Haishan Liu
MoTiAC: Multi-Objective Actor-Critics for Real-Time Bidding
Feb 18, 2020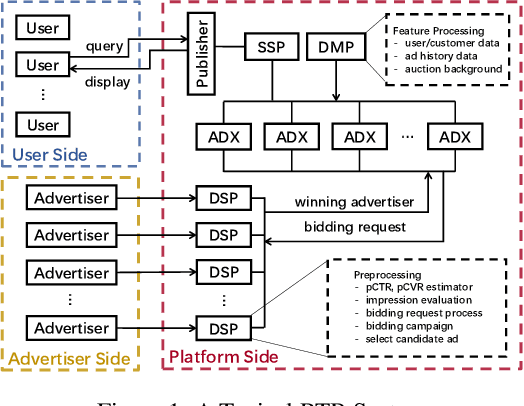
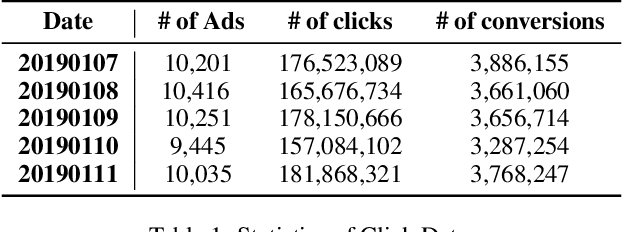
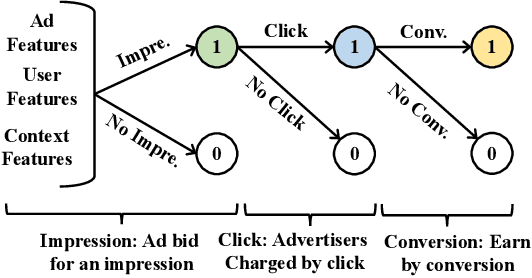
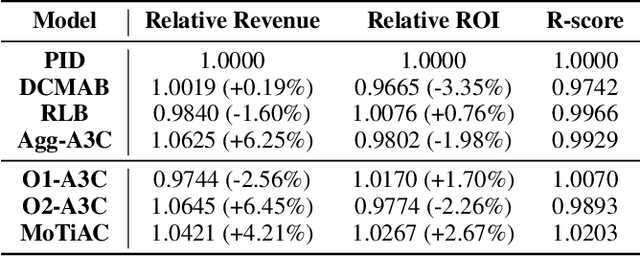
Abstract:Online real-time bidding (RTB) is known as a complex auction game where ad platforms seek to consider various influential key performance indicators (KPIs), like revenue and return on investment (ROI). The trade-off among these competing goals needs to be balanced on a massive scale. To address the problem, we propose a multi-objective reinforcement learning algorithm, named MoTiAC, for the problem of bidding optimization with various goals. Specifically, in MoTiAC, instead of using a fixed and linear combination of multiple objectives, we compute adaptive weights overtime on the basis of how well the current state agrees with the agent's prior. In addition, we provide interesting properties of model updating and further prove that Pareto optimality could be guaranteed. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on a real-world commercial dataset. Experiments show that the model outperforms all state-of-the-art baselines.
Measuring Long-term Impact of Ads on LinkedIn Feed
Jan 29, 2019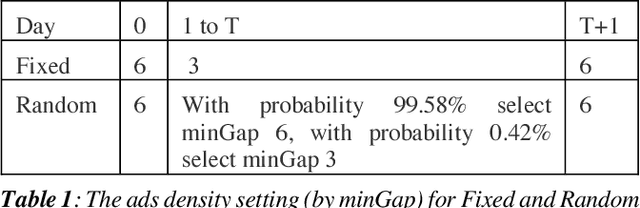
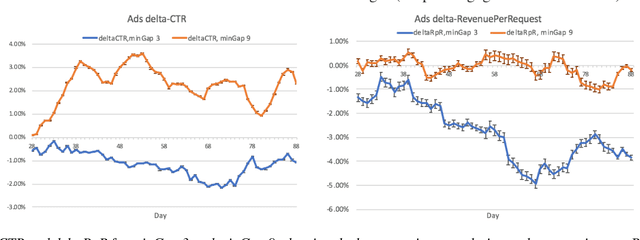
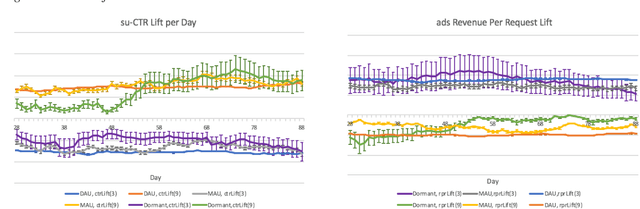
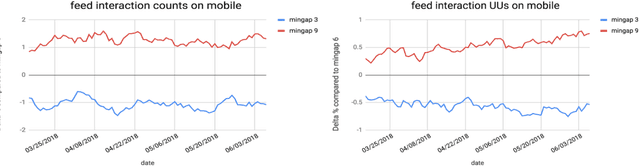
Abstract:Organic updates (from a member's network) and sponsored updates (or ads, from advertisers) together form the newsfeed on LinkedIn. The newsfeed, the default homepage for members, attracts them to engage, brings them value and helps LinkedIn grow. Engagement and Revenue on feed are two critical, yet often conflicting objectives. Hence, it is important to design a good Revenue-Engagement Tradeoff (RENT) mechanism to blend ads in the feed. In this paper, we design experiments to understand how members' behavior evolve over time given different ads experiences. These experiences vary on ads density, while the quality of ads (ensured by relevance models) is held constant. Our experiments have been conducted on randomized member buckets and we use two experimental designs to measure the short term and long term effects of the various treatments. Based on the first three months' data, we observe that the long term impact is at a much smaller scale than the short term impact in our application. Furthermore, we observe different member cohorts (based on user activity level) adapt and react differently over time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge