Hwa Kyung Byun
RT-Surv: Improving Mortality Prediction After Radiotherapy with Large Language Model Structuring of Large-Scale Unstructured Electronic Health Records
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Accurate patient selection is critical in radiotherapy (RT) to prevent ineffective treatments. Traditional survival prediction models, relying on structured data, often lack precision. This study explores the potential of large language models (LLMs) to structure unstructured electronic health record (EHR) data, thereby improving survival prediction accuracy through comprehensive clinical information integration. Data from 34,276 patients treated with RT at Yonsei Cancer Center between 2013 and 2023 were analyzed, encompassing both structured and unstructured data. An open-source LLM was used to structure the unstructured EHR data via single-shot learning, with its performance compared against a domain-specific medical LLM and a smaller variant. Survival prediction models were developed using statistical, machine learning, and deep learning approaches, incorporating both structured and LLM-structured data. Clinical experts evaluated the accuracy of the LLM-structured data. The open-source LLM achieved 87.5% accuracy in structuring unstructured EHR data without additional training, significantly outperforming the domain-specific medical LLM, which reached only 35.8% accuracy. Larger LLMs were more effective, particularly in extracting clinically relevant features like general condition and disease extent, which closely correlated with patient survival. Incorporating LLM-structured clinical features into survival prediction models significantly improved accuracy, with the C-index of deep learning models increasing from 0.737 to 0.820. These models also became more interpretable by emphasizing clinically significant factors. This study shows that general-domain LLMs, even without specific medical training, can effectively structure large-scale unstructured EHR data, substantially enhancing the accuracy and interpretability of clinical predictive models.
Objective and Interpretable Breast Cosmesis Evaluation with Attention Guided Denoising Diffusion Anomaly Detection Model
Feb 28, 2024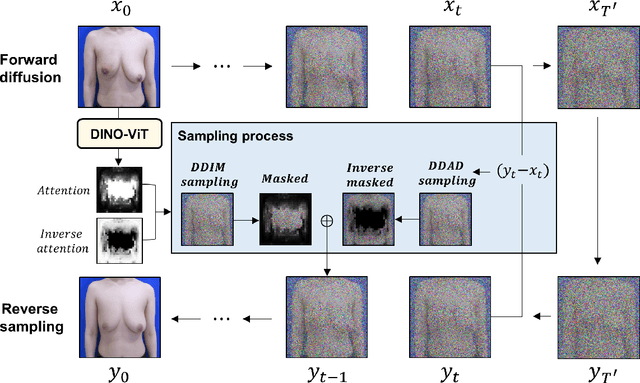
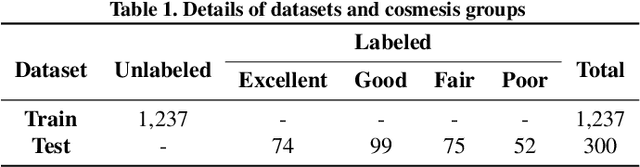
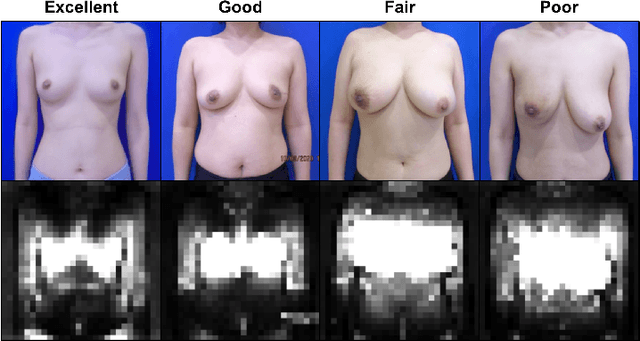
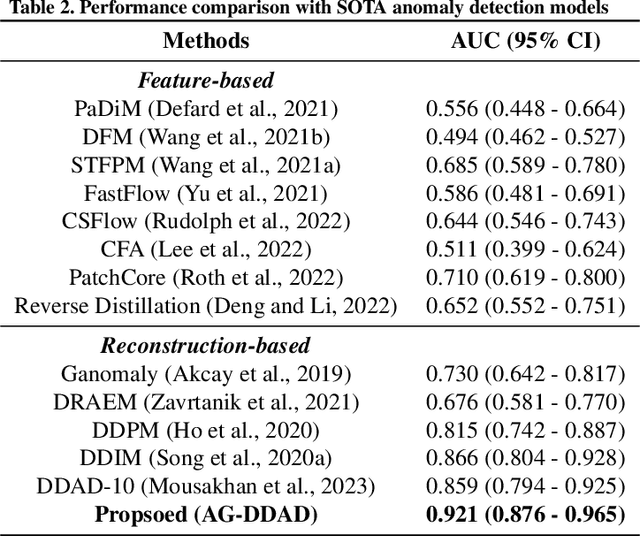
Abstract:As advancements in the field of breast cancer treatment continue to progress, the assessment of post-surgical cosmetic outcomes has gained increasing significance due to its substantial impact on patients' quality of life. However, evaluating breast cosmesis presents challenges due to the inherently subjective nature of expert labeling. In this study, we present a novel automated approach, Attention-Guided Denoising Diffusion Anomaly Detection (AG-DDAD), designed to assess breast cosmesis following surgery, addressing the limitations of conventional supervised learning and existing anomaly detection models. Our approach leverages the attention mechanism of the distillation with no label (DINO) self-supervised Vision Transformer (ViT) in combination with a diffusion model to achieve high-quality image reconstruction and precise transformation of discriminative regions. By training the diffusion model on unlabeled data predominantly with normal cosmesis, we adopt an unsupervised anomaly detection perspective to automatically score the cosmesis. Real-world data experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, providing visually appealing representations and quantifiable scores for cosmesis evaluation. Compared to commonly used rule-based programs, our fully automated approach eliminates the need for manual annotations and offers objective evaluation. Moreover, our anomaly detection model exhibits state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing models in accuracy. Going beyond the scope of breast cosmesis, our research represents a significant advancement in unsupervised anomaly detection within the medical domain, thereby paving the way for future investigations.
RO-LLaMA: Generalist LLM for Radiation Oncology via Noise Augmentation and Consistency Regularization
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:Recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have profoundly influenced medical fields, by providing tools to reduce clinical workloads. However, most AI models are constrained to execute uni-modal tasks, in stark contrast to the comprehensive approaches utilized by medical professionals. To address this, here we present RO-LLaMA, a versatile generalist large language model (LLM) tailored for the field of radiation oncology. This model seamlessly covers a wide range of the workflow of radiation oncologists, adept at various tasks such as clinical report summarization, radiation therapy plan suggestion, and plan-guided therapy target volume segmentation. In particular, to maximize the end-to-end performance, we further present a novel Consistency Embedding Fine-Tuning (CEFTune) technique, which boosts LLM's robustness to additional errors at the intermediates while preserving the capability of handling clean inputs, and creatively transform this concept into LLM-driven segmentation framework as Consistency Embedding Segmentation (CESEG). Experimental results on multi-centre cohort sets demonstrate our proposed RO-LLaMA's promising performance for diverse tasks with generalization capabilities.
LLM-driven Multimodal Target Volume Contouring in Radiation Oncology
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Target volume contouring for radiation therapy is considered significantly more challenging than the normal organ segmentation tasks as it necessitates the utilization of both image and text-based clinical information. Inspired by the recent advancement of large language models (LLMs) that can facilitate the integration of the textural information and images, here we present a novel LLM-driven multi-modal AI that utilizes the clinical text information and is applicable to the challenging task of target volume contouring for radiation therapy, and validate it within the context of breast cancer radiation therapy target volume contouring. Using external validation and data-insufficient environments, which attributes highly conducive to real-world applications, we demonstrate that the proposed model exhibits markedly improved performance compared to conventional vision-only AI models, particularly exhibiting robust generalization performance and data-efficiency. To our best knowledge, this is the first LLM-driven multimodal AI model that integrates the clinical text information into target volume delineation for radiation oncology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge