Hans J. G. A. Dolfing
Whole page recognition of historical handwriting
Sep 22, 2020
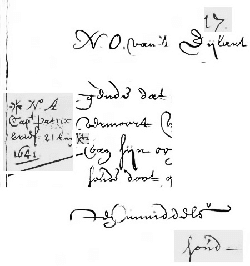
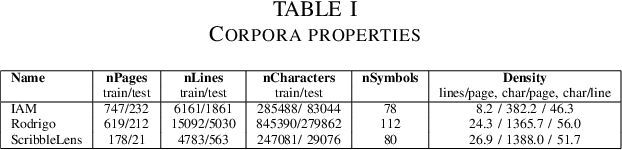
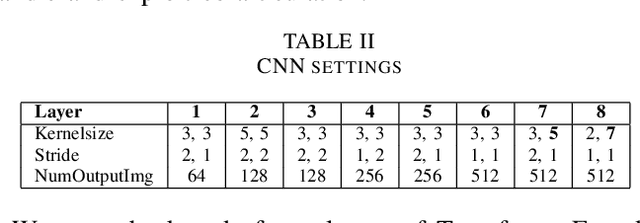
Abstract:Historical handwritten documents guard an important part of human knowledge only within reach of a few scholars and experts. Recent developments in machine learning and handwriting research have the potential of rendering this information accessible and searchable to a larger audience. To this end, we investigate an end-to-end inference approach without text localization which takes a handwritten page and transcribes its full text. No explicit character, word or line segmentation is involved in inference which is why we call this approach "segmentation free". We explore its robustness and accuracy compared to a line-by-line segmented approach based on the IAM, RODRIGO and ScribbleLens corpora, in three languages with handwriting styles spanning 400 years. We concentrate on model types and sizes which can be deployed on a hand-held or embedded device. We conclude that a whole page inference approach without text localization and segmentation is competitive.
Robust Training of Vector Quantized Bottleneck Models
May 18, 2020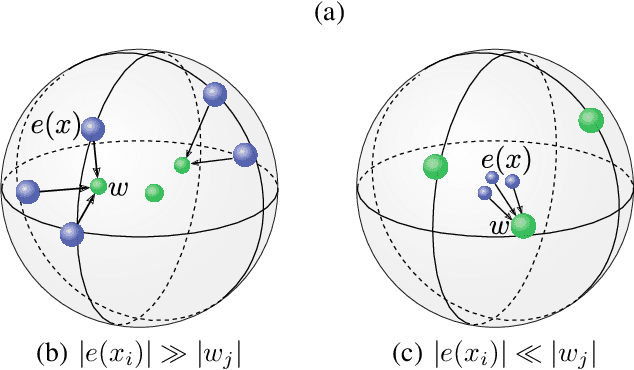
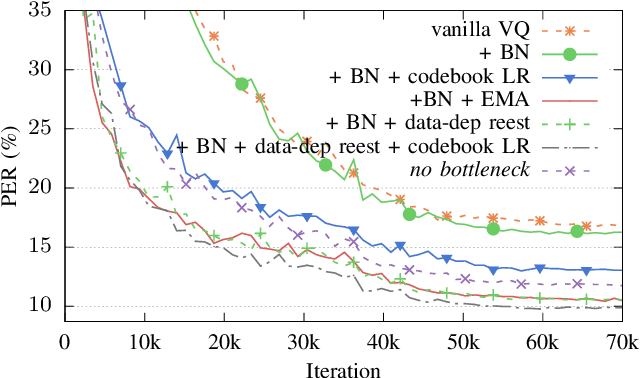
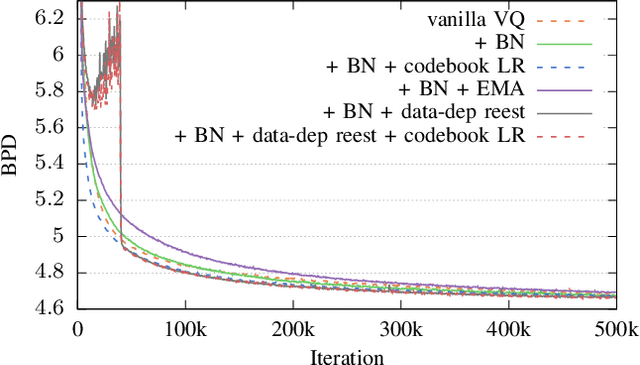
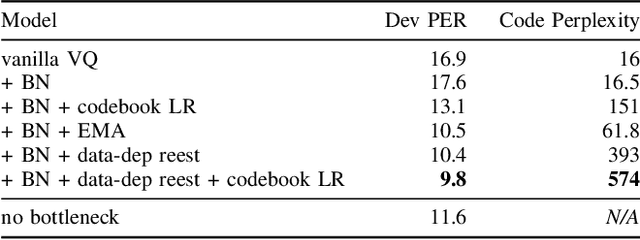
Abstract:In this paper we demonstrate methods for reliable and efficient training of discrete representation using Vector-Quantized Variational Auto-Encoder models (VQ-VAEs). Discrete latent variable models have been shown to learn nontrivial representations of speech, applicable to unsupervised voice conversion and reaching state-of-the-art performance on unit discovery tasks. For unsupervised representation learning, they became viable alternatives to continuous latent variable models such as the Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE). However, training deep discrete variable models is challenging, due to the inherent non-differentiability of the discretization operation. In this paper we focus on VQ-VAE, a state-of-the-art discrete bottleneck model shown to perform on par with its continuous counterparts. It quantizes encoder outputs with on-line $k$-means clustering. We show that the codebook learning can suffer from poor initialization and non-stationarity of clustered encoder outputs. We demonstrate that these can be successfully overcome by increasing the learning rate for the codebook and periodic date-dependent codeword re-initialization. As a result, we achieve more robust training across different tasks, and significantly increase the usage of latent codewords even for large codebooks. This has practical benefit, for instance, in unsupervised representation learning, where large codebooks may lead to disentanglement of latent representations.
Embedded Large-Scale Handwritten Chinese Character Recognition
Apr 13, 2020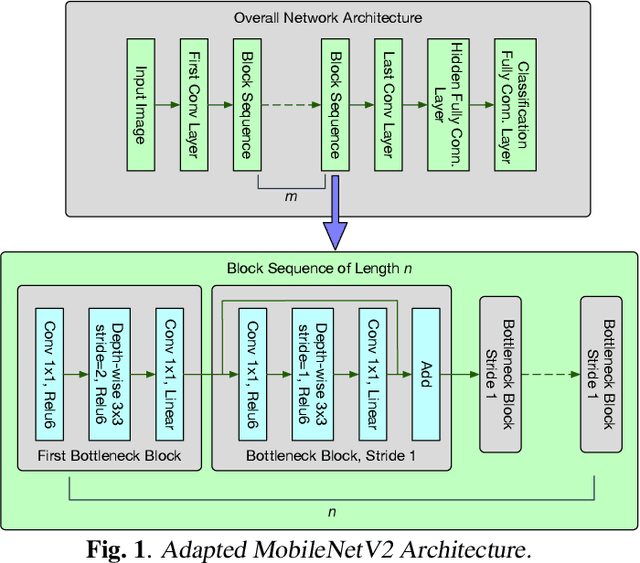
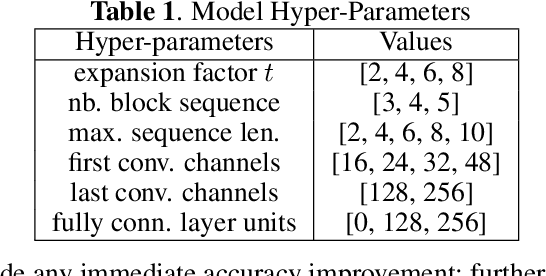
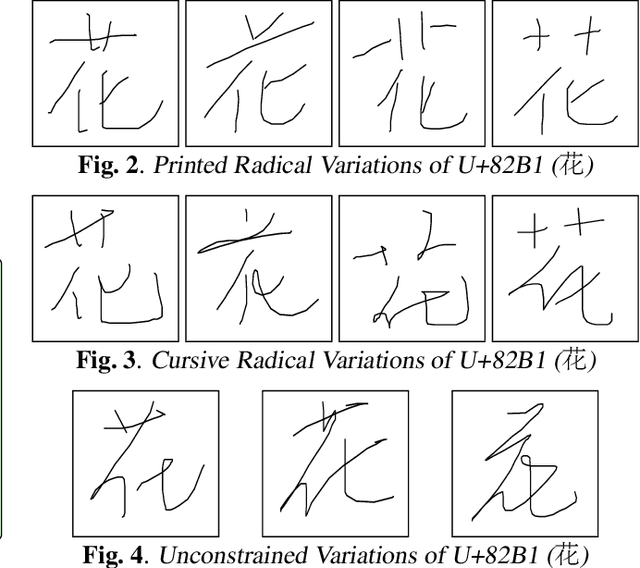
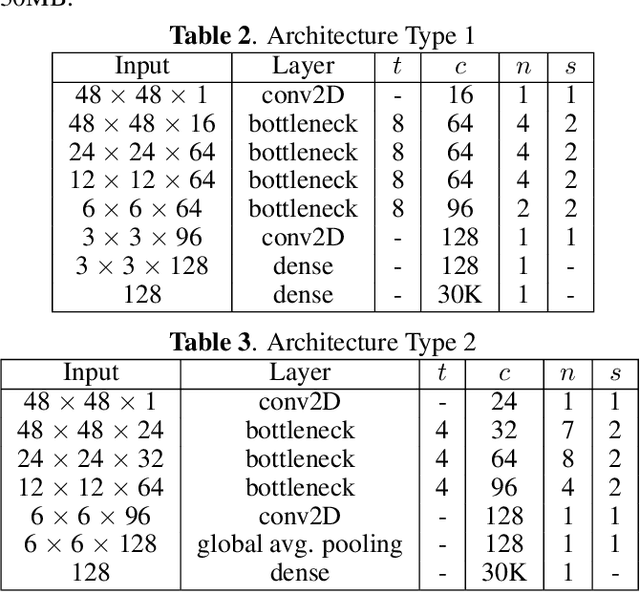
Abstract:As handwriting input becomes more prevalent, the large symbol inventory required to support Chinese handwriting recognition poses unique challenges. This paper describes how the Apple deep learning recognition system can accurately handle up to 30,000 Chinese characters while running in real-time across a range of mobile devices. To achieve acceptable accuracy, we paid particular attention to data collection conditions, representativeness of writing styles, and training regimen. We found that, with proper care, even larger inventories are within reach. Our experiments show that accuracy only degrades slowly as the inventory increases, as long as we use training data of sufficient quality and in sufficient quantity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge