Junyu Ren
Scaling Multiagent Systems with Process Rewards
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:While multiagent systems have shown promise for tackling complex tasks via specialization, finetuning multiple agents simultaneously faces two key challenges: (1) credit assignment across agents, and (2) sample efficiency of expensive multiagent rollouts. In this work, we propose finetuning multiagent systems with per-action process rewards from AI feedback (MAPPA) to address both. Through assigning credit to individual agent actions rather than only at task completion, MAPPA enables fine-grained supervision without ground truth labels while extracting maximal training signal from each rollout. We demonstrate our approach on competition math problems and tool-augmented data analysis tasks. On unseen math problems, MAPPA achieves +5.0--17.5pp on AIME and +7.8--17.2pp on AMC. For data analysis tasks, our method improves success rate by +12.5pp while quality metrics improve by up to 30%, validating that per-action supervision can lead to improvements across different multiagent system on various domains. By addressing these challenges, our work takes a first step toward scaling multiagent systems for complex, long-horizon tasks with minimal human supervision.
Pre-Training and Prompting for Few-Shot Node Classification on Text-Attributed Graphs
Jul 22, 2024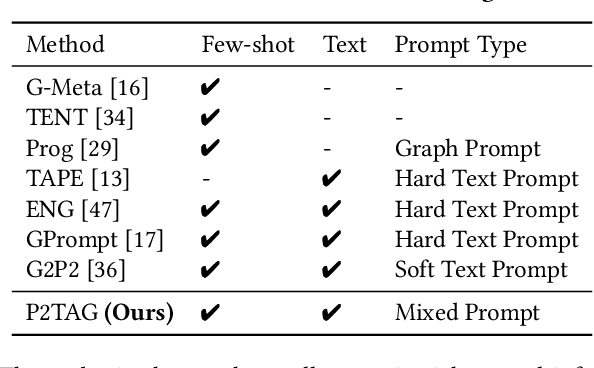
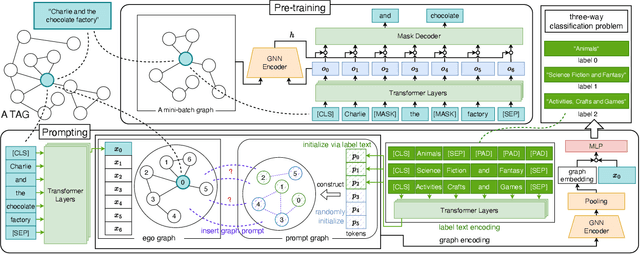
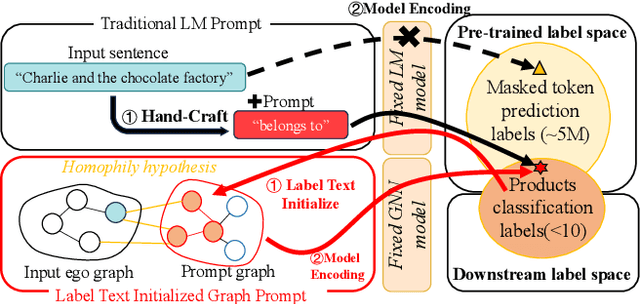
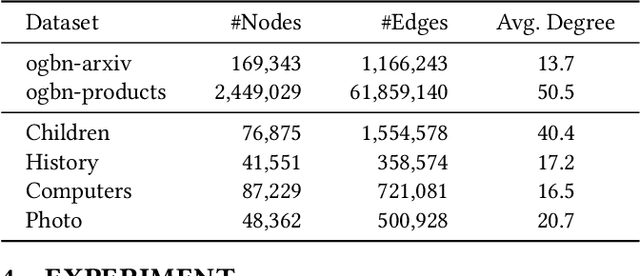
Abstract:The text-attributed graph (TAG) is one kind of important real-world graph-structured data with each node associated with raw texts. For TAGs, traditional few-shot node classification methods directly conduct training on the pre-processed node features and do not consider the raw texts. The performance is highly dependent on the choice of the feature pre-processing method. In this paper, we propose P2TAG, a framework designed for few-shot node classification on TAGs with graph pre-training and prompting. P2TAG first pre-trains the language model (LM) and graph neural network (GNN) on TAGs with self-supervised loss. To fully utilize the ability of language models, we adapt the masked language modeling objective for our framework. The pre-trained model is then used for the few-shot node classification with a mixed prompt method, which simultaneously considers both text and graph information. We conduct experiments on six real-world TAGs, including paper citation networks and product co-purchasing networks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework outperforms existing graph few-shot learning methods on these datasets with +18.98% ~ +35.98% improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge