Haibo Xing
Masked Diffusion Generative Recommendation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Generative recommendation (GR) typically first quantizes continuous item embeddings into multi-level semantic IDs (SIDs), and then generates the next item via autoregressive decoding. Although existing methods are already competitive in terms of recommendation performance, directly inheriting the autoregressive decoding paradigm from language models still suffers from three key limitations: (1) autoregressive decoding struggles to jointly capture global dependencies among the multi-dimensional features associated with different positions of SID; (2) using a unified, fixed decoding path for the same item implicitly assumes that all users attend to item attributes in the same order; (3) autoregressive decoding is inefficient at inference time and struggles to meet real-time requirements. To tackle these challenges, we propose MDGR, a Masked Diffusion Generative Recommendation framework that reshapes the GR pipeline from three perspectives: codebook, training, and inference. (1) We adopt a parallel codebook to provide a structural foundation for diffusion-based GR. (2) During training, we adaptively construct masking supervision signals along both the temporal and sample dimensions. (3) During inference, we develop a warm-up-based two-stage parallel decoding strategy for efficient generation of SIDs. Extensive experiments on multiple public and industrial-scale datasets show that MDGR outperforms ten state-of-the-art baselines by up to 10.78%. Furthermore, by deploying MDGR on a large-scale online advertising platform, we achieve a 1.20% increase in revenue, demonstrating its practical value. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Synergistic Integration and Discrepancy Resolution of Contextualized Knowledge for Personalized Recommendation
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) into recommendation systems has revealed promising potential through their capacity to extract world knowledge for enhanced reasoning capabilities. However, current methodologies that adopt static schema-based prompting mechanisms encounter significant limitations: (1) they employ universal template structures that neglect the multi-faceted nature of user preference diversity; (2) they implement superficial alignment between semantic knowledge representations and behavioral feature spaces without achieving comprehensive latent space integration. To address these challenges, we introduce CoCo, an end-to-end framework that dynamically constructs user-specific contextual knowledge embeddings through a dual-mechanism approach. Our method realizes profound integration of semantic and behavioral latent dimensions via adaptive knowledge fusion and contradiction resolution modules. Experimental evaluations across diverse benchmark datasets and an enterprise-level e-commerce platform demonstrate CoCo's superiority, achieving a maximum 8.58% improvement over seven cutting-edge methods in recommendation accuracy. The framework's deployment on a production advertising system resulted in a 1.91% sales growth, validating its practical effectiveness. With its modular design and model-agnostic architecture, CoCo provides a versatile solution for next-generation recommendation systems requiring both knowledge-enhanced reasoning and personalized adaptation.
CSMF: Cascaded Selective Mask Fine-Tuning for Multi-Objective Embedding-Based Retrieval
Apr 17, 2025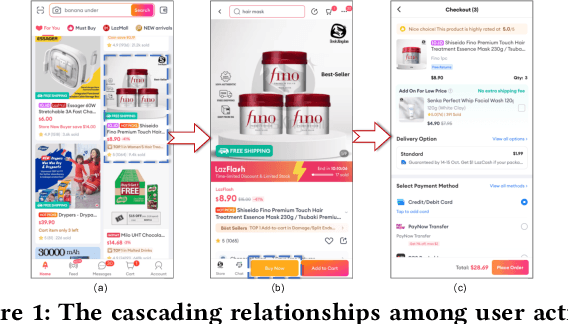
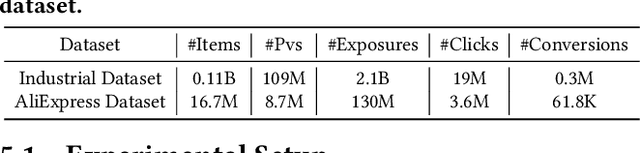
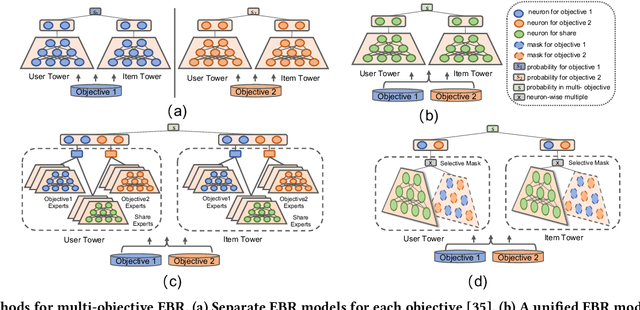
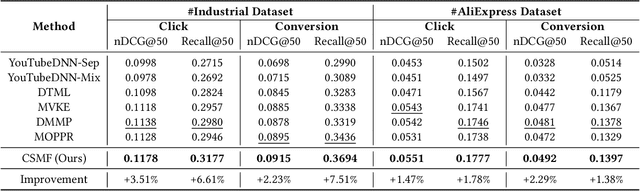
Abstract:Multi-objective embedding-based retrieval (EBR) has become increasingly critical due to the growing complexity of user behaviors and commercial objectives. While traditional approaches often suffer from data sparsity and limited information sharing between objectives, recent methods utilizing a shared network alongside dedicated sub-networks for each objective partially address these limitations. However, such methods significantly increase the model parameters, leading to an increased retrieval latency and a limited ability to model causal relationships between objectives. To address these challenges, we propose the Cascaded Selective Mask Fine-Tuning (CSMF), a novel method that enhances both retrieval efficiency and serving performance for multi-objective EBR. The CSMF framework selectively masks model parameters to free up independent learning space for each objective, leveraging the cascading relationships between objectives during the sequential fine-tuning. Without increasing network parameters or online retrieval overhead, CSMF computes a linearly weighted fusion score for multiple objective probabilities while supporting flexible adjustment of each objective's weight across various recommendation scenarios. Experimental results on real-world datasets demonstrate the superior performance of CSMF, and online experiments validate its significant practical value.
Hierarchical Causal Transformer with Heterogeneous Information for Expandable Sequential Recommendation
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Sequential recommendation systems leveraging transformer architectures have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in capturing user behavior patterns. At the core of these systems lies the critical challenge of constructing effective item representations. Traditional approaches employ feature fusion through simple concatenation or basic neural architectures to create uniform representation sequences. However, these conventional methods fail to address the intrinsic diversity of item attributes, thereby constraining the transformer's capacity to discern fine-grained patterns and hindering model extensibility. Although recent research has begun incorporating user-related heterogeneous features into item sequences, the equally crucial item-side heterogeneous feature continue to be neglected. To bridge this methodological gap, we present HeterRec - an innovative framework featuring two novel components: the Heterogeneous Token Flattening Layer (HTFL) and Hierarchical Causal Transformer (HCT). HTFL pioneers a sophisticated tokenization mechanism that decomposes items into multi-dimensional token sets and structures them into heterogeneous sequences, enabling scalable performance enhancement through model expansion. The HCT architecture further enhances pattern discovery through token-level and item-level attention mechanisms. furthermore, we develop a Listwise Multi-step Prediction (LMP) objective function to optimize learning process. Rigorous validation, including real-world industrial platforms, confirms HeterRec's state-of-the-art performance in both effective and efficiency.
ESANS: Effective and Semantic-Aware Negative Sampling for Large-Scale Retrieval Systems
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommendation systems typically involve a two-stage process: retrieval and ranking, which aims to match users with millions of items. In the retrieval stage, classic embedding-based retrieval (EBR) methods depend on effective negative sampling techniques to enhance both performance and efficiency. However, existing techniques often suffer from false negatives, high cost for ensuring sampling quality and semantic information deficiency. To address these limitations, we propose Effective and Semantic-Aware Negative Sampling (ESANS), which integrates two key components: Effective Dense Interpolation Strategy (EDIS) and Multimodal Semantic-Aware Clustering (MSAC). EDIS generates virtual samples within the low-dimensional embedding space to improve the diversity and density of the sampling distribution while minimizing computational costs. MSAC refines the negative sampling distribution by hierarchically clustering item representations based on multimodal information (visual, textual, behavioral), ensuring semantic consistency and reducing false negatives. Extensive offline and online experiments demonstrate the superior efficiency and performance of ESANS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge