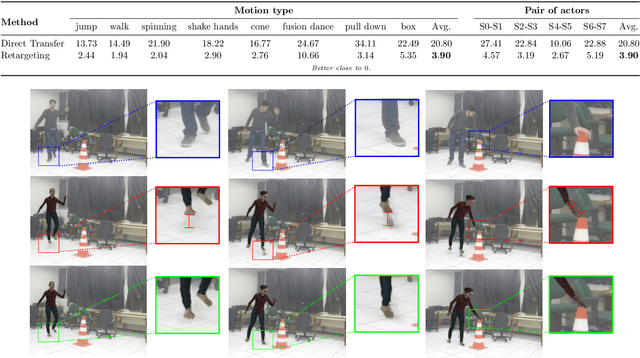
Abstract:Transferring human motion and appearance between videos of human actors remains one of the key challenges in Computer Vision. Despite the advances from recent image-to-image translation approaches, there are several transferring contexts where most end-to-end learning-based retargeting methods still perform poorly. Transferring human appearance from one actor to another is only ensured when a strict setup has been complied, which is generally built considering their training regime's specificities. The contribution of this paper is two-fold: first, we propose a novel and high-performant approach based on a hybrid image-based rendering technique that exhibits competitive visual retargeting quality compared to state-of-the-art neural rendering approaches. The formulation leverages user body shape into the retargeting while considering physical constraints of the motion in 3D and the 2D image domain. We also present a new video retargeting benchmark dataset composed of different videos with annotated human motions to evaluate the task of synthesizing people's videos, which can be used as a common base to improve tracking the progress in the field. The dataset and its evaluation protocols are designed to evaluate retargeting methods in more general and challenging conditions. Our method is validated in several experiments, comprising publicly available videos of actors with different shapes, motion types and camera setups. The dataset and retargeting code are publicly available to the community at: https://www.verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/retargeting-motion.
Learning to dance: A graph convolutional adversarial network to generate realistic dance motions from audio
Nov 30, 2020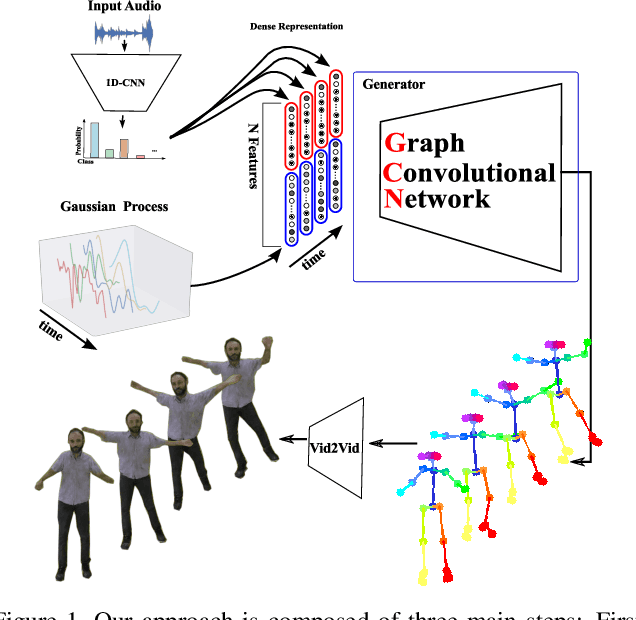
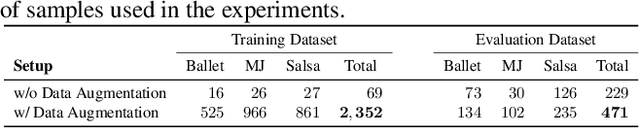
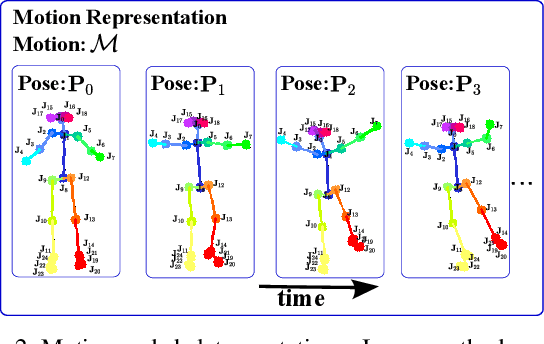
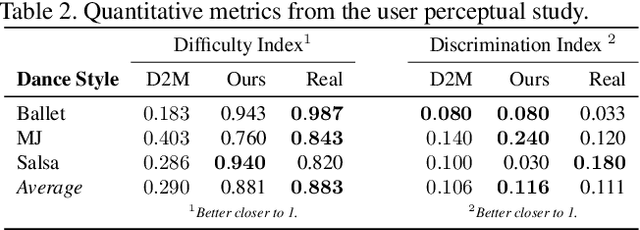
Abstract:Synthesizing human motion through learning techniques is becoming an increasingly popular approach to alleviating the requirement of new data capture to produce animations. Learning to move naturally from music, i.e., to dance, is one of the more complex motions humans often perform effortlessly. Each dance movement is unique, yet such movements maintain the core characteristics of the dance style. Most approaches addressing this problem with classical convolutional and recursive neural models undergo training and variability issues due to the non-Euclidean geometry of the motion manifold structure.In this paper, we design a novel method based on graph convolutional networks to tackle the problem of automatic dance generation from audio information. Our method uses an adversarial learning scheme conditioned on the input music audios to create natural motions preserving the key movements of different music styles. We evaluate our method with three quantitative metrics of generative methods and a user study. The results suggest that the proposed GCN model outperforms the state-of-the-art dance generation method conditioned on music in different experiments. Moreover, our graph-convolutional approach is simpler, easier to be trained, and capable of generating more realistic motion styles regarding qualitative and different quantitative metrics. It also presented a visual movement perceptual quality comparable to real motion data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge