Hossein Amirkhani
Guide the Learner: Controlling Product of Experts Debiasing Method Based on Token Attribution Similarities
Feb 06, 2023

Abstract:Several proposals have been put forward in recent years for improving out-of-distribution (OOD) performance through mitigating dataset biases. A popular workaround is to train a robust model by re-weighting training examples based on a secondary biased model. Here, the underlying assumption is that the biased model resorts to shortcut features. Hence, those training examples that are correctly predicted by the biased model are flagged as being biased and are down-weighted during the training of the main model. However, assessing the importance of an instance merely based on the predictions of the biased model may be too naive. It is possible that the prediction of the main model can be derived from another decision-making process that is distinct from the behavior of the biased model. To circumvent this, we introduce a fine-tuning strategy that incorporates the similarity between the main and biased model attribution scores in a Product of Experts (PoE) loss function to further improve OOD performance. With experiments conducted on natural language inference and fact verification benchmarks, we show that our method improves OOD results while maintaining in-distribution (ID) performance.
Multi-view graph structure learning using subspace merging on Grassmann manifold
Apr 11, 2022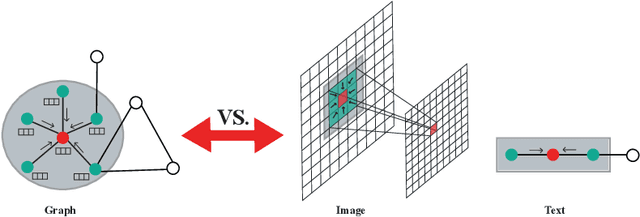
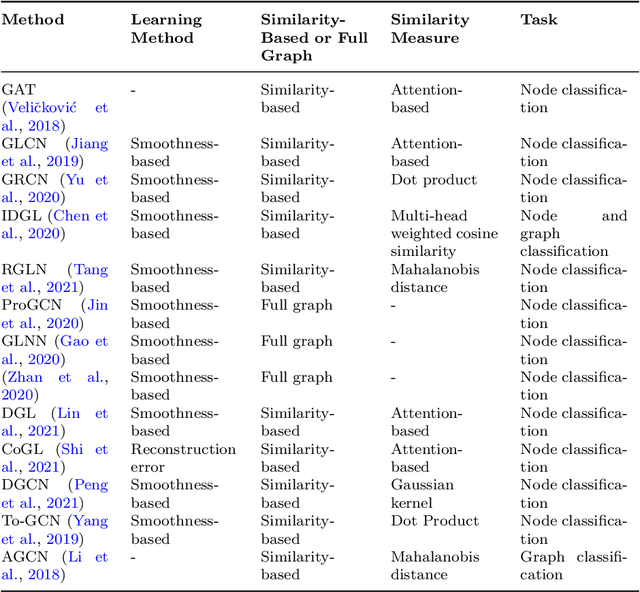
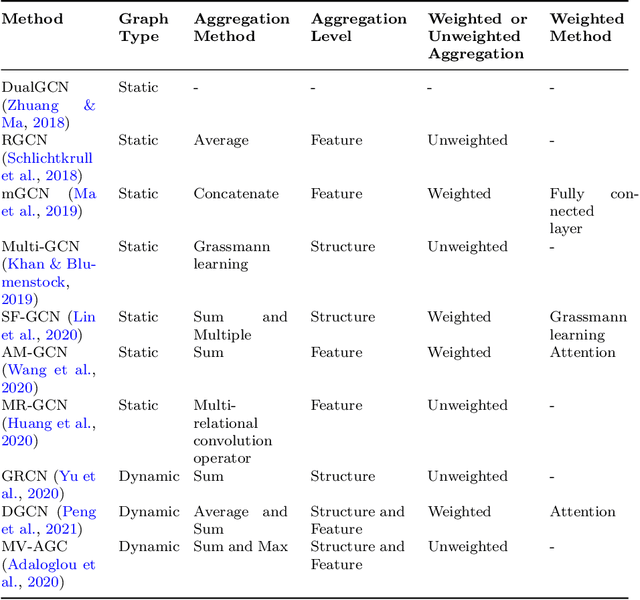
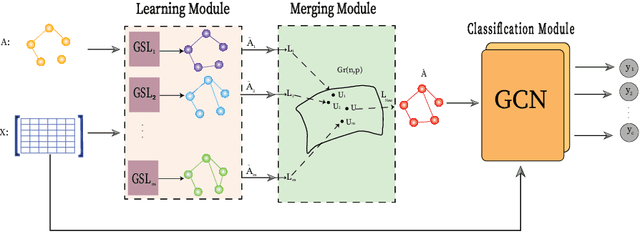
Abstract:Many successful learning algorithms have been recently developed to represent graph-structured data. For example, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved considerable successes in various tasks such as node classification, graph classification, and link prediction. However, these methods are highly dependent on the quality of the input graph structure. One used approach to alleviate this problem is to learn the graph structure instead of relying on a manually designed graph. In this paper, we introduce a new graph structure learning approach using multi-view learning, named MV-GSL (Multi-View Graph Structure Learning), in which we aggregate different graph structure learning methods using subspace merging on Grassmann manifold to improve the quality of the learned graph structures. Extensive experiments are performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method on two benchmark datasets, Cora and Citeseer. Our experiments show that the proposed method has promising performance compared to single and other combined graph structure learning methods.
Graph Neural Networks: a bibliometrics overview
Jan 03, 2022



Abstract:Recently, graph neural networks have become a hot topic in machine learning community. This paper presents a Scopus based bibliometric overview of the GNNs research since 2004, when GNN papers were first published. The study aims to evaluate GNN research trend, both quantitatively and qualitatively. We provide the trend of research, distribution of subjects, active and influential authors and institutions, sources of publications, most cited documents, and hot topics. Our investigations reveal that the most frequent subject categories in this field are computer science, engineering, telecommunications, linguistics, operations research and management science, information science and library science, business and economics, automation and control systems, robotics, and social sciences. In addition, the most active source of GNN publications is Lecture Notes in Computer Science. The most prolific or impactful institutions are found in the United States, China, and Canada. We also provide must read papers and future directions. Finally, the application of graph convolutional networks and attention mechanism are now among hot topics of GNN research.
Don't Discard All the Biased Instances: Investigating a Core Assumption in Dataset Bias Mitigation Techniques
Sep 01, 2021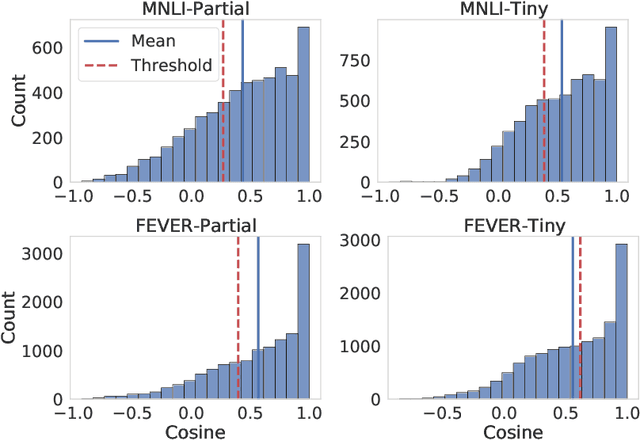
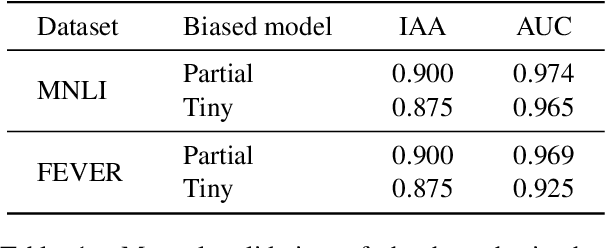
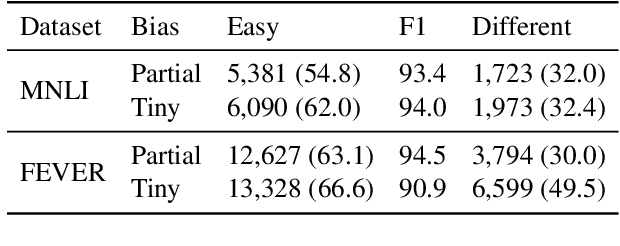
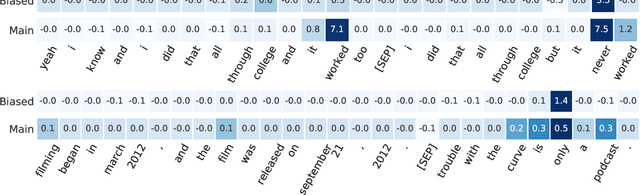
Abstract:Existing techniques for mitigating dataset bias often leverage a biased model to identify biased instances. The role of these biased instances is then reduced during the training of the main model to enhance its robustness to out-of-distribution data. A common core assumption of these techniques is that the main model handles biased instances similarly to the biased model, in that it will resort to biases whenever available. In this paper, we show that this assumption does not hold in general. We carry out a critical investigation on two well-known datasets in the domain, MNLI and FEVER, along with two biased instance detection methods, partial-input and limited-capacity models. Our experiments show that in around a third to a half of instances, the biased model is unable to predict the main model's behavior, highlighted by the significantly different parts of the input on which they base their decisions. Based on a manual validation, we also show that this estimate is highly in line with human interpretation. Our findings suggest that down-weighting of instances detected by bias detection methods, which is a widely-practiced procedure, is an unnecessary waste of training data. We release our code to facilitate reproducibility and future research.
Ensemble Learning-Based Approach for Improving Generalization Capability of Machine Reading Comprehension Systems
Jul 15, 2021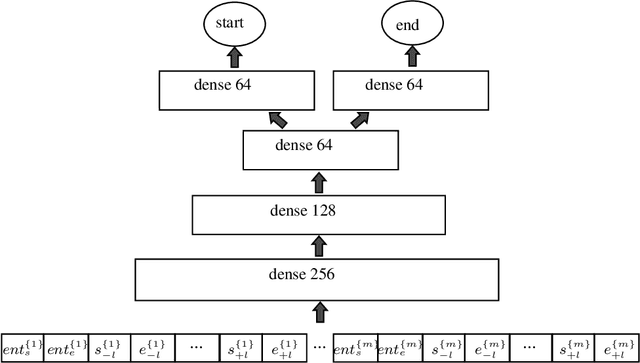
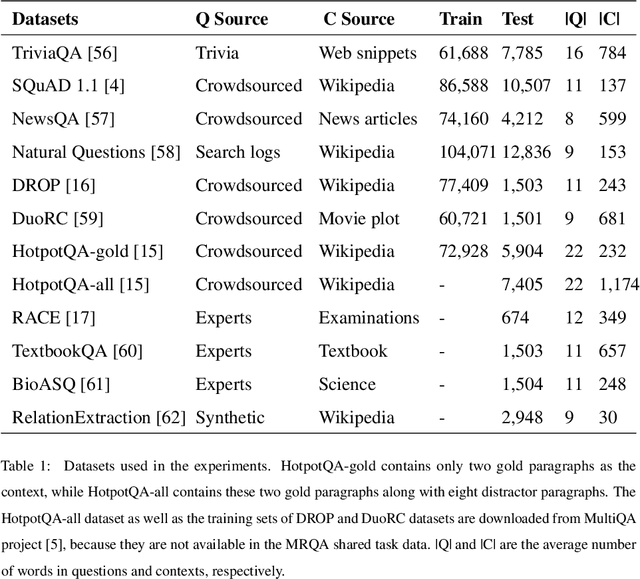
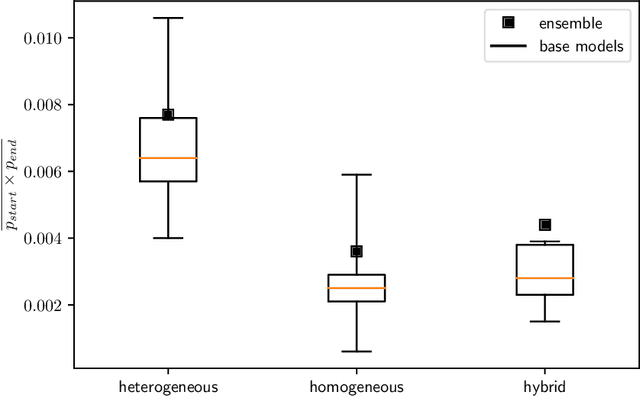
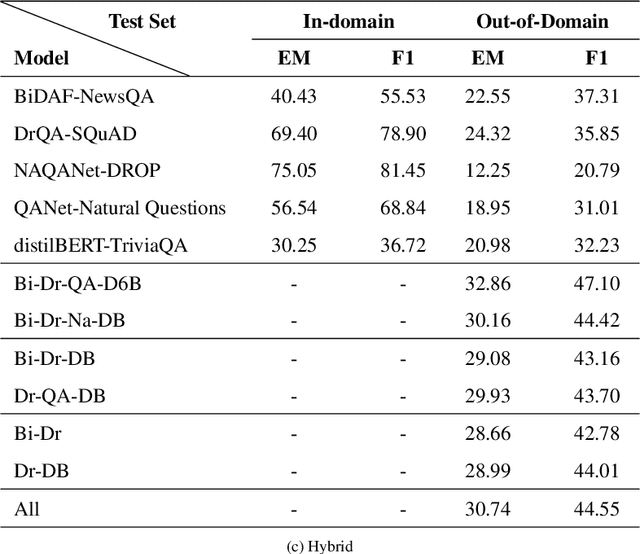
Abstract:Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) is an active field in natural language processing with many successful developed models in recent years. Despite their high in-distribution accuracy, these models suffer from two issues: high training cost and low out-of-distribution accuracy. Even though some approaches have been presented to tackle the generalization problem, they have high, intolerable training costs. In this paper, we investigate the effect of ensemble learning approach to improve generalization of MRC systems without retraining a big model. After separately training the base models with different structures on different datasets, they are ensembled using weighting and stacking approaches in probabilistic and non-probabilistic settings. Three configurations are investigated including heterogeneous, homogeneous, and hybrid on eight datasets and six state-of-the-art models. We identify the important factors in the effectiveness of ensemble methods. Also, we compare the robustness of ensemble and fine-tuned models against data distribution shifts. The experimental results show the effectiveness and robustness of the ensemble approach in improving the out-of-distribution accuracy of MRC systems, especially when the base models are similar in accuracies.
Zero-Shot Estimation of Base Models' Weights in Ensemble of Machine Reading Comprehension Systems for Robust Generalization
Jun 30, 2021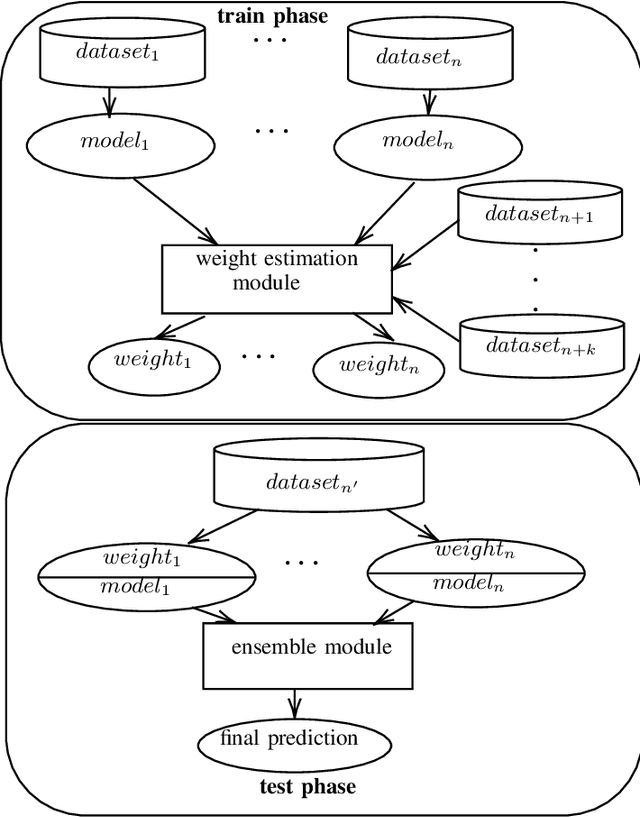
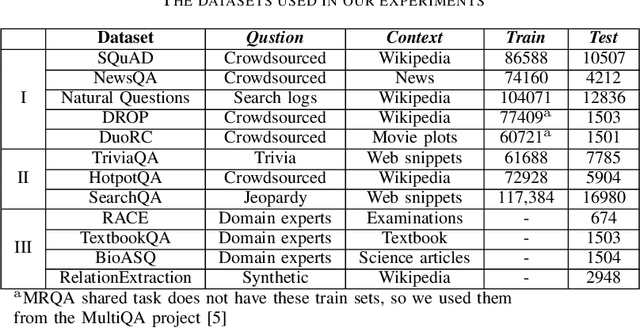
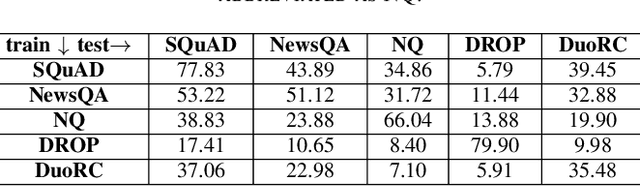
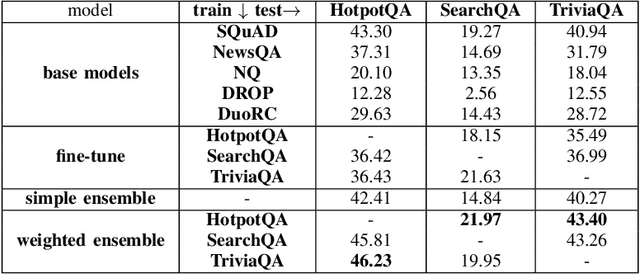
Abstract:One of the main challenges of the machine reading comprehension (MRC) models is their fragile out-of-domain generalization, which makes these models not properly applicable to real-world general-purpose question answering problems. In this paper, we leverage a zero-shot weighted ensemble method for improving the robustness of out-of-domain generalization in MRC models. In the proposed method, a weight estimation module is used to estimate out-of-domain weights, and an ensemble module aggregate several base models' predictions based on their weights. The experiments indicate that the proposed method not only improves the final accuracy, but also is robust against domain changes.
FarsTail: A Persian Natural Language Inference Dataset
Sep 18, 2020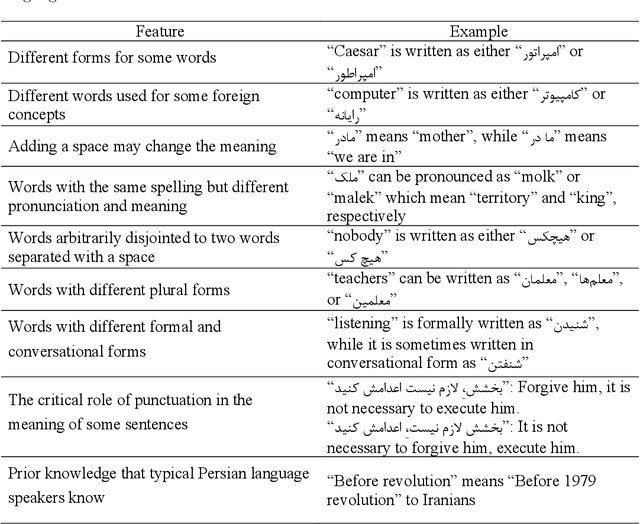
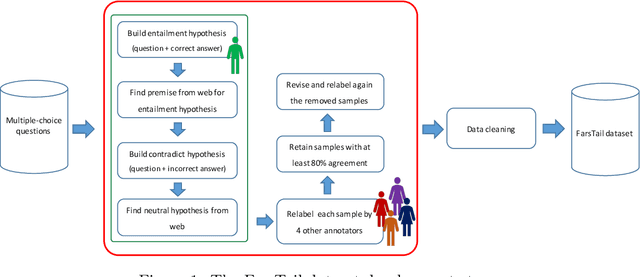
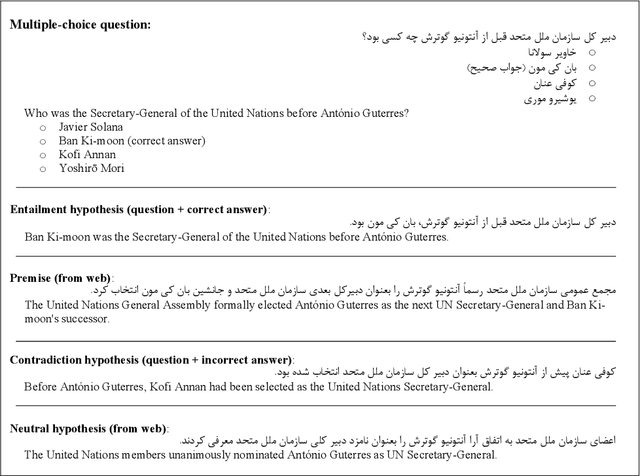
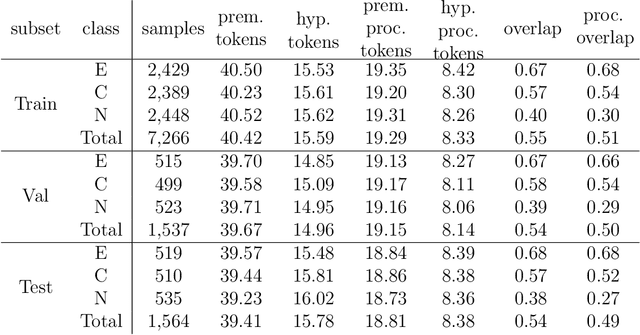
Abstract:Natural language inference (NLI) is known as one of the central tasks in natural language processing (NLP) which encapsulates many fundamental aspects of language understanding. With the considerable achievements of data-hungry deep learning methods in NLP tasks, a great amount of effort has been devoted to develop more diverse datasets for different languages. In this paper, we present a new dataset for the NLI task in the Persian language, also known as Farsi, which is one of the dominant languages in the Middle East. This dataset, named FarsTail, includes 10,367 samples which are provided in both the Persian language as well as the indexed format to be useful for non-Persian researchers. The samples are generated from 3,539 multiple-choice questions with the least amount of annotator interventions in a way similar to the SciTail dataset. A carefully designed multi-step process is adopted to ensure the quality of the dataset. We also present the results of traditional and state-of-the-art methods on FarsTail including different embedding methods such as word2vec, fastText, ELMo, BERT, and LASER, as well as different modeling approaches such as DecompAtt, ESIM, HBMP, ULMFiT, and cross-lingual transfer approach to provide a solid baseline for the future research. The best obtained test accuracy is 78.13% which shows that there is a big room for improving the current methods to be useful for real-world NLP applications in different languages. The dataset is available at https://github.com/dml-qom/FarsTail.
A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension Systems
Jan 06, 2020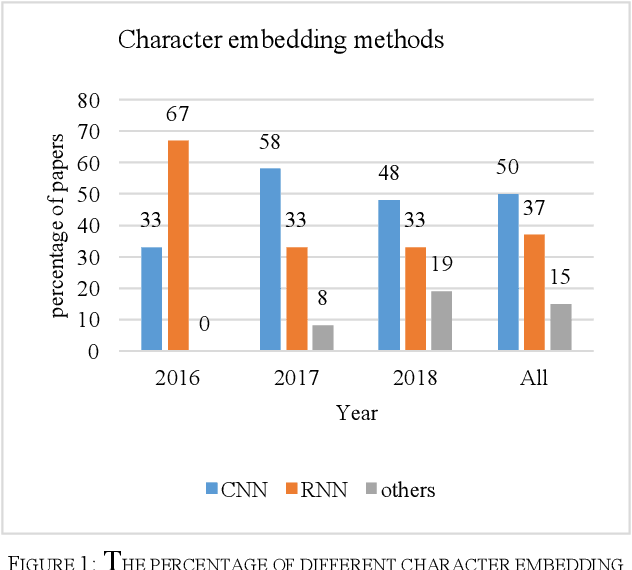
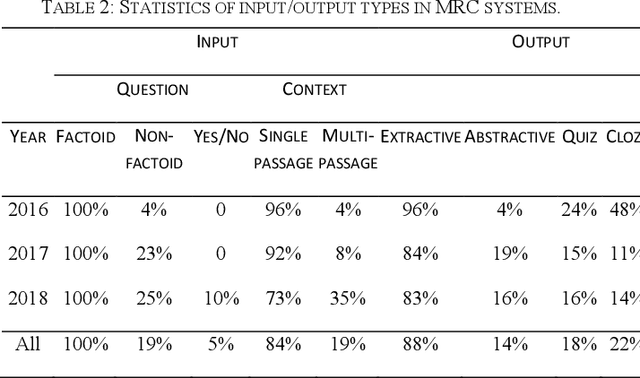
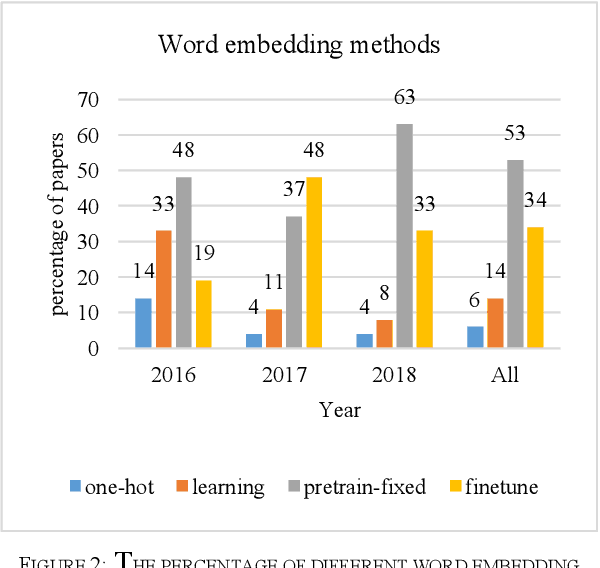
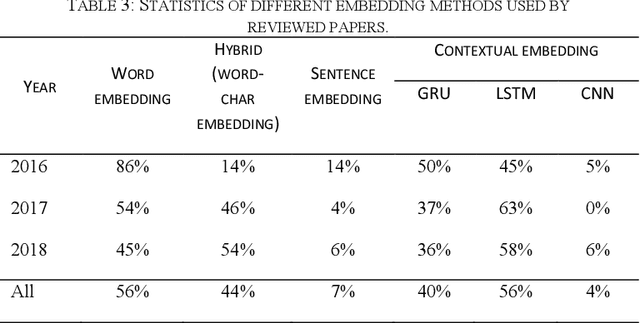
Abstract:Machine reading comprehension is a challenging task and hot topic in natural language processing. Its goal is to develop systems to answer the questions regarding a given context. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey on different aspects of machine reading comprehension systems, including their approaches, structures, input/outputs, and research novelties. We illustrate the recent trends in this field based on 124 reviewed papers from 2016 to 2018. Our investigations demonstrate that the focus of research has changed in recent years from answer extraction to answer generation, from single to multi-document reading comprehension, and from learning from scratch to using pre-trained embeddings. We also discuss the popular datasets and the evaluation metrics in this field. The paper ends with investigating the most cited papers and their contributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge