Guillaume Salha-Galvan
FairExpand: Individual Fairness on Graphs with Partial Similarity Information
Dec 20, 2025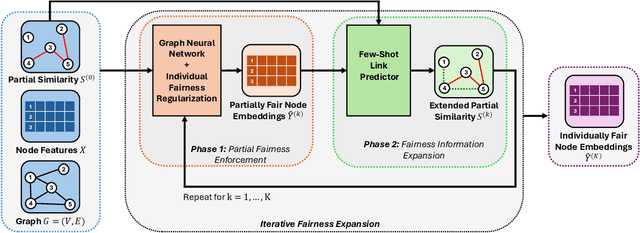
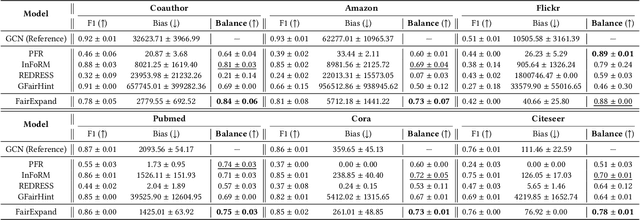
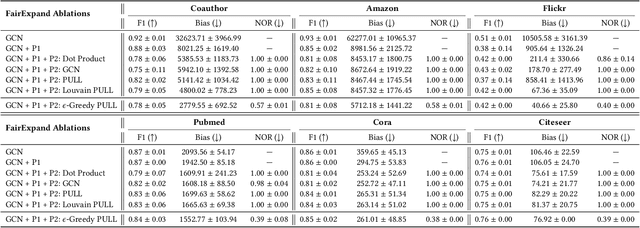
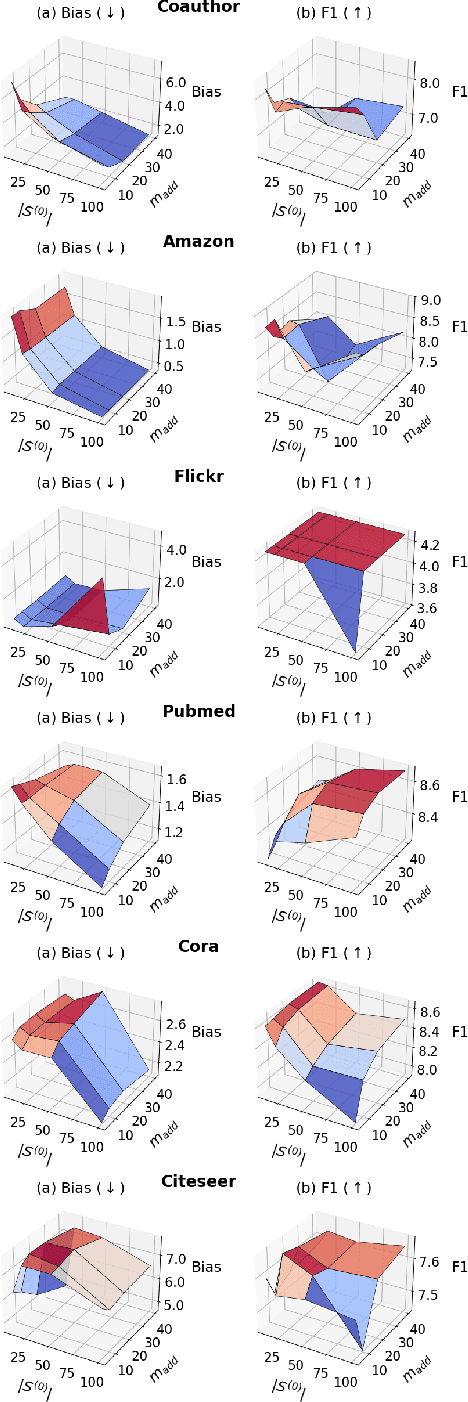
Abstract:Individual fairness, which requires that similar individuals should be treated similarly by algorithmic systems, has become a central principle in fair machine learning. Individual fairness has garnered traction in graph representation learning due to its practical importance in high-stakes Web areas such as user modeling, recommender systems, and search. However, existing methods assume the existence of predefined similarity information over all node pairs, an often unrealistic requirement that prevents their operationalization in practice. In this paper, we assume the similarity information is only available for a limited subset of node pairs and introduce FairExpand, a flexible framework that promotes individual fairness in this more realistic partial information scenario. FairExpand follows a two-step pipeline that alternates between refining node representations using a backbone model (e.g., a graph neural network) and gradually propagating similarity information, which allows fairness enforcement to effectively expand to the entire graph. Extensive experiments show that FairExpand consistently enhances individual fairness while preserving performance, making it a practical solution for enabling graph-based individual fairness in real-world applications with partial similarity information.
To Share or Not to Share: Investigating Weight Sharing in Variational Graph Autoencoders
Feb 23, 2025

Abstract:This paper investigates the understudied practice of weight sharing (WS) in variational graph autoencoders (VGAE). WS presents both benefits and drawbacks for VGAE model design and node embedding learning, leaving its overall relevance unclear and the question of whether it should be adopted unresolved. We rigorously analyze its implications and, through extensive experiments on a wide range of graphs and VGAE variants, demonstrate that the benefits of WS consistently outweigh its drawbacks. Based on our findings, we recommend WS as an effective approach to optimize, regularize, and simplify VGAE models without significant performance loss.
Transformers Meet ACT-R: Repeat-Aware and Sequential Listening Session Recommendation
Aug 29, 2024Abstract:Music streaming services often leverage sequential recommender systems to predict the best music to showcase to users based on past sequences of listening sessions. Nonetheless, most sequential recommendation methods ignore or insufficiently account for repetitive behaviors. This is a crucial limitation for music recommendation, as repeatedly listening to the same song over time is a common phenomenon that can even change the way users perceive this song. In this paper, we introduce PISA (Psychology-Informed Session embedding using ACT-R), a session-level sequential recommender system that overcomes this limitation. PISA employs a Transformer architecture learning embedding representations of listening sessions and users using attention mechanisms inspired by Anderson's ACT-R (Adaptive Control of Thought-Rational), a cognitive architecture modeling human information access and memory dynamics. This approach enables us to capture dynamic and repetitive patterns from user behaviors, allowing us to effectively predict the songs they will listen to in subsequent sessions, whether they are repeated or new ones. We demonstrate the empirical relevance of PISA using both publicly available listening data from Last.fm and proprietary data from Deezer, a global music streaming service, confirming the critical importance of repetition modeling for sequential listening session recommendation. Along with this paper, we publicly release our proprietary dataset to foster future research in this field, as well as the source code of PISA to facilitate its future use.
Do Recommender Systems Promote Local Music? A Reproducibility Study Using Music Streaming Data
Aug 29, 2024Abstract:This paper examines the influence of recommender systems on local music representation, discussing prior findings from an empirical study on the LFM-2b public dataset. This prior study argued that different recommender systems exhibit algorithmic biases shifting music consumption either towards or against local content. However, LFM-2b users do not reflect the diverse audience of music streaming services. To assess the robustness of this study's conclusions, we conduct a comparative analysis using proprietary listening data from a global music streaming service, which we publicly release alongside this paper. We observe significant differences in local music consumption patterns between our dataset and LFM-2b, suggesting that caution should be exercised when drawing conclusions on local music based solely on LFM-2b. Moreover, we show that the algorithmic biases exhibited in the original work vary in our dataset, and that several unexplored model parameters can significantly influence these biases and affect the study's conclusion on both datasets. Finally, we discuss the complexity of accurately labeling local music, emphasizing the risk of misleading conclusions due to unreliable, biased, or incomplete labels. To encourage further research and ensure reproducibility, we have publicly shared our dataset and code.
Let's Get It Started: Fostering the Discoverability of New Releases on Deezer
Jan 05, 2024


Abstract:This paper presents our recent initiatives to foster the discoverability of new releases on the music streaming service Deezer. After introducing our search and recommendation features dedicated to new releases, we outline our shift from editorial to personalized release suggestions using cold start embeddings and contextual bandits. Backed by online experiments, we discuss the advantages of this shift in terms of recommendation quality and exposure of new releases on the service.
On the Consistency of Average Embeddings for Item Recommendation
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:A prevalent practice in recommender systems consists in averaging item embeddings to represent users or higher-level concepts in the same embedding space. This paper investigates the relevance of such a practice. For this purpose, we propose an expected precision score, designed to measure the consistency of an average embedding relative to the items used for its construction. We subsequently analyze the mathematical expression of this score in a theoretical setting with specific assumptions, as well as its empirical behavior on real-world data from music streaming services. Our results emphasize that real-world averages are less consistent for recommendation, which paves the way for future research to better align real-world embeddings with assumptions from our theoretical setting.
Track Mix Generation on Music Streaming Services using Transformers
Jul 06, 2023


Abstract:This paper introduces Track Mix, a personalized playlist generation system released in 2022 on the music streaming service Deezer. Track Mix automatically generates "mix" playlists inspired by initial music tracks, allowing users to discover music similar to their favorite content. To generate these mixes, we consider a Transformer model trained on millions of track sequences from user playlists. In light of the growing popularity of Transformers in recent years, we analyze the advantages, drawbacks, and technical challenges of using such a model for mix generation on the service, compared to a more traditional collaborative filtering approach. Since its release, Track Mix has been generating playlists for millions of users daily, enhancing their music discovery experience on Deezer.
Attention Mixtures for Time-Aware Sequential Recommendation
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:Transformers emerged as powerful methods for sequential recommendation. However, existing architectures often overlook the complex dependencies between user preferences and the temporal context. In this short paper, we introduce MOJITO, an improved Transformer sequential recommender system that addresses this limitation. MOJITO leverages Gaussian mixtures of attention-based temporal context and item embedding representations for sequential modeling. Such an approach permits to accurately predict which items should be recommended next to users depending on past actions and the temporal context. We demonstrate the relevance of our approach, by empirically outperforming existing Transformers for sequential recommendation on several real-world datasets.
A Scalable Framework for Automatic Playlist Continuation on Music Streaming Services
Apr 12, 2023Abstract:Music streaming services often aim to recommend songs for users to extend the playlists they have created on these services. However, extending playlists while preserving their musical characteristics and matching user preferences remains a challenging task, commonly referred to as Automatic Playlist Continuation (APC). Besides, while these services often need to select the best songs to recommend in real-time and among large catalogs with millions of candidates, recent research on APC mainly focused on models with few scalability guarantees and evaluated on relatively small datasets. In this paper, we introduce a general framework to build scalable yet effective APC models for large-scale applications. Based on a represent-then-aggregate strategy, it ensures scalability by design while remaining flexible enough to incorporate a wide range of representation learning and sequence modeling techniques, e.g., based on Transformers. We demonstrate the relevance of this framework through in-depth experimental validation on Spotify's Million Playlist Dataset (MPD), the largest public dataset for APC. We also describe how, in 2022, we successfully leveraged this framework to improve APC in production on Deezer. We report results from a large-scale online A/B test on this service, emphasizing the practical impact of our approach in such a real-world application.
New Frontiers in Graph Autoencoders: Joint Community Detection and Link Prediction
Nov 16, 2022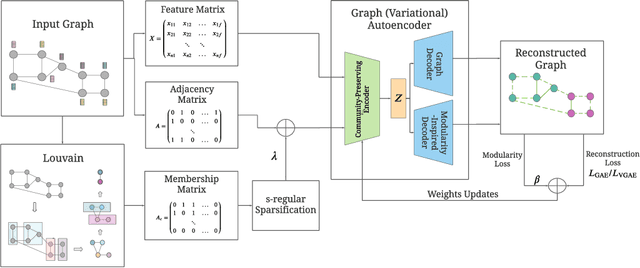
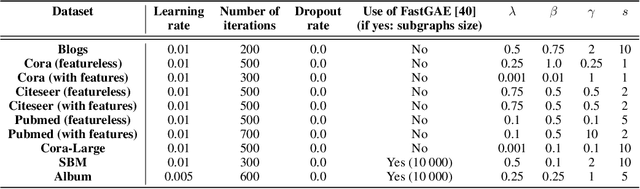
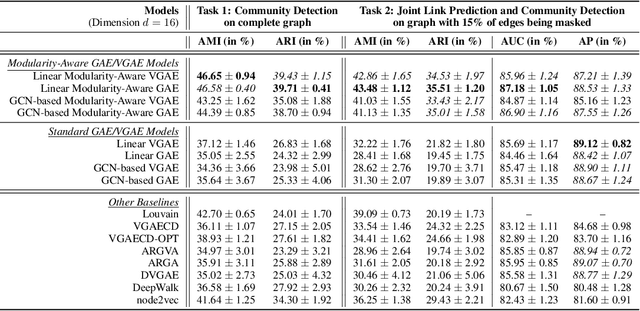
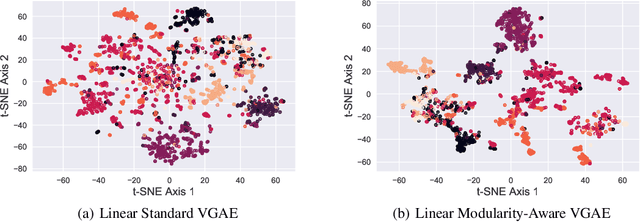
Abstract:Graph autoencoders (GAE) and variational graph autoencoders (VGAE) emerged as powerful methods for link prediction (LP). Their performances are less impressive on community detection (CD), where they are often outperformed by simpler alternatives such as the Louvain method. It is still unclear to what extent one can improve CD with GAE and VGAE, especially in the absence of node features. It is moreover uncertain whether one could do so while simultaneously preserving good performances on LP in a multi-task setting. In this workshop paper, summarizing results from our journal publication (Salha-Galvan et al. 2022), we show that jointly addressing these two tasks with high accuracy is possible. For this purpose, we introduce a community-preserving message passing scheme, doping our GAE and VGAE encoders by considering both the initial graph and Louvain-based prior communities when computing embedding spaces. Inspired by modularity-based clustering, we further propose novel training and optimization strategies specifically designed for joint LP and CD. We demonstrate the empirical effectiveness of our approach, referred to as Modularity-Aware GAE and VGAE, on various real-world graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge