Haishan Huang
Task-Specific Knowledge Distillation from the Vision Foundation Model for Enhanced Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained models, such as Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), have demonstrated impressive performance across various downstream tasks by transferring generalized knowledge, especially when target data is limited. However, their high computational cost and the domain gap between natural and medical images limit their practical application in medical segmentation tasks. Motivated by this, we pose the following important question: "How can we effectively utilize the knowledge of large pre-trained VFMs to train a small, task-specific model for medical image segmentation when training data is limited?" To address this problem, we propose a novel and generalizable task-specific knowledge distillation framework. Our method fine-tunes the VFM on the target segmentation task to capture task-specific features before distilling the knowledge to smaller models, leveraging Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to reduce the computational cost of fine-tuning. Additionally, we incorporate synthetic data generated by diffusion models to augment the transfer set, enhancing model performance in data-limited scenarios. Experimental results across five medical image datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms task-agnostic knowledge distillation and self-supervised pretraining approaches like MoCo v3 and Masked Autoencoders (MAE). For example, on the KidneyUS dataset, our method achieved a 28% higher Dice score than task-agnostic KD using 80 labeled samples for fine-tuning. On the CHAOS dataset, it achieved an 11% improvement over MAE with 100 labeled samples. These results underscore the potential of task-specific knowledge distillation to train accurate, efficient models for medical image segmentation in data-constrained settings.
Semantic Prior Distillation with Vision Foundation Model for Enhanced Rapid Bone Scintigraphy Image Restoration
Mar 04, 2025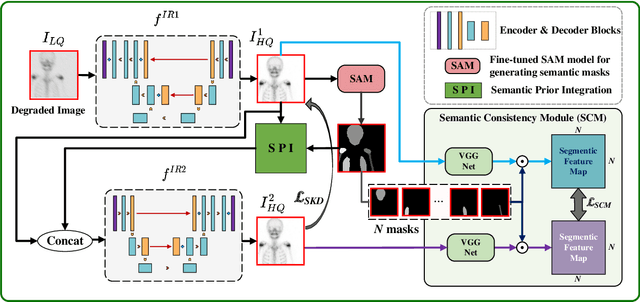
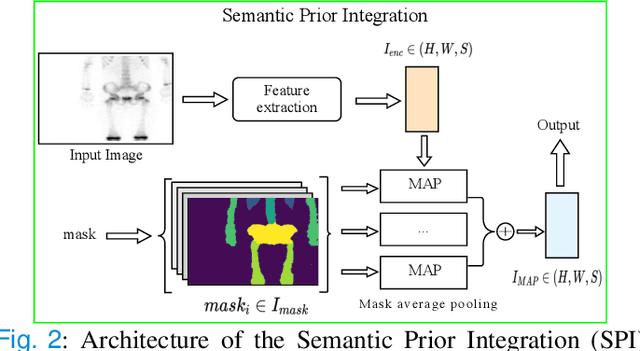
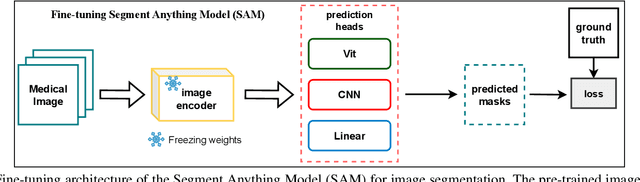
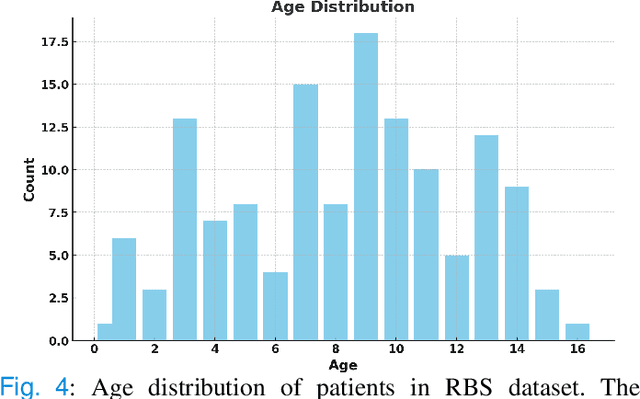
Abstract:Rapid bone scintigraphy is an essential tool for diagnosing skeletal diseases and tumor metastasis in pediatric patients, as it reduces scan time and minimizes patient discomfort. However, rapid scans often result in poor image quality, potentially affecting diagnosis due to reduced resolution and detail, which make it challenging to identify and evaluate finer anatomical structures. To address this issue, we propose the first application of SAM-based semantic priors for medical image restoration, leveraging the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to enhance rapid bone scintigraphy images in pediatric populations. Our method comprises two cascaded networks, $f^{IR1}$ and $f^{IR2}$, augmented by three key modules: a Semantic Prior Integration (SPI) module, a Semantic Knowledge Distillation (SKD) module, and a Semantic Consistency Module (SCM). The SPI and SKD modules incorporate domain-specific semantic information from a fine-tuned SAM, while the SCM maintains consistent semantic feature representation throughout the cascaded networks. In addition, we will release a novel Rapid Bone Scintigraphy dataset called RBS, the first dataset dedicated to rapid bone scintigraphy image restoration in pediatric patients. RBS consists of 137 pediatric patients aged between 0.5 and 16 years who underwent both standard and rapid bone scans. The dataset includes scans performed at 20 cm/min (standard) and 40 cm/min (rapid), representing a $2\times$ acceleration. We conducted extensive experiments on both the publicly available endoscopic dataset and RBS. The results demonstrate that our method outperforms all existing methods across various metrics, including PSNR, SSIM, FID, and LPIPS.
Vision Foundation Models in Medical Image Analysis: Advances and Challenges
Feb 21, 2025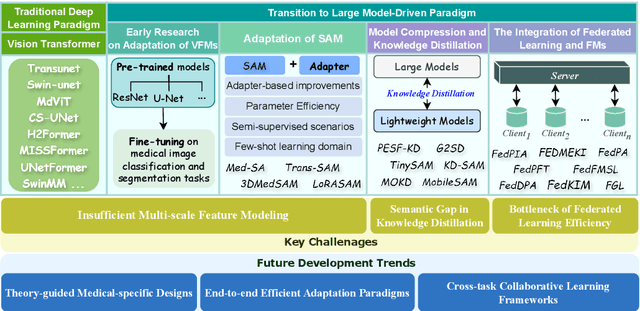
Abstract:The rapid development of Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), particularly Vision Transformers (ViT) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), has sparked significant advances in the field of medical image analysis. These models have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in capturing long-range dependencies and achieving high generalization in segmentation tasks. However, adapting these large models to medical image analysis presents several challenges, including domain differences between medical and natural images, the need for efficient model adaptation strategies, and the limitations of small-scale medical datasets. This paper reviews the state-of-the-art research on the adaptation of VFMs to medical image segmentation, focusing on the challenges of domain adaptation, model compression, and federated learning. We discuss the latest developments in adapter-based improvements, knowledge distillation techniques, and multi-scale contextual feature modeling, and propose future directions to overcome these bottlenecks. Our analysis highlights the potential of VFMs, along with emerging methodologies such as federated learning and model compression, to revolutionize medical image analysis and enhance clinical applications. The goal of this work is to provide a comprehensive overview of current approaches and suggest key areas for future research that can drive the next wave of innovation in medical image segmentation.
Topology-Aware Wavelet Mamba for Airway Structure Segmentation in Postoperative Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma CT Scans
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients often undergo radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which can lead to postoperative complications such as limited mouth opening and joint stiffness, particularly in recurrent cases that require re-surgery. These complications can affect airway function, making accurate postoperative airway risk assessment essential for managing patient care. Accurate segmentation of airway-related structures in postoperative CT scans is crucial for assessing these risks. This study introduces TopoWMamba (Topology-aware Wavelet Mamba), a novel segmentation model specifically designed to address the challenges of postoperative airway risk evaluation in recurrent NPC patients. TopoWMamba combines wavelet-based multi-scale feature extraction, state-space sequence modeling, and topology-aware modules to segment airway-related structures in CT scans robustly. By leveraging the Wavelet-based Mamba Block (WMB) for hierarchical frequency decomposition and the Snake Conv VSS (SCVSS) module to preserve anatomical continuity, TopoWMamba effectively captures both fine-grained boundaries and global structural context, crucial for accurate segmentation in complex postoperative scenarios. Through extensive testing on the NPCSegCT dataset, TopoWMamba achieves an average Dice score of 88.02%, outperforming existing models such as UNet, Attention UNet, and SwinUNet. Additionally, TopoWMamba is tested on the SegRap 2023 Challenge dataset, where it shows a significant improvement in trachea segmentation with a Dice score of 95.26%. The proposed model provides a strong foundation for automated segmentation, enabling more accurate postoperative airway risk evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge