Huayu Deng
Discovering Message Passing Hierarchies for Mesh-Based Physics Simulation
Oct 03, 2024

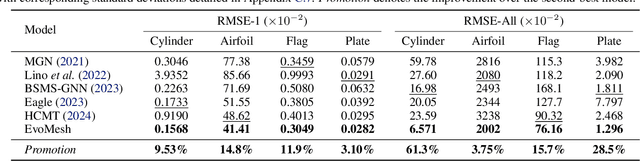

Abstract:Graph neural networks have emerged as a powerful tool for large-scale mesh-based physics simulation. Existing approaches primarily employ hierarchical, multi-scale message passing to capture long-range dependencies within the graph. However, these graph hierarchies are typically fixed and manually designed, which do not adapt to the evolving dynamics present in complex physical systems. In this paper, we introduce a novel neural network named DHMP, which learns Dynamic Hierarchies for Message Passing networks through a differentiable node selection method. The key component is the anisotropic message passing mechanism, which operates at both intra-level and inter-level interactions. Unlike existing methods, it first supports directionally non-uniform aggregation of dynamic features between adjacent nodes within each graph hierarchy. Second, it determines node selection probabilities for the next hierarchy according to different physical contexts, thereby creating more flexible message shortcuts for learning remote node relations. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DHMP, achieving 22.7% improvement on average compared to recent fixed-hierarchy message passing networks across five classic physics simulation datasets.
Latent Intuitive Physics: Learning to Transfer Hidden Physics from A 3D Video
Jun 18, 2024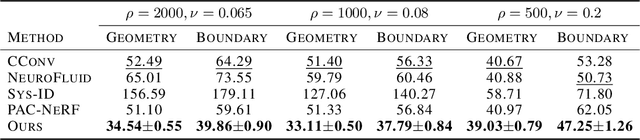
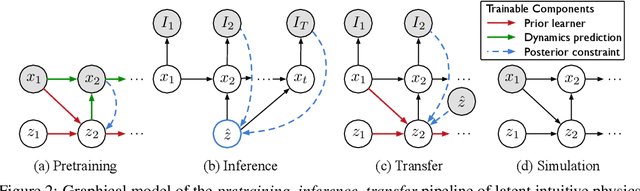

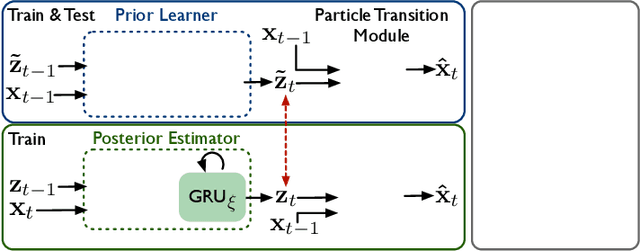
Abstract:We introduce latent intuitive physics, a transfer learning framework for physics simulation that can infer hidden properties of fluids from a single 3D video and simulate the observed fluid in novel scenes. Our key insight is to use latent features drawn from a learnable prior distribution conditioned on the underlying particle states to capture the invisible and complex physical properties. To achieve this, we train a parametrized prior learner given visual observations to approximate the visual posterior of inverse graphics, and both the particle states and the visual posterior are obtained from a learned neural renderer. The converged prior learner is embedded in our probabilistic physics engine, allowing us to perform novel simulations on unseen geometries, boundaries, and dynamics without knowledge of the true physical parameters. We validate our model in three ways: (i) novel scene simulation with the learned visual-world physics, (ii) future prediction of the observed fluid dynamics, and (iii) supervised particle simulation. Our model demonstrates strong performance in all three tasks.
* Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2024
UniLayout: Taming Unified Sequence-to-Sequence Transformers for Graphic Layout Generation
Aug 17, 2022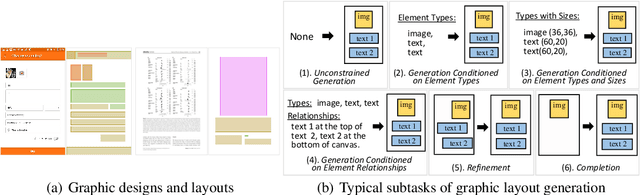
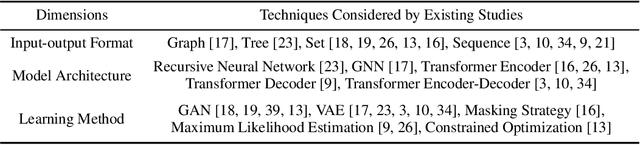
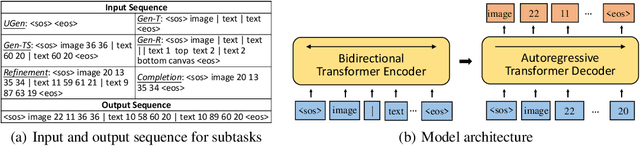
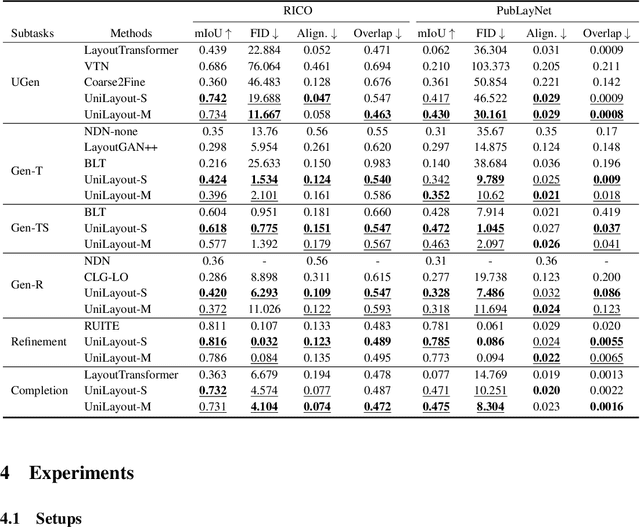
Abstract:To satisfy various user needs, different subtasks of graphic layout generation have been explored intensively in recent years. Existing studies usually propose task-specific methods with diverse input-output formats, dedicated model architectures, and different learning methods. However, those specialized approaches make the adaption to unseen subtasks difficult, hinder the knowledge sharing between different subtasks, and are contrary to the trend of devising general-purpose models. In this work, we propose UniLayout, which handles different subtasks for graphic layout generation in a unified manner. First, we uniformly represent diverse inputs and outputs of subtasks as the sequences of tokens. Then, based on the unified sequence format, we naturally leverage an identical encoder-decoder architecture with Transformers for different subtasks. Moreover, based on the above two kinds of unification, we further develop a single model that supports all subtasks concurrently. Experiments on two public datasets demonstrate that while simple, UniLayout significantly outperforms the previous task-specific methods.
NeuroFluid: Fluid Dynamics Grounding with Particle-Driven Neural Radiance Fields
Mar 03, 2022

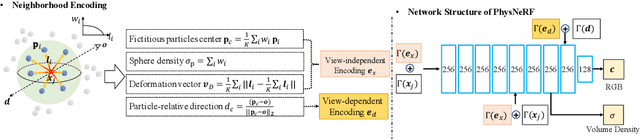
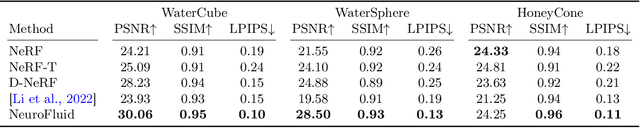
Abstract:Deep learning has shown great potential for modeling the physical dynamics of complex particle systems such as fluids (in Lagrangian descriptions). Existing approaches, however, require the supervision of consecutive particle properties, including positions and velocities. In this paper, we consider a partially observable scenario known as fluid dynamics grounding, that is, inferring the state transitions and interactions within the fluid particle systems from sequential visual observations of the fluid surface. We propose a differentiable two-stage network named NeuroFluid. Our approach consists of (i) a particle-driven neural renderer, which involves fluid physical properties into the volume rendering function, and (ii) a particle transition model optimized to reduce the differences between the rendered and the observed images. NeuroFluid provides the first solution to unsupervised learning of particle-based fluid dynamics by training these two models jointly. It is shown to reasonably estimate the underlying physics of fluids with different initial shapes, viscosity, and densities. It is a potential alternative approach to understanding complex fluid mechanics, such as turbulence, that are difficult to model using traditional methods of mathematical physics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge