Haojie Fu
Kernel-Free Universum Quadratic Surface Twin Support Vector Machines for Imbalanced Data
Dec 02, 2024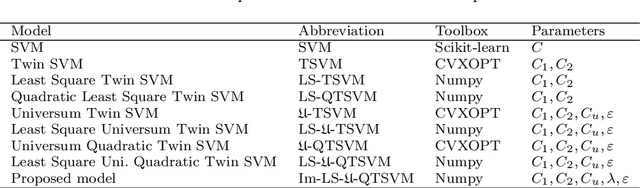
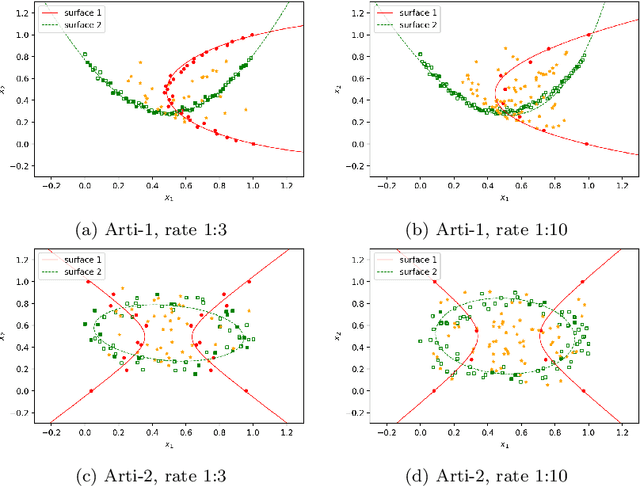
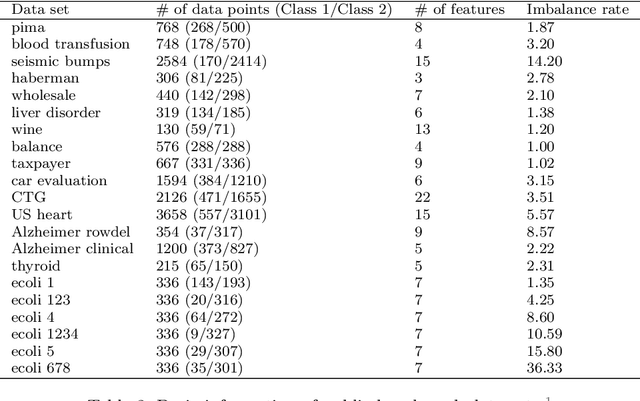
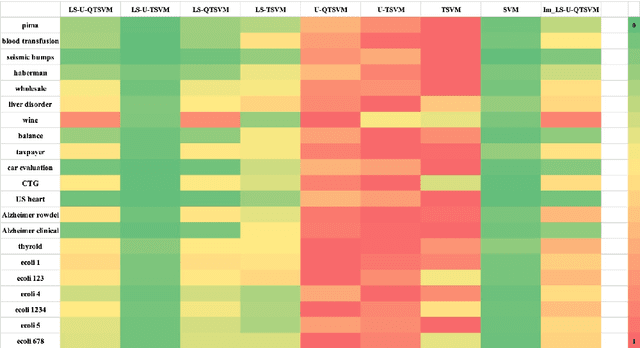
Abstract:Binary classification tasks with imbalanced classes pose significant challenges in machine learning. Traditional classifiers often struggle to accurately capture the characteristics of the minority class, resulting in biased models with subpar predictive performance. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to tackle this issue by leveraging Universum points to support the minority class within quadratic twin support vector machine models. Unlike traditional classifiers, our models utilize quadratic surfaces instead of hyperplanes for binary classification, providing greater flexibility in modeling complex decision boundaries. By incorporating Universum points, our approach enhances classification accuracy and generalization performance on imbalanced datasets. We generated four artificial datasets to demonstrate the flexibility of the proposed methods. Additionally, we validated the effectiveness of our approach through empirical evaluations on benchmark datasets, showing superior performance compared to conventional classifiers and existing methods for imbalanced classification.
YOLOCS: Object Detection based on Dense Channel Compression for Feature Spatial Solidification
May 07, 2023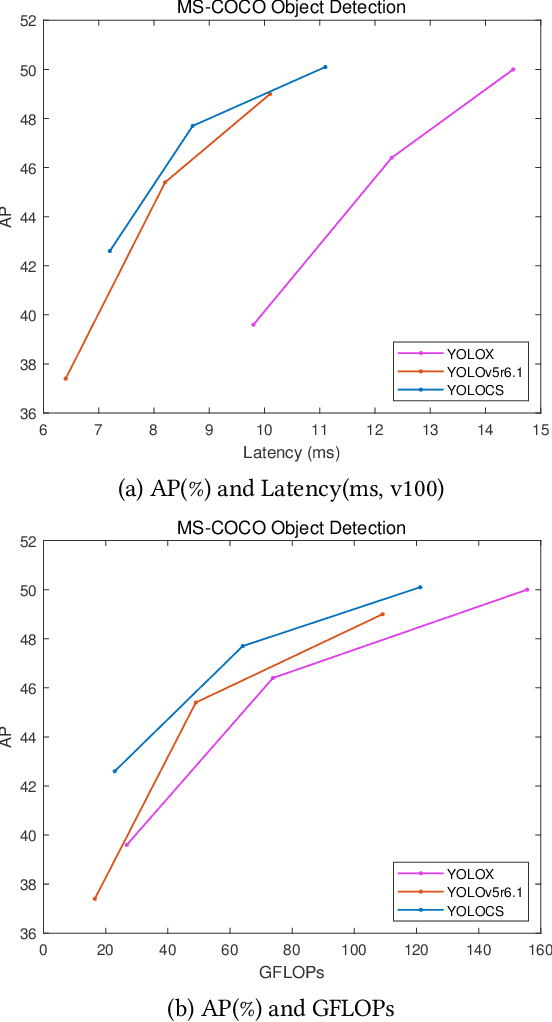
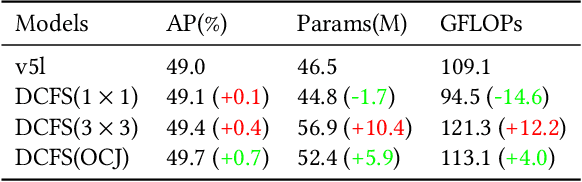
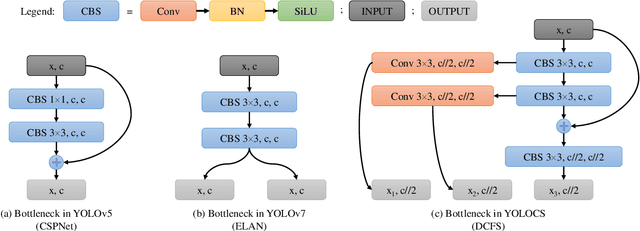
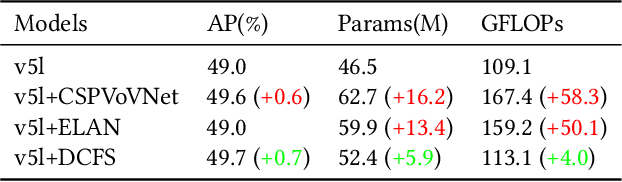
Abstract:In this study, we examine the associations between channel features and convolutional kernels during the processes of feature purification and gradient backpropagation, with a focus on the forward and backward propagation within the network. Consequently, we propose a method called Dense Channel Compression for Feature Spatial Solidification. Drawing upon the central concept of this method, we introduce two innovative modules for backbone and head networks: the Dense Channel Compression for Feature Spatial Solidification Structure (DCFS) and the Asymmetric Multi-Level Compression Decoupled Head (ADH). When integrated into the YOLOv5 model, these two modules demonstrate exceptional performance, resulting in a modified model referred to as YOLOCS. Evaluated on the MSCOCO dataset, the large, medium, and small YOLOCS models yield AP of 50.1%, 47.6%, and 42.5%, respectively. Maintaining inference speeds remarkably similar to those of the YOLOv5 model, the large, medium, and small YOLOCS models surpass the YOLOv5 model's AP by 1.1%, 2.3%, and 5.2%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge