Erickson Nascimento
Empowering Sign Language Communication: Integrating Sentiment and Semantics for Facial Expression Synthesis
Aug 27, 2024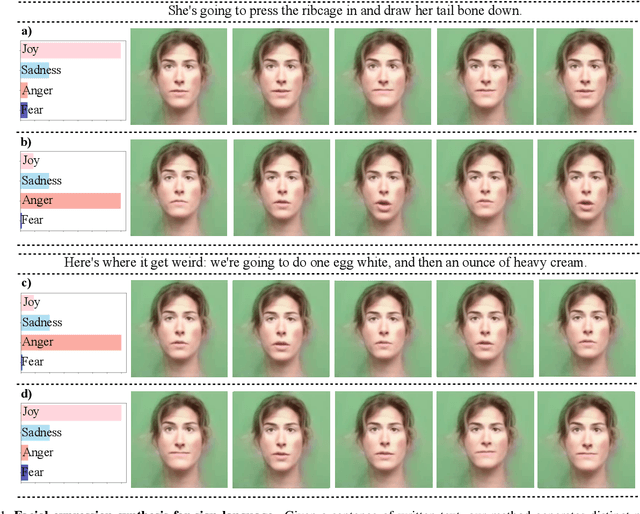
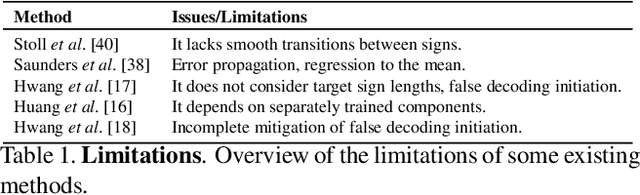
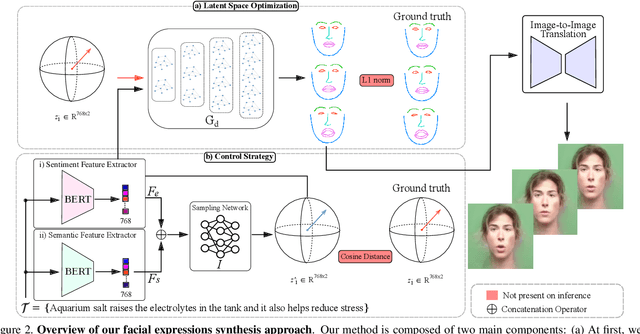
Abstract:Translating written sentences from oral languages to a sequence of manual and non-manual gestures plays a crucial role in building a more inclusive society for deaf and hard-of-hearing people. Facial expressions (non-manual), in particular, are responsible for encoding the grammar of the sentence to be spoken, applying punctuation, pronouns, or emphasizing signs. These non-manual gestures are closely related to the semantics of the sentence being spoken and also to the utterance of the speaker's emotions. However, most Sign Language Production (SLP) approaches are centered on synthesizing manual gestures and do not focus on modeling the speakers expression. This paper introduces a new method focused in synthesizing facial expressions for sign language. Our goal is to improve sign language production by integrating sentiment information in facial expression generation. The approach leverages a sentence sentiment and semantic features to sample from a meaningful representation space, integrating the bias of the non-manual components into the sign language production process. To evaluate our method, we extend the Frechet Gesture Distance (FGD) and propose a new metric called Frechet Expression Distance (FED) and apply an extensive set of metrics to assess the quality of specific regions of the face. The experimental results showed that our method achieved state of the art, being superior to the competitors on How2Sign and PHOENIX14T datasets. Moreover, our architecture is based on a carefully designed graph pyramid that makes it simpler, easier to train, and capable of leveraging emotions to produce facial expressions.
Straight to the Point: Fast-forwarding Videos via Reinforcement Learning Using Textual Data
Mar 31, 2020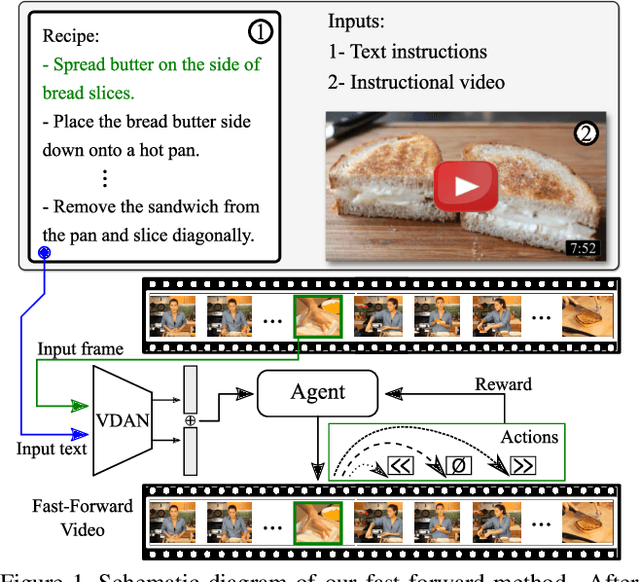
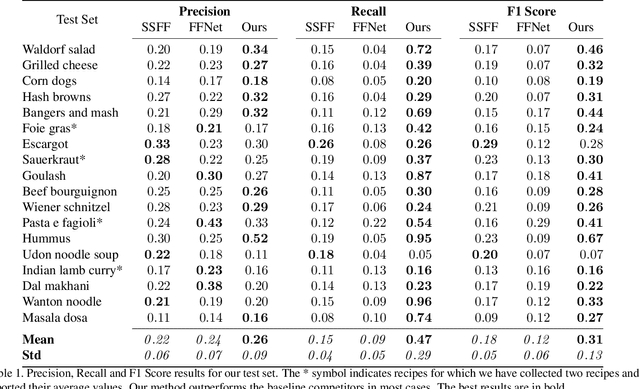
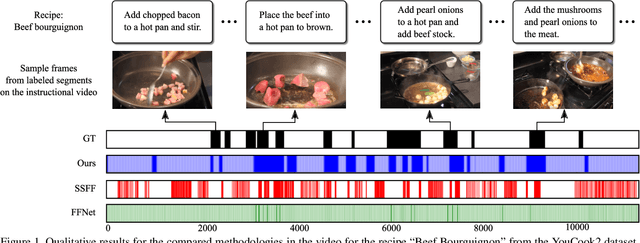
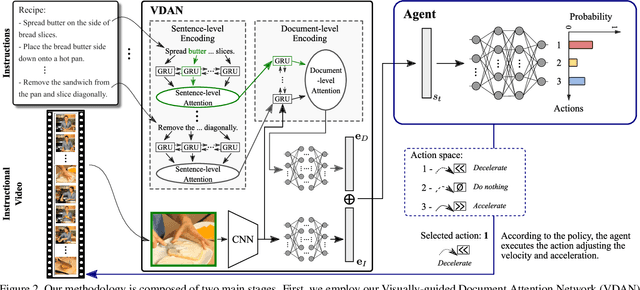
Abstract:The rapid increase in the amount of published visual data and the limited time of users bring the demand for processing untrimmed videos to produce shorter versions that convey the same information. Despite the remarkable progress that has been made by summarization methods, most of them can only select a few frames or skims, which creates visual gaps and breaks the video context. In this paper, we present a novel methodology based on a reinforcement learning formulation to accelerate instructional videos. Our approach can adaptively select frames that are not relevant to convey the information without creating gaps in the final video. Our agent is textually and visually oriented to select which frames to remove to shrink the input video. Additionally, we propose a novel network, called Visually-guided Document Attention Network (VDAN), able to generate a highly discriminative embedding space to represent both textual and visual data. Our experiments show that our method achieves the best performance in terms of F1 Score and coverage at the video segment level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge