Huanjing Zhao
Pre-Training and Prompting for Few-Shot Node Classification on Text-Attributed Graphs
Jul 22, 2024
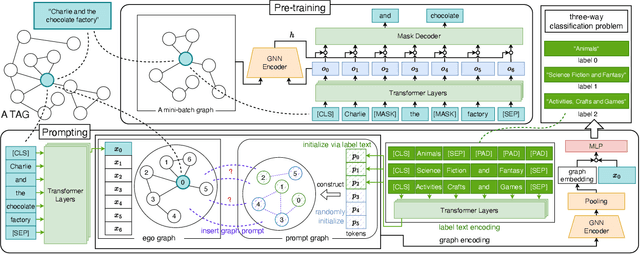
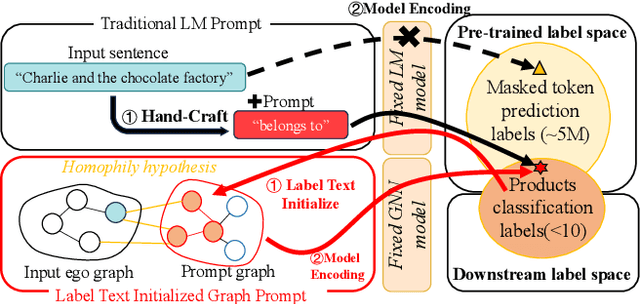
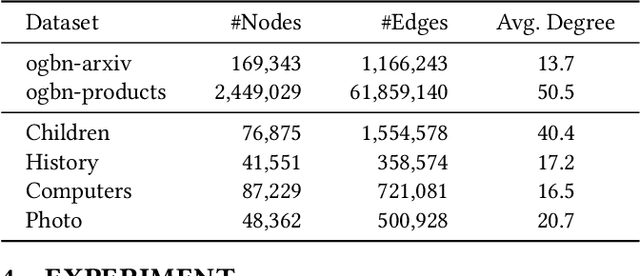
Abstract:The text-attributed graph (TAG) is one kind of important real-world graph-structured data with each node associated with raw texts. For TAGs, traditional few-shot node classification methods directly conduct training on the pre-processed node features and do not consider the raw texts. The performance is highly dependent on the choice of the feature pre-processing method. In this paper, we propose P2TAG, a framework designed for few-shot node classification on TAGs with graph pre-training and prompting. P2TAG first pre-trains the language model (LM) and graph neural network (GNN) on TAGs with self-supervised loss. To fully utilize the ability of language models, we adapt the masked language modeling objective for our framework. The pre-trained model is then used for the few-shot node classification with a mixed prompt method, which simultaneously considers both text and graph information. We conduct experiments on six real-world TAGs, including paper citation networks and product co-purchasing networks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework outperforms existing graph few-shot learning methods on these datasets with +18.98% ~ +35.98% improvements.
Why are hyperbolic neural networks effective? A study on hierarchical representation capability
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Hyperbolic Neural Networks (HNNs), operating in hyperbolic space, have been widely applied in recent years, motivated by the existence of an optimal embedding in hyperbolic space that can preserve data hierarchical relationships (termed Hierarchical Representation Capability, HRC) more accurately than Euclidean space. However, there is no evidence to suggest that HNNs can achieve this theoretical optimal embedding, leading to much research being built on flawed motivations. In this paper, we propose a benchmark for evaluating HRC and conduct a comprehensive analysis of why HNNs are effective through large-scale experiments. Inspired by the analysis results, we propose several pre-training strategies to enhance HRC and improve the performance of downstream tasks, further validating the reliability of the analysis. Experiments show that HNNs cannot achieve the theoretical optimal embedding. The HRC is significantly affected by the optimization objectives and hierarchical structures, and enhancing HRC through pre-training strategies can significantly improve the performance of HNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge