Guoyao Deng
SAM-U: Multi-box prompts triggered uncertainty estimation for reliable SAM in medical image
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:Recently, Segmenting Anything has taken an important step towards general artificial intelligence. At the same time, its reliability and fairness have also attracted great attention, especially in the field of health care. In this study, we propose multi-box prompts triggered uncertainty estimation for SAM cues to demonstrate the reliability of segmented lesions or tissues. We estimate the distribution of SAM predictions via Monte Carlo with prior distribution parameters, which employs different prompts as formulation of test-time augmentation. Our experimental results found that multi-box prompts augmentation improve the SAM performance, and endowed each pixel with uncertainty. This provides the first paradigm for a reliable SAM.
A Multi-view Impartial Decision Network for Frontotemporal Dementia Diagnosis
Jul 11, 2023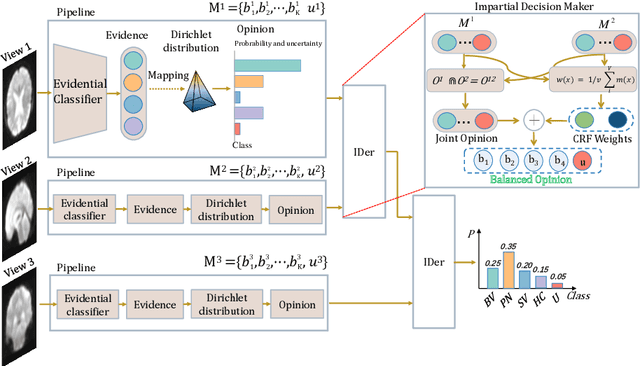
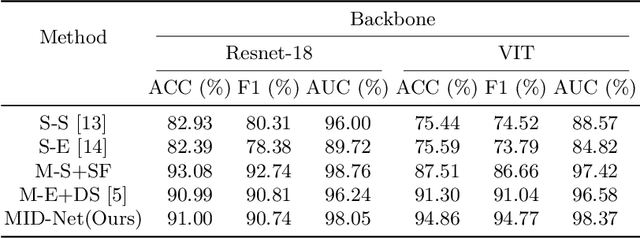
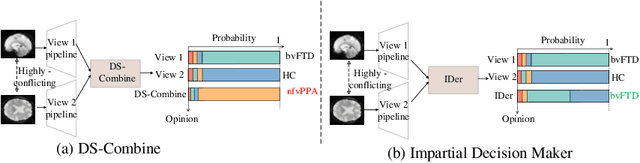
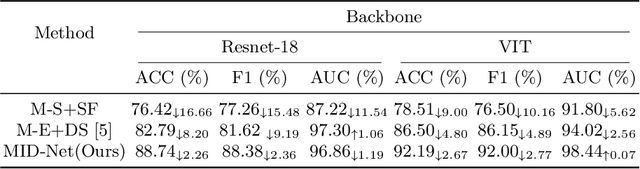
Abstract:Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD) diagnosis has been successfully progress using deep learning techniques. However, current FTD identification methods suffer from two limitations. Firstly, they do not exploit the potential of multi-view functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for classifying FTD. Secondly, they do not consider the reliability of the multi-view FTD diagnosis. To address these limitations, we propose a reliable multi-view impartial decision network (MID-Net) for FTD diagnosis in fMRI. Our MID-Net provides confidence for each view and generates a reliable prediction without any conflict. To achieve this, we employ multiple expert models to extract evidence from the abundant neural network information contained in fMRI images. We then introduce the Dirichlet Distribution to characterize the expert class probability distribution from an evidence level. Additionally, a novel Impartial Decision Maker (IDer) is proposed to combine the different opinions inductively to arrive at an unbiased prediction without additional computation cost. Overall, our MID-Net dynamically integrates the decisions of different experts on FTD disease, especially when dealing with multi-view high-conflict cases. Extensive experiments on a high-quality FTD fMRI dataset demonstrate that our model outperforms previous methods and provides high uncertainty for hard-to-classify examples. We believe that our approach represents a significant step toward the deployment of reliable FTD decision-making under multi-expert conditions. We will release the codes for reproduction after acceptance.
Uncertainty-inspired Open Set Learning for Retinal Anomaly Identification
Apr 08, 2023
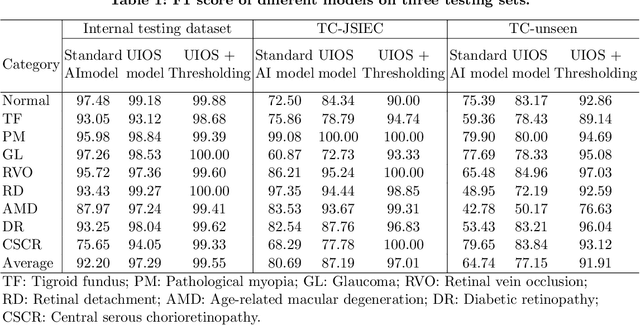


Abstract:Failure to recognize samples from the classes unseen during training is a major limit of artificial intelligence (AI) in real-world implementation of retinal anomaly classification. To resolve this obstacle, we propose an uncertainty-inspired open-set (UIOS) model which was trained with fundus images of 9 common retinal conditions. Besides the probability of each category, UIOS also calculates an uncertainty score to express its confidence. Our UIOS model with thresholding strategy achieved an F1 score of 99.55%, 97.01% and 91.91% for the internal testing set, external testing set and non-typical testing set, respectively, compared to the F1 score of 92.20%, 80.69% and 64.74% by the standard AI model. Furthermore, UIOS correctly predicted high uncertainty scores, which prompted the need for a manual check, in the datasets of rare retinal diseases, low-quality fundus images, and non-fundus images. This work provides a robust method for real-world screening of retinal anomalies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge