Haiyan Fu
RoNet: Rotation-oriented Continuous Image Translation
Apr 06, 2024Abstract:The generation of smooth and continuous images between domains has recently drawn much attention in image-to-image (I2I) translation. Linear relationship acts as the basic assumption in most existing approaches, while applied to different aspects including features, models or labels. However, the linear assumption is hard to conform with the element dimension increases and suffers from the limit that having to obtain both ends of the line. In this paper, we propose a novel rotation-oriented solution and model the continuous generation with an in-plane rotation over the style representation of an image, achieving a network named RoNet. A rotation module is implanted in the generation network to automatically learn the proper plane while disentangling the content and the style of an image. To encourage realistic texture, we also design a patch-based semantic style loss that learns the different styles of the similar object in different domains. We conduct experiments on forest scenes (where the complex texture makes the generation very challenging), faces, streetscapes and the iphone2dslr task. The results validate the superiority of our method in terms of visual quality and continuity.
Prefix-diffusion: A Lightweight Diffusion Model for Diverse Image Captioning
Sep 10, 2023



Abstract:While impressive performance has been achieved in image captioning, the limited diversity of the generated captions and the large parameter scale remain major barriers to the real-word application of these systems. In this work, we propose a lightweight image captioning network in combination with continuous diffusion, called Prefix-diffusion. To achieve diversity, we design an efficient method that injects prefix image embeddings into the denoising process of the diffusion model. In order to reduce trainable parameters, we employ a pre-trained model to extract image features and further design an extra mapping network. Prefix-diffusion is able to generate diverse captions with relatively less parameters, while maintaining the fluency and relevance of the captions benefiting from the generative capabilities of the diffusion model. Our work paves the way for scaling up diffusion models for image captioning, and achieves promising performance compared with recent approaches.
Pseudo-positive regularization for deep person re-identification
Nov 17, 2017
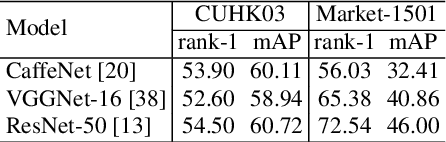

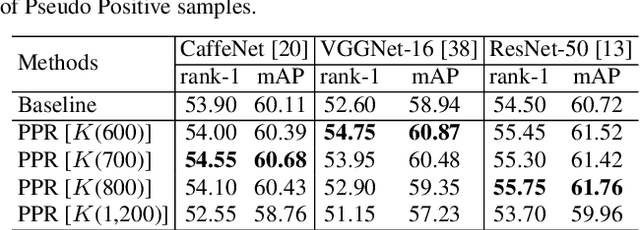
Abstract:An intrinsic challenge of person re-identification (re-ID) is the annotation difficulty. This typically means 1) few training samples per identity, and 2) thus the lack of diversity among the training samples. Consequently, we face high risk of over-fitting when training the convolutional neural network (CNN), a state-of-the-art method in person re-ID. To reduce the risk of over-fitting, this paper proposes a Pseudo Positive Regularization (PPR) method to enrich the diversity of the training data. Specifically, unlabeled data from an independent pedestrian database is retrieved using the target training data as query. A small proportion of these retrieved samples are randomly selected as the Pseudo Positive samples and added to the target training set for the supervised CNN training. The addition of Pseudo Positive samples is therefore a data augmentation method to reduce the risk of over-fitting during CNN training. We implement our idea in the identification CNN models (i.e., CaffeNet, VGGNet-16 and ResNet-50). On CUHK03 and Market-1501 datasets, experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently improves the baseline and yields competitive performance to the state-of-the-art person re-ID methods.
Part-based Deep Hashing for Large-scale Person Re-identification
May 05, 2017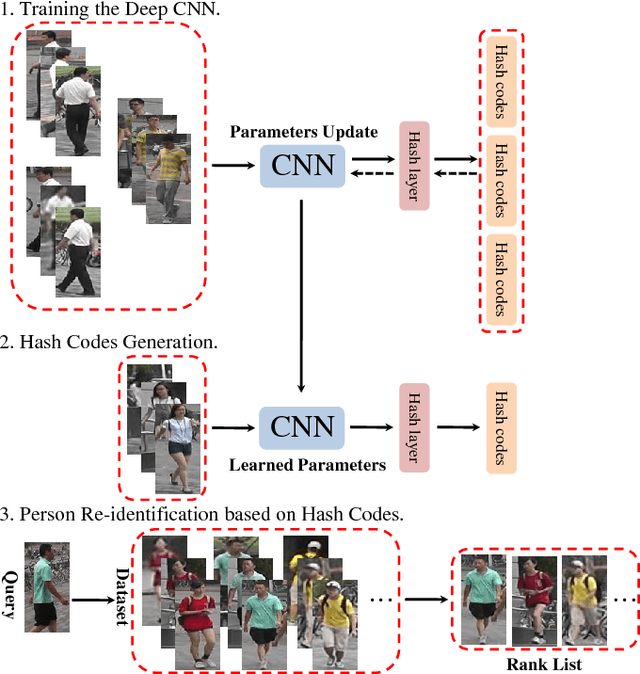


Abstract:Large-scale is a trend in person re-identification (re-id). It is important that real-time search be performed in a large gallery. While previous methods mostly focus on discriminative learning, this paper makes the attempt in integrating deep learning and hashing into one framework to evaluate the efficiency and accuracy for large-scale person re-id. We integrate spatial information for discriminative visual representation by partitioning the pedestrian image into horizontal parts. Specifically, Part-based Deep Hashing (PDH) is proposed, in which batches of triplet samples are employed as the input of the deep hashing architecture. Each triplet sample contains two pedestrian images (or parts) with the same identity and one pedestrian image (or part) of the different identity. A triplet loss function is employed with a constraint that the Hamming distance of pedestrian images (or parts) with the same identity is smaller than ones with the different identity. In the experiment, we show that the proposed Part-based Deep Hashing method yields very competitive re-id accuracy on the large-scale Market-1501 and Market-1501+500K datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge