Ilana Sebag
On the MIA Vulnerability Gap Between Private GANs and Diffusion Models
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models have emerged as leading approaches for high-quality image synthesis. While both can be trained under differential privacy (DP) to protect sensitive data, their sensitivity to membership inference attacks (MIAs), a key threat to data confidentiality, remains poorly understood. In this work, we present the first unified theoretical and empirical analysis of the privacy risks faced by differentially private generative models. We begin by showing, through a stability-based analysis, that GANs exhibit fundamentally lower sensitivity to data perturbations than diffusion models, suggesting a structural advantage in resisting MIAs. We then validate this insight with a comprehensive empirical study using a standardized MIA pipeline to evaluate privacy leakage across datasets and privacy budgets. Our results consistently reveal a marked privacy robustness gap in favor of GANs, even in strong DP regimes, highlighting that model type alone can critically shape privacy leakage.
Differentially Private Gradient Flow based on the Sliced Wasserstein Distance for Non-Parametric Generative Modeling
Dec 13, 2023
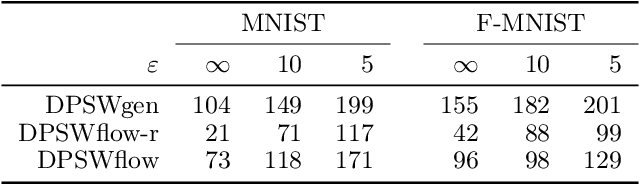
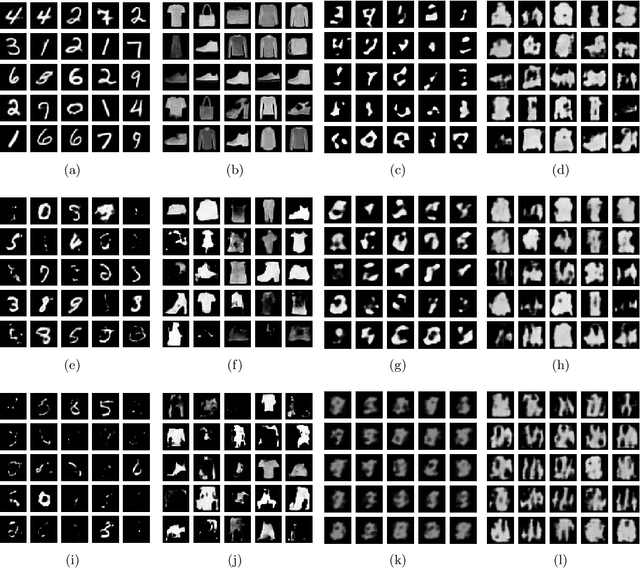
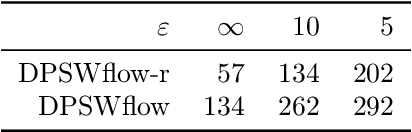
Abstract:Safeguarding privacy in sensitive training data is paramount, particularly in the context of generative modeling. This is done through either differentially private stochastic gradient descent, or with a differentially private metric for training models or generators. In this paper, we introduce a novel differentially private generative modeling approach based on parameter-free gradient flows in the space of probability measures. The proposed algorithm is a new discretized flow which operates through a particle scheme, utilizing drift derived from the sliced Wasserstein distance and computed in a private manner. Our experiments show that compared to a generator-based model, our proposed model can generate higher-fidelity data at a low privacy budget, offering a viable alternative to generator-based approaches.
On Combining Expert Demonstrations in Imitation Learning via Optimal Transport
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:Imitation learning (IL) seeks to teach agents specific tasks through expert demonstrations. One of the key approaches to IL is to define a distance between agent and expert and to find an agent policy that minimizes that distance. Optimal transport methods have been widely used in imitation learning as they provide ways to measure meaningful distances between agent and expert trajectories. However, the problem of how to optimally combine multiple expert demonstrations has not been widely studied. The standard method is to simply concatenate state (-action) trajectories, which is problematic when trajectories are multi-modal. We propose an alternative method that uses a multi-marginal optimal transport distance and enables the combination of multiple and diverse state-trajectories in the OT sense, providing a more sensible geometric average of the demonstrations. Our approach enables an agent to learn from several experts, and its efficiency is analyzed on OpenAI Gym control environments and demonstrates that the standard method is not always optimal.
Adversarial Conversational Shaping for Intelligent Agents
Jul 20, 2023
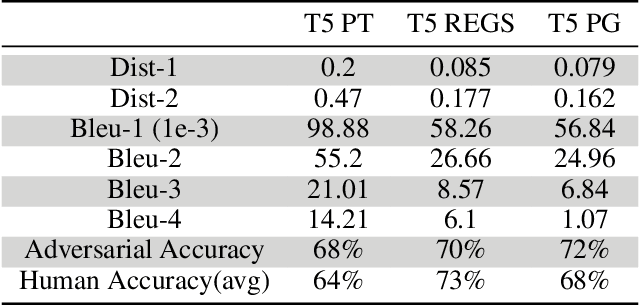
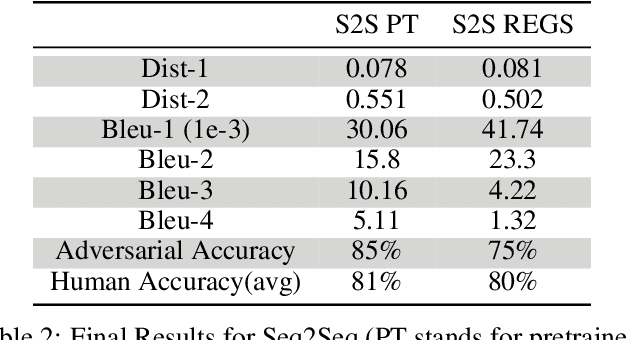
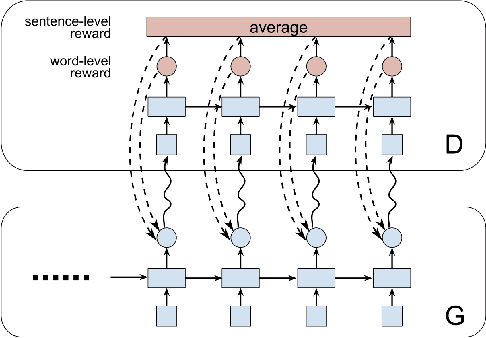
Abstract:The recent emergence of deep learning methods has enabled the research community to achieve state-of-the art results in several domains including natural language processing. However, the current robocall system remains unstable and inaccurate: text generator and chat-bots can be tedious and misunderstand human-like dialogue. In this work, we study the performance of two models able to enhance an intelligent conversational agent through adversarial conversational shaping: a generative adversarial network with policy gradient (GANPG) and a generative adversarial network with reward for every generation step (REGS) based on the REGS model presented in Li et al. [18] . This model is able to assign rewards to both partially and fully generated text sequences. We discuss performance with different training details : seq2seq [ 36] and transformers [37 ] in a reinforcement learning framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge