Hongfei Wang
Enhancing Node-Level Graph Domain Adaptation by Alleviating Local Dependency
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in machine learning methods on graphs. However, transferring knowledge effectively from one graph to another remains a critical challenge. This highlights the need for algorithms capable of applying information extracted from a source graph to an unlabeled target graph, a task known as unsupervised graph domain adaptation (GDA). One key difficulty in unsupervised GDA is conditional shift, which hinders transferability. In this paper, we show that conditional shift can be observed only if there exists local dependencies among node features. To support this claim, we perform a rigorous analysis and also further provide generalization bounds of GDA when dependent node features are modeled using markov chains. Guided by the theoretical findings, we propose to improve GDA by decorrelating node features, which can be specifically implemented through decorrelated GCN layers and graph transformer layers. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach, showing not only substantial performance enhancements over baseline GDA methods but also clear visualizations of small intra-class distances in the learned representations. Our code is available at https://github.com/TechnologyAiGroup/DFT
ArgusCogito: Chain-of-Thought for Cross-Modal Synergy and Omnidirectional Reasoning in Camouflaged Object Segmentation
Aug 25, 2025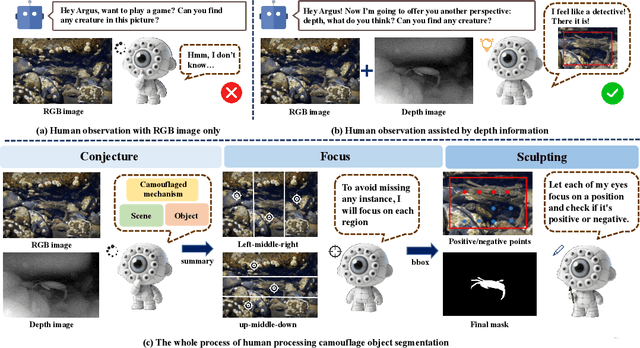
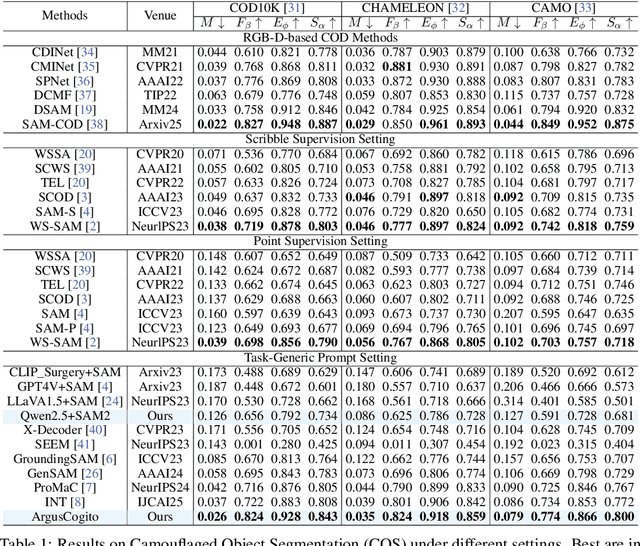
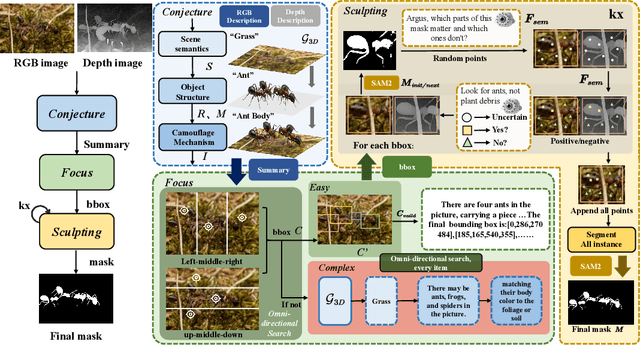
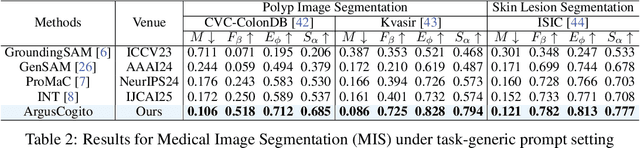
Abstract:Camouflaged Object Segmentation (COS) poses a significant challenge due to the intrinsic high similarity between targets and backgrounds, demanding models capable of profound holistic understanding beyond superficial cues. Prevailing methods, often limited by shallow feature representation, inadequate reasoning mechanisms, and weak cross-modal integration, struggle to achieve this depth of cognition, resulting in prevalent issues like incomplete target separation and imprecise segmentation. Inspired by the perceptual strategy of the Hundred-eyed Giant-emphasizing holistic observation, omnidirectional focus, and intensive scrutiny-we introduce ArgusCogito, a novel zero-shot, chain-of-thought framework underpinned by cross-modal synergy and omnidirectional reasoning within Vision-Language Models (VLMs). ArgusCogito orchestrates three cognitively-inspired stages: (1) Conjecture: Constructs a strong cognitive prior through global reasoning with cross-modal fusion (RGB, depth, semantic maps), enabling holistic scene understanding and enhanced target-background disambiguation. (2) Focus: Performs omnidirectional, attention-driven scanning and focused reasoning, guided by semantic priors from Conjecture, enabling precise target localization and region-of-interest refinement. (3) Sculpting: Progressively sculpts high-fidelity segmentation masks by integrating cross-modal information and iteratively generating dense positive/negative point prompts within focused regions, emulating Argus' intensive scrutiny. Extensive evaluations on four challenging COS benchmarks and three Medical Image Segmentation (MIS) benchmarks demonstrate that ArgusCogito achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, validating the framework's exceptional efficacy, superior generalization capability, and robustness.
Self-similarity Analysis in Deep Neural Networks
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Current research has found that some deep neural networks exhibit strong hierarchical self-similarity in feature representation or parameter distribution. However, aside from preliminary studies on how the power-law distribution of weights across different training stages affects model performance,there has been no quantitative analysis on how the self-similarity of hidden space geometry influences model weight optimization, nor is there a clear understanding of the dynamic behavior of internal neurons. Therefore, this paper proposes a complex network modeling method based on the output features of hidden-layer neurons to investigate the self-similarity of feature networks constructed at different hidden layers, and analyzes how adjusting the degree of self-similarity in feature networks can enhance the classification performance of deep neural networks. Validated on three types of networks MLP architectures, convolutional networks, and attention architectures this study reveals that the degree of self-similarity exhibited by feature networks varies across different model architectures. Furthermore, embedding constraints on the self-similarity of feature networks during the training process can improve the performance of self-similar deep neural networks (MLP architectures and attention architectures) by up to 6 percentage points.
Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Enhanced Transformer Denoising with Functional Diffusive GANs for Constructing Brain Effective Connectivity in MCI analysis
May 18, 2023



Abstract:Effective connectivity can describe the causal patterns among brain regions. These patterns have the potential to reveal the pathological mechanism and promote early diagnosis and effective drug development for cognitive disease. However, the current studies mainly focus on using empirical functional time series to calculate effective connections, which may not comprehensively capture the complex causal relationships between brain regions. In this paper, a novel Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Enhanced Transformer Denoising (MSETD) network with an adversarially functional diffusion model is proposed to map functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) into effective connectivity for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) analysis. To be specific, the denoising framework leverages a conditional diffusion process that progressively translates the noise and conditioning fMRI to effective connectivity in an end-to-end manner. To ensure reverse diffusion quality and diversity, the multi-resolution enhanced transformer generator is designed to extract local and global spatiotemporal features. Furthermore, a multi-scale diffusive transformer discriminator is devised to capture the temporal patterns at different scales for generation stability. Evaluations of the ADNI datasets demonstrate the feasibility and efficacy of the proposed model. The proposed model not only achieves superior prediction performance compared with other competing methods but also identifies MCI-related causal connections that are consistent with clinical studies.
DiffuseRoll: Multi-track multi-category music generation based on diffusion model
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have shown remarkable progress in music generation. However, most existing methods focus on generating monophonic or homophonic music, while the generation of polyphonic and multi-track music with rich attributes is still a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for multi-track, multi-attribute symphonic music generation using the diffusion model. Specifically, we generate piano-roll representations with a diffusion model and map them to MIDI format for output. To capture rich attribute information, we introduce a color coding scheme to encode note sequences into color and position information that represents pitch,velocity, and instrument. This scheme enables a seamless mapping between discrete music sequences and continuous images. We also propose a post-processing method to optimize the generated scores for better performance. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of polyphonic music generation with rich attribute information compared to the figure methods.
Chinese Grammatical Correction Using BERT-based Pre-trained Model
Nov 04, 2020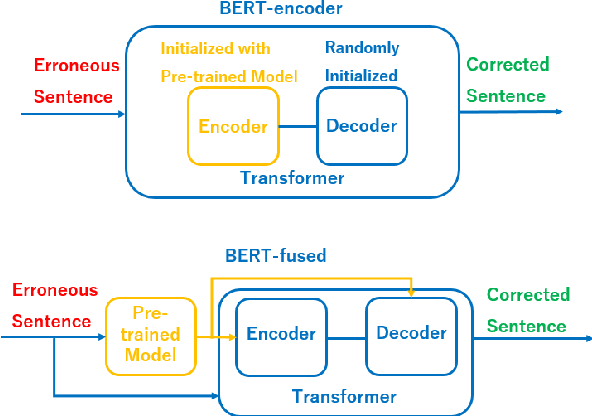
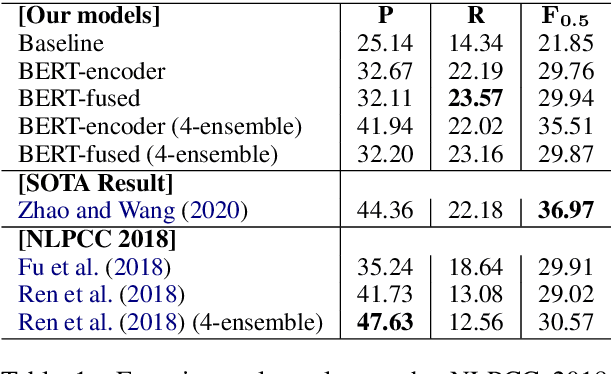

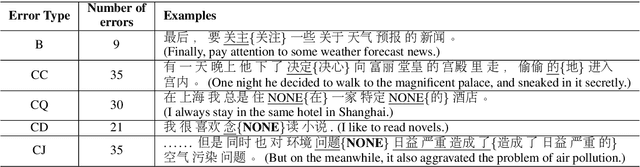
Abstract:In recent years, pre-trained models have been extensively studied, and several downstream tasks have benefited from their utilization. In this study, we verify the effectiveness of two methods that incorporate a BERT-based pre-trained model developed by Cui et al. (2020) into an encoder-decoder model on Chinese grammatical error correction tasks. We also analyze the error type and conclude that sentence-level errors are yet to be addressed.
Mobile APP User Attribute Prediction by Heterogeneous Information Network Modeling
Oct 06, 2019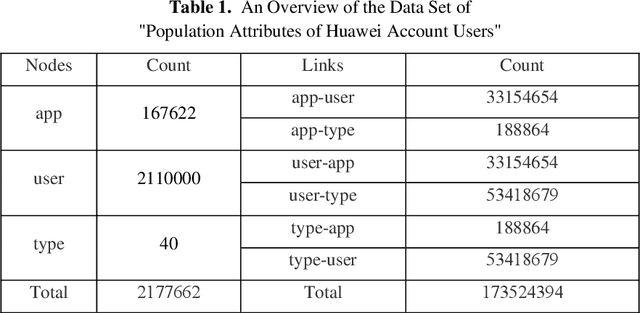


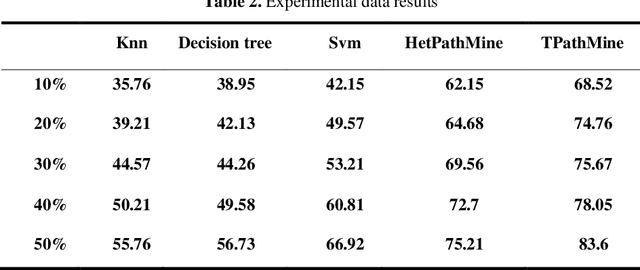
Abstract:User-based attribute information, such as age and gender, is usually considered as user privacy information. It is difficult for enterprises to obtain user-based privacy attribute information. However, user-based privacy attribute information has a wide range of applications in personalized services, user behavior analysis and other aspects. this paper advances the HetPathMine model and puts forward TPathMine model. With applying the number of clicks of attributes under each node to express the user's emotional preference information, optimizations of the solution of meta-path weight are also presented. Based on meta-path in heterogeneous information networks, the new model integrates all relationships among objects into isomorphic relationships of classified objects. Matrix is used to realize the knowledge dissemination of category knowledge among isomorphic objects. The experimental results show that: (1) the prediction of user attributes based on heterogeneous information networks can achieve higher accuracy than traditional machine learning classification methods; (2) TPathMine model based on the number of clicks is more accurate in classifying users of different age groups, and the weight of each meta-path is consistent with human intuition or the real world situation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge