Haoran Hu
MedAgentBoard: Benchmarking Multi-Agent Collaboration with Conventional Methods for Diverse Medical Tasks
May 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has stimulated interest in multi-agent collaboration for addressing complex medical tasks. However, the practical advantages of multi-agent collaboration approaches remain insufficiently understood. Existing evaluations often lack generalizability, failing to cover diverse tasks reflective of real-world clinical practice, and frequently omit rigorous comparisons against both single-LLM-based and established conventional methods. To address this critical gap, we introduce MedAgentBoard, a comprehensive benchmark for the systematic evaluation of multi-agent collaboration, single-LLM, and conventional approaches. MedAgentBoard encompasses four diverse medical task categories: (1) medical (visual) question answering, (2) lay summary generation, (3) structured Electronic Health Record (EHR) predictive modeling, and (4) clinical workflow automation, across text, medical images, and structured EHR data. Our extensive experiments reveal a nuanced landscape: while multi-agent collaboration demonstrates benefits in specific scenarios, such as enhancing task completeness in clinical workflow automation, it does not consistently outperform advanced single LLMs (e.g., in textual medical QA) or, critically, specialized conventional methods that generally maintain better performance in tasks like medical VQA and EHR-based prediction. MedAgentBoard offers a vital resource and actionable insights, emphasizing the necessity of a task-specific, evidence-based approach to selecting and developing AI solutions in medicine. It underscores that the inherent complexity and overhead of multi-agent collaboration must be carefully weighed against tangible performance gains. All code, datasets, detailed prompts, and experimental results are open-sourced at https://medagentboard.netlify.app/.
A Comparative and Experimental Study on Automatic Question Answering Systems and its Robustness against Word Jumbling
Nov 27, 2023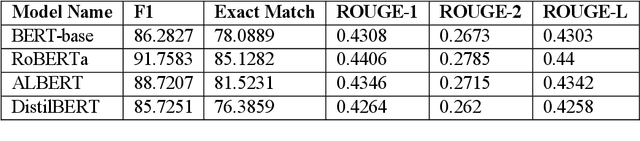
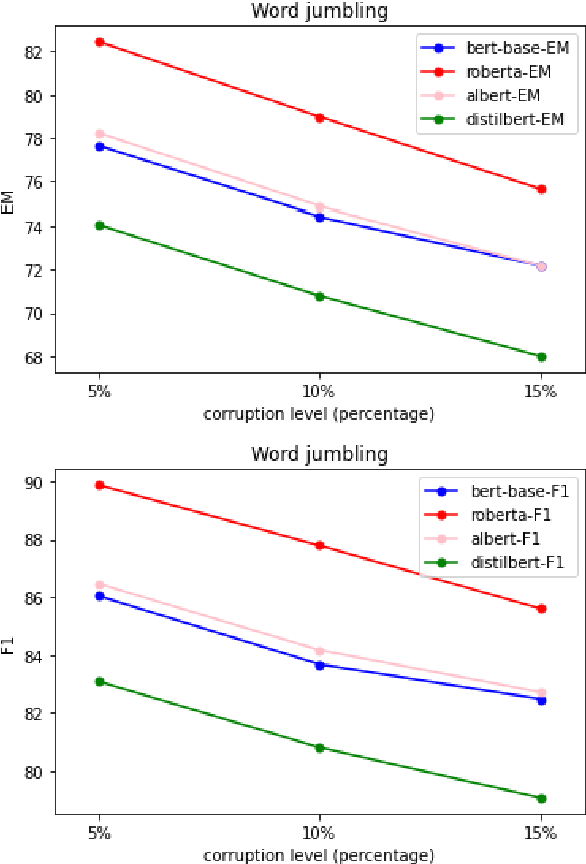
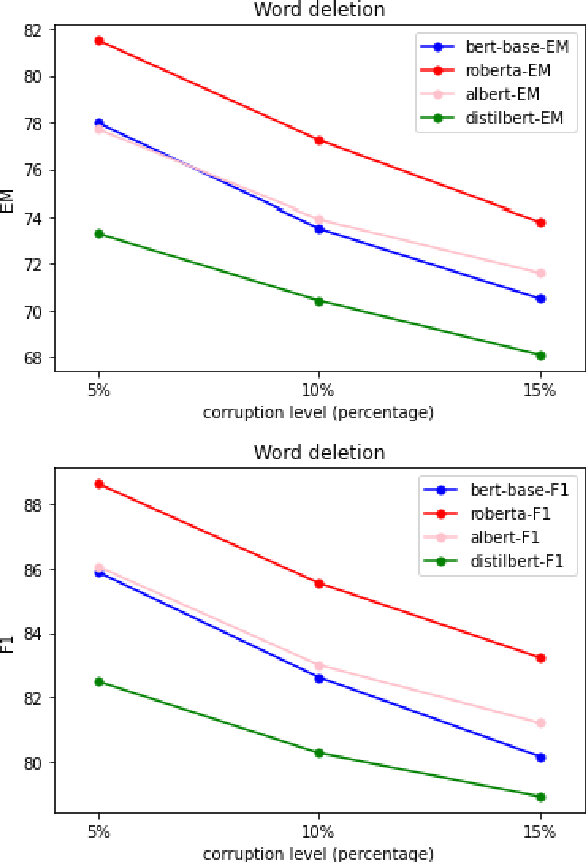
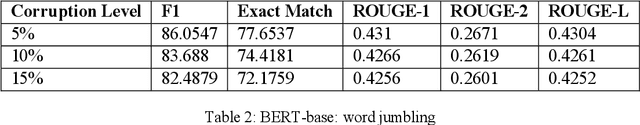
Abstract:Question answer generation using Natural Language Processing models is ubiquitous in the world around us. It is used in many use cases such as the building of chat bots, suggestive prompts in google search and also as a way of navigating information in banking mobile applications etc. It is highly relevant because a frequently asked questions (FAQ) list can only have a finite amount of questions but a model which can perform question answer generation could be able to answer completely new questions that are within the scope of the data. This helps us to be able to answer new questions accurately as long as it is a relevant question. In commercial applications, it can be used to increase customer satisfaction and ease of usage. However a lot of data is generated by humans so it is susceptible to human error and this can adversely affect the model's performance and we are investigating this through our work
A Modified PINN Approach for Identifiable Compartmental Models in Epidemiology with Applications to COVID-19
Aug 01, 2022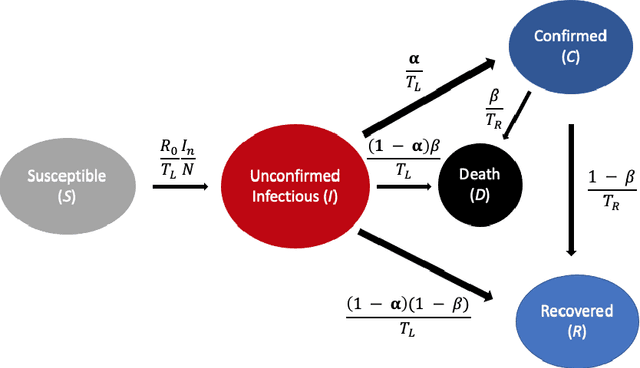
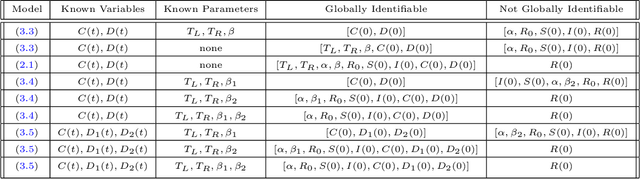
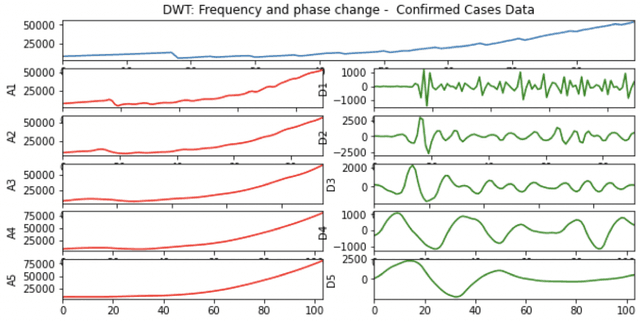
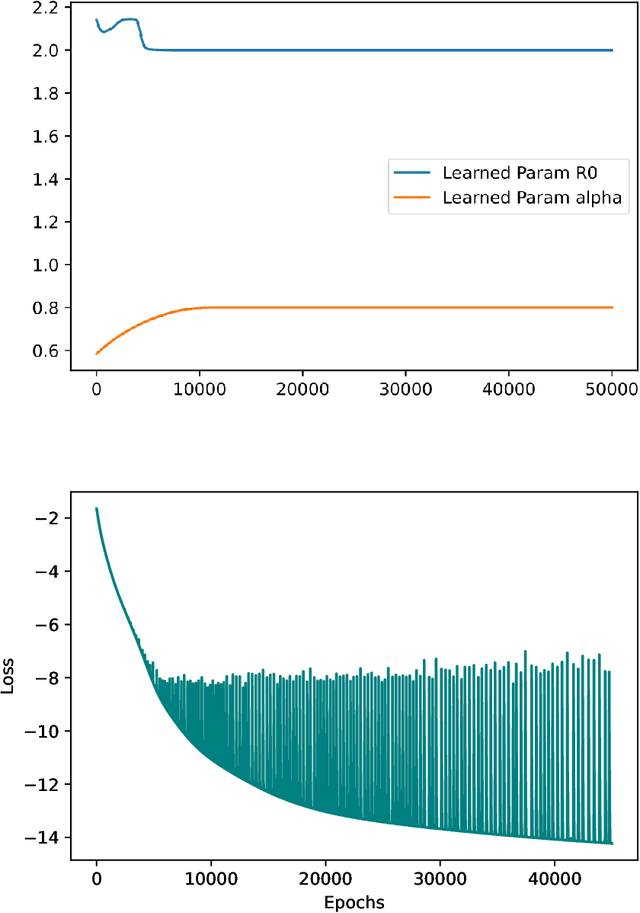
Abstract:A variety of approaches using compartmental models have been used to study the COVID-19 pandemic and the usage of machine learning methods with these models has had particularly notable success. We present here an approach toward analyzing accessible data on Covid-19's U.S. development using a variation of the "Physics Informed Neural Networks" (PINN) which is capable of using the knowledge of the model to aid learning. We illustrate the challenges of using the standard PINN approach, then how with appropriate and novel modifications to the loss function the network can perform well even in our case of incomplete information. Aspects of identifiability of the model parameters are also assessed, as well as methods of denoising available data using a wavelet transform. Finally, we discuss the capability of the neural network methodology to work with models of varying parameter values, as well as a concrete application in estimating how effectively cases are being tested for in a population, providing a ranking of U.S. states by means of their respective testing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge