Haoqi Gu
Optimizing Factual Accuracy in Text Generation through Dynamic Knowledge Selection
Aug 30, 2023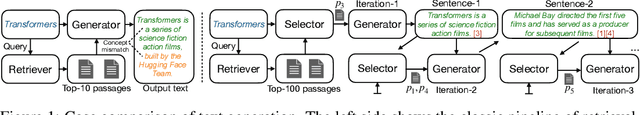
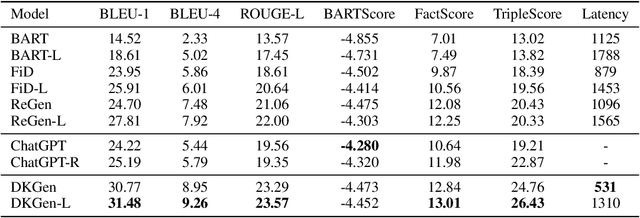
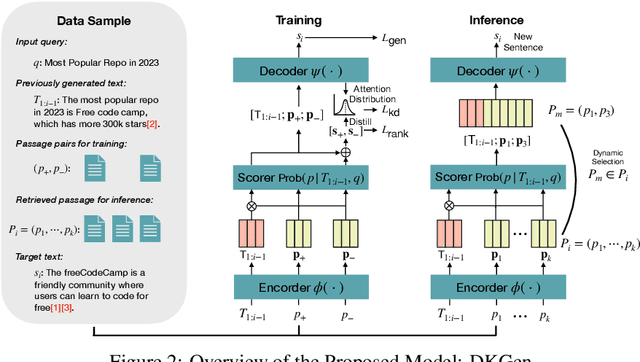
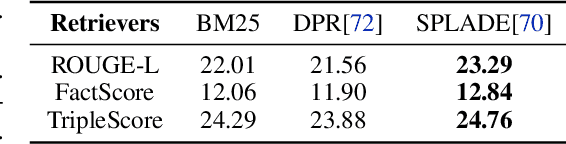
Abstract:Language models (LMs) have revolutionized the way we interact with information, but they often generate nonfactual text, raising concerns about their reliability. Previous methods use external knowledge as references for text generation to enhance factuality but often struggle with the knowledge mix-up(e.g., entity mismatch) of irrelevant references. Besides,as the length of the output text grows, the randomness of sampling can escalate, detrimentally impacting the factual accuracy of the generated text. In this paper, we present DKGen, which divide the text generation process into an iterative process. In each iteration, DKGen takes the input query, the previously generated text and a subset of the reference passages as input to generate short text. During the process, the subset is dynamically selected from the full passage set based on their relevance to the previously generated text and the query, largely eliminating the irrelevant references from input. To further enhance DKGen's ability to correctly use these external knowledge, DKGen distills the relevance order of reference passages to the cross-attention distribution of decoder. We train and evaluate DKGen on a large-scale benchmark dataset. Experiment results show that DKGen outperforms all baseline models.
WebBrain: Learning to Generate Factually Correct Articles for Queries by Grounding on Large Web Corpus
Apr 10, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a new NLP task -- generating short factual articles with references for queries by mining supporting evidence from the Web. In this task, called WebBrain, the ultimate goal is to generate a fluent, informative, and factually-correct short article (e.g., a Wikipedia article) for a factual query unseen in Wikipedia. To enable experiments on WebBrain, we construct a large-scale dataset WebBrain-Raw by extracting English Wikipedia articles and their crawlable Wikipedia references. WebBrain-Raw is ten times larger than the previous biggest peer dataset, which can greatly benefit the research community. From WebBrain-Raw, we construct two task-specific datasets: WebBrain-R and WebBrain-G, which are used to train in-domain retriever and generator, respectively. Besides, we empirically analyze the performances of the current state-of-the-art NLP techniques on WebBrain and introduce a new framework ReGen, which enhances the generation factualness by improved evidence retrieval and task-specific pre-training for generation. Experiment results show that ReGen outperforms all baselines in both automatic and human evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge