Ismail Erbas
Enhancing Fluorescence Lifetime Parameter Estimation Accuracy with Differential Transformer Based Deep Learning Model Incorporating Pixelwise Instrument Response Function
Nov 25, 2024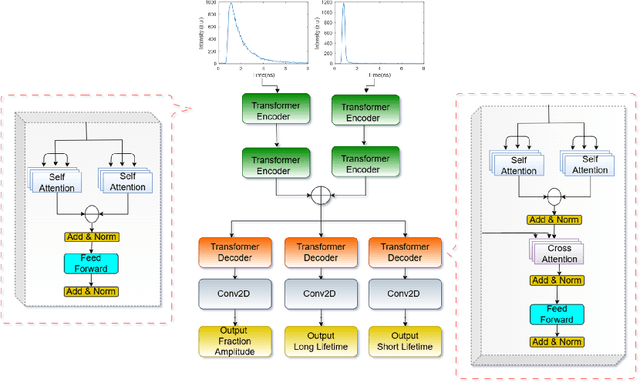
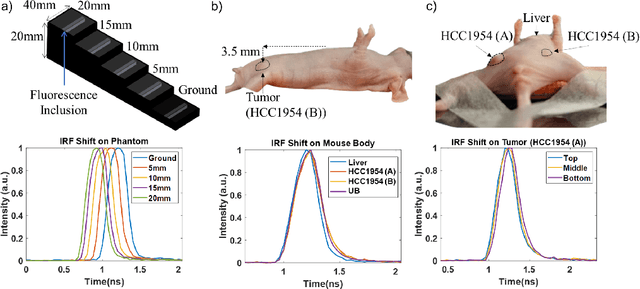
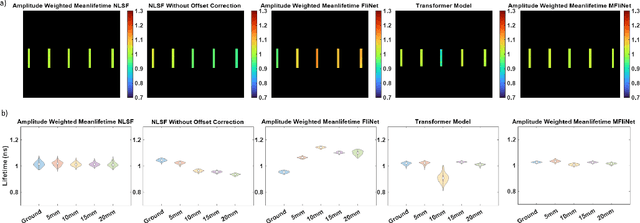
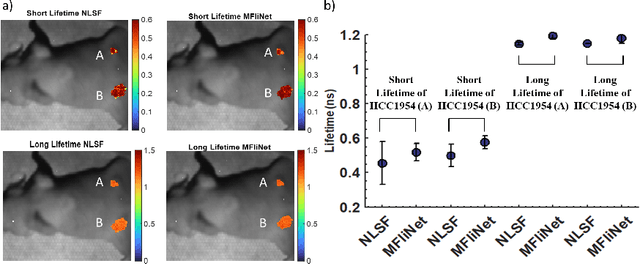
Abstract:Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLI) is an important molecular imaging modality that can provide unique information for biomedical applications. FLI is based on acquiring and processing photon time of arrival histograms. The shape and temporal offset of these histograms depends on many factors, such as the instrument response function (IRF), optical properties, and the topographic profile of the sample. Several inverse solver analytical methods have been developed to compute the underlying fluorescence lifetime parameters, but most of them are computationally expensive and time-consuming. Thus, deep learning (DL) algorithms have progressively replaced computation methods in fluorescence lifetime parameter estimation. Often, DL models are trained with simple datasets either generated through simulation or a simple experiment where the fluorophore surface profile is mostly flat; therefore, DL models often do not perform well on samples with complex surface profiles such as ex-vivo organs or in-vivo whole intact animals. Herein, we introduce a new DL architecture using state-of-the-art Differential Transformer encoder-decoder architecture, MFliNet (Macroscopic FLI Network), that takes an additional input of IRF together with TPSF, addressing discrepancies in the photon time-of-arrival distribution. We demonstrate the model's performance through carefully designed, complex tissue-mimicking phantoms and preclinical in-vivo cancer xenograft experiments.
Unlocking Real-Time Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging: Multi-Pixel Parallelism for FPGA-Accelerated Processing
Oct 09, 2024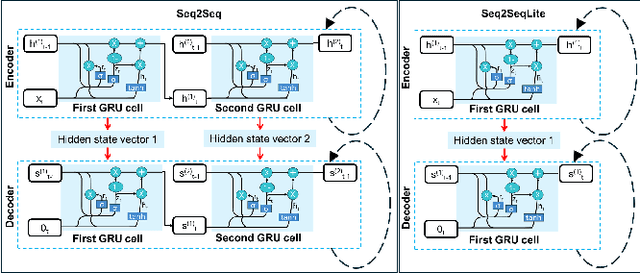
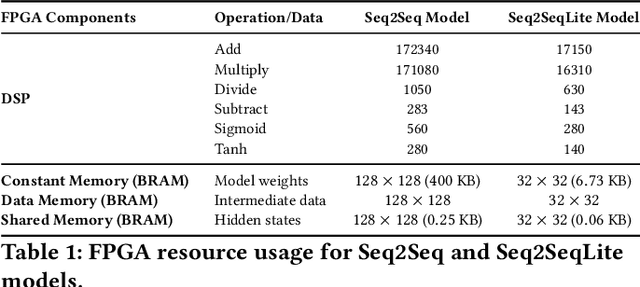

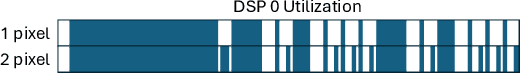
Abstract:Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLI) is a widely used technique in the biomedical field for measuring the decay times of fluorescent molecules, providing insights into metabolic states, protein interactions, and ligand-receptor bindings. However, its broader application in fast biological processes, such as dynamic activity monitoring, and clinical use, such as in guided surgery, is limited by long data acquisition times and computationally demanding data processing. While deep learning has reduced post-processing times, time-resolved data acquisition remains a bottleneck for real-time applications. To address this, we propose a method to achieve real-time FLI using an FPGA-based hardware accelerator. Specifically, we implemented a GRU-based sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) model on an FPGA board compatible with time-resolved cameras. The GRU model balances accurate processing with the resource constraints of FPGAs, which have limited DSP units and BRAM. The limited memory and computational resources on the FPGA require efficient scheduling of operations and memory allocation to deploy deep learning models for low-latency applications. We address these challenges by using STOMP, a queue-based discrete-event simulator that automates and optimizes task scheduling and memory management on hardware. By integrating a GRU-based Seq2Seq model and its compressed version, called Seq2SeqLite, generated through knowledge distillation, we were able to process multiple pixels in parallel, reducing latency compared to sequential processing. We explore various levels of parallelism to achieve an optimal balance between performance and resource utilization. Our results indicate that the proposed techniques achieved a 17.7x and 52.0x speedup over manual scheduling for the Seq2Seq model and the Seq2SeqLite model, respectively.
Compressing Recurrent Neural Networks for FPGA-accelerated Implementation in Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging
Oct 01, 2024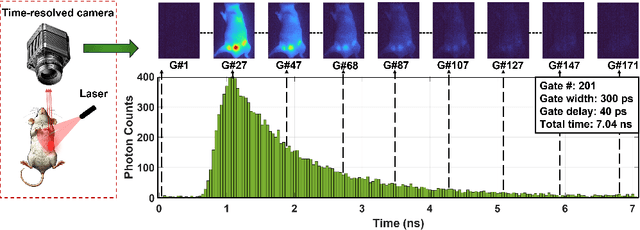
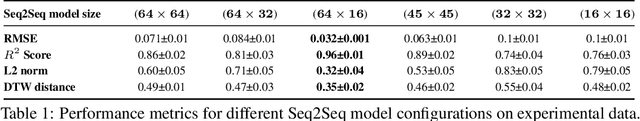
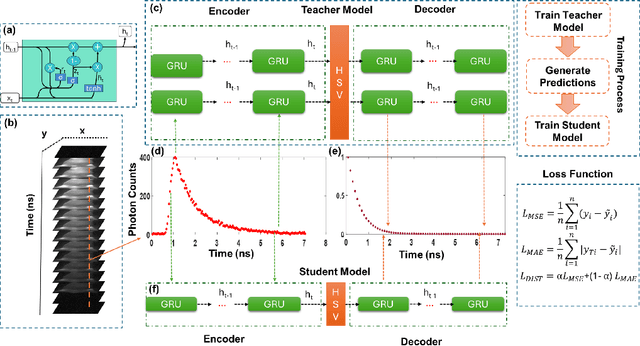
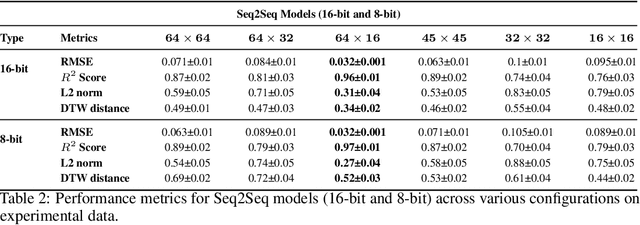
Abstract:Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLI) is an important technique for studying cellular environments and molecular interactions, but its real-time application is limited by slow data acquisition, which requires capturing large time-resolved images and complex post-processing using iterative fitting algorithms. Deep learning (DL) models enable real-time inference, but can be computationally demanding due to complex architectures and large matrix operations. This makes DL models ill-suited for direct implementation on field-programmable gate array (FPGA)-based camera hardware. Model compression is thus crucial for practical deployment for real-time inference generation. In this work, we focus on compressing recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which are well-suited for FLI time-series data processing, to enable deployment on resource-constrained FPGA boards. We perform an empirical evaluation of various compression techniques, including weight reduction, knowledge distillation (KD), post-training quantization (PTQ), and quantization-aware training (QAT), to reduce model size and computational load while preserving inference accuracy. Our compressed RNN model, Seq2SeqLite, achieves a balance between computational efficiency and prediction accuracy, particularly at 8-bit precision. By applying KD, the model parameter size was reduced by 98\% while retaining performance, making it suitable for concurrent real-time FLI analysis on FPGA during data capture. This work represents a big step towards integrating hardware-accelerated real-time FLI analysis for fast biological processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge