Hongyi Huang
Power-Law Decay Loss for Large Language Model Finetuning: Focusing on Information Sparsity to Enhance Generation Quality
May 22, 2025Abstract:During the finetuning stage of text generation tasks, standard cross-entropy loss treats all tokens equally. This can lead models to overemphasize high-frequency, low-information tokens, neglecting lower-frequency tokens crucial for specificity and informativeness in generated content. This paper introduces a novel loss function, Power-Law Decay Loss (PDL), specifically designed to optimize the finetuning process for text generation. The core motivation for PDL stems from observations in information theory and linguistics: the informativeness of a token is often inversely proportional to its frequency of occurrence. PDL re-weights the contribution of each token in the standard cross-entropy loss based on its frequency in the training corpus, following a power-law decay. Specifically, the weights for high-frequency tokens are reduced, while low-frequency, information-dense tokens are assigned higher weights. This mechanism guides the model during finetuning to focus more on learning and generating tokens that convey specific and unique information, thereby enhancing the quality, diversity, and informativeness of the generated text. We theoretically elaborate on the motivation and construction of PDL and discuss its potential applications and advantages across various text generation finetuning tasks, such as abstractive summarization, dialogue systems, and style transfer.
ComplexFormer: Disruptively Advancing Transformer Inference Ability via Head-Specific Complex Vector Attention
May 15, 2025Abstract:Transformer models rely on self-attention to capture token dependencies but face challenges in effectively integrating positional information while allowing multi-head attention (MHA) flexibility. Prior methods often model semantic and positional differences disparately or apply uniform positional adjustments across heads, potentially limiting representational capacity. This paper introduces ComplexFormer, featuring Complex Multi-Head Attention-CMHA. CMHA empowers each head to independently model semantic and positional differences unified within the complex plane, representing interactions as rotations and scaling. ComplexFormer incorporates two key improvements: (1) a per-head Euler transformation, converting real-valued query/key projections into polar-form complex vectors for head-specific complex subspace operation; and (2) a per-head adaptive differential rotation mechanism, exp[i(Adapt(ASmn,i) + Delta(Pmn),i)], allowing each head to learn distinct strategies for integrating semantic angle differences (ASmn,i) with relative positional encodings (Delta(Pmn),i). Extensive experiments on language modeling, text generation, code generation, and mathematical reasoning show ComplexFormer achieves superior performance, significantly lower generation perplexity , and improved long-context coherence compared to strong baselines like RoPE-Transformers. ComplexFormer demonstrates strong parameter efficiency, offering a more expressive, adaptable attention mechanism.
VQ-Logits: Compressing the Output Bottleneck of Large Language Models via Vector Quantized Logits
May 15, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success but face significant computational and memory challenges, particularly due to their extensive output vocabularies. The final linear projection layer, mapping hidden states to vocabulary-sized logits, often constitutes a substantial portion of the model's parameters and computational cost during inference. Existing methods like adaptive softmax or hierarchical softmax introduce structural complexities. In this paper, we propose VQ-Logits, a novel approach that leverages Vector Quantization (VQ) to drastically reduce the parameter count and computational load of the LLM output layer. VQ-Logits replaces the large V * dmodel output embedding matrix with a small, shared codebook of K embedding vectors (K << V ). Each token in the vocabulary is mapped to one of these K codebook vectors. The LLM predicts logits over this compact codebook, which are then efficiently "scattered" to the full vocabulary space using the learned or preassigned mapping. We demonstrate through extensive experiments on standard language modeling benchmarks (e.g., WikiText-103, C4) that VQ-Logits can achieve up to 99% parameter reduction in the output layer and 6x speedup in logit computation, with only a marginal 4% increase in perplexity compared to full softmax baselines. We further provide detailed ablation studies on codebook size, initialization, and learning strategies, showcasing the robustness and effectiveness of our approach.
X-PuDu at SemEval-2022 Task 6: Multilingual Learning for English and Arabic Sarcasm Detection
Nov 30, 2022Abstract:Detecting sarcasm and verbal irony from people's subjective statements is crucial to understanding their intended meanings and real sentiments and positions in social scenarios. This paper describes the X-PuDu system that participated in SemEval-2022 Task 6, iSarcasmEval - Intended Sarcasm Detection in English and Arabic, which aims at detecting intended sarcasm in various settings of natural language understanding. Our solution finetunes pre-trained language models, such as ERNIE-M and DeBERTa, under the multilingual settings to recognize the irony from Arabic and English texts. Our system ranked second out of 43, and ninth out of 32 in Task A: one-sentence detection in English and Arabic; fifth out of 22 in Task B: binary multi-label classification in English; first out of 16, and fifth out of 13 in Task C: sentence-pair detection in English and Arabic.
Structured Neural Topic Models for Reviews
Jan 02, 2019
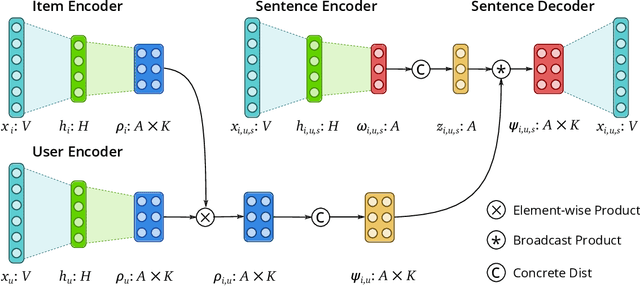

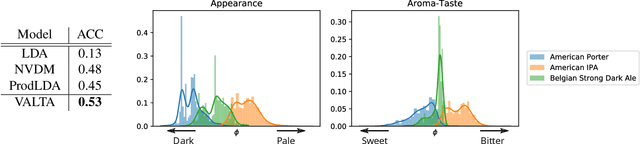
Abstract:We present Variational Aspect-based Latent Topic Allocation (VALTA), a family of autoencoding topic models that learn aspect-based representations of reviews. VALTA defines a user-item encoder that maps bag-of-words vectors for combined reviews associated with each paired user and item onto structured embeddings, which in turn define per-aspect topic weights. We model individual reviews in a structured manner by inferring an aspect assignment for each sentence in a given review, where the per-aspect topic weights obtained by the user-item encoder serve to define a mixture over topics, conditioned on the aspect. The result is an autoencoding neural topic model for reviews, which can be trained in a fully unsupervised manner to learn topics that are structured into aspects. Experimental evaluation on large number of datasets demonstrates that aspects are interpretable, yield higher coherence scores than non-structured autoencoding topic model variants, and can be utilized to perform aspect-based comparison and genre discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge