Benjamin Chapus
Let's Get It Started: Fostering the Discoverability of New Releases on Deezer
Jan 05, 2024


Abstract:This paper presents our recent initiatives to foster the discoverability of new releases on the music streaming service Deezer. After introducing our search and recommendation features dedicated to new releases, we outline our shift from editorial to personalized release suggestions using cold start embeddings and contextual bandits. Backed by online experiments, we discuss the advantages of this shift in terms of recommendation quality and exposure of new releases on the service.
Track Mix Generation on Music Streaming Services using Transformers
Jul 06, 2023


Abstract:This paper introduces Track Mix, a personalized playlist generation system released in 2022 on the music streaming service Deezer. Track Mix automatically generates "mix" playlists inspired by initial music tracks, allowing users to discover music similar to their favorite content. To generate these mixes, we consider a Transformer model trained on millions of track sequences from user playlists. In light of the growing popularity of Transformers in recent years, we analyze the advantages, drawbacks, and technical challenges of using such a model for mix generation on the service, compared to a more traditional collaborative filtering approach. Since its release, Track Mix has been generating playlists for millions of users daily, enhancing their music discovery experience on Deezer.
Flow Moods: Recommending Music by Moods on Deezer
Jul 15, 2022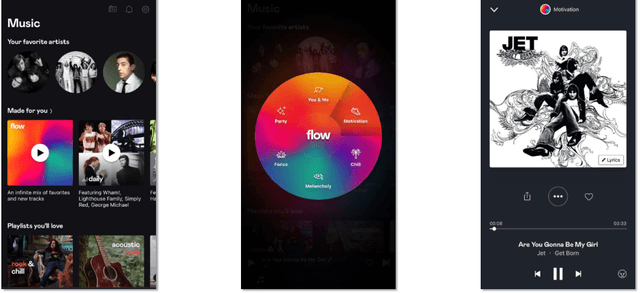
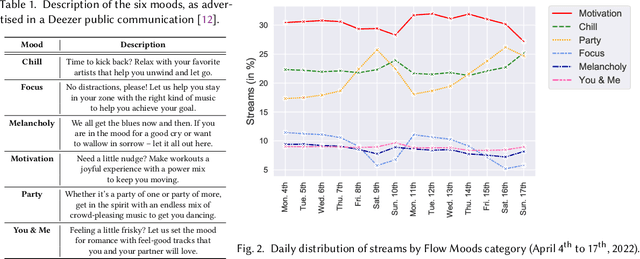
Abstract:The music streaming service Deezer extensively relies on its Flow algorithm, which generates personalized radio-style playlists of songs, to help users discover musical content. Nonetheless, despite promising results over the past years, Flow used to ignore the moods of users when providing recommendations. In this paper, we present Flow Moods, an improved version of Flow that addresses this limitation. Flow Moods leverages collaborative filtering, audio content analysis, and mood annotations from professional music curators to generate personalized mood-specific playlists at scale. We detail the motivations, the development, and the deployment of this system on Deezer. Since its release in 2021, Flow Moods has been recommending music by moods to millions of users every day.
Cold Start Similar Artists Ranking with Gravity-Inspired Graph Autoencoders
Aug 02, 2021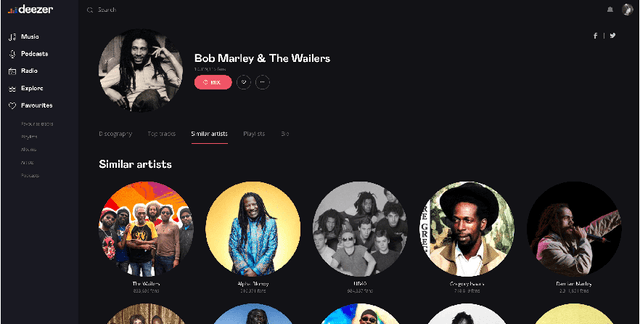
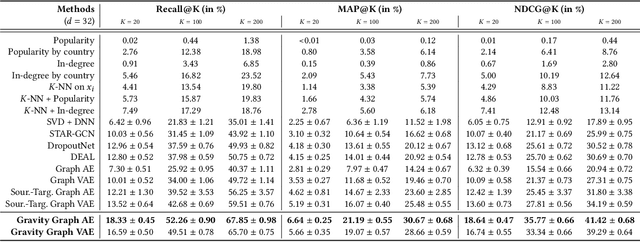
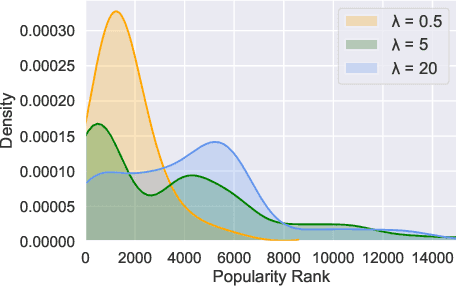
Abstract:On an artist's profile page, music streaming services frequently recommend a ranked list of "similar artists" that fans also liked. However, implementing such a feature is challenging for new artists, for which usage data on the service (e.g. streams or likes) is not yet available. In this paper, we model this cold start similar artists ranking problem as a link prediction task in a directed and attributed graph, connecting artists to their top-k most similar neighbors and incorporating side musical information. Then, we leverage a graph autoencoder architecture to learn node embedding representations from this graph, and to automatically rank the top-k most similar neighbors of new artists using a gravity-inspired mechanism. We empirically show the flexibility and the effectiveness of our framework, by addressing a real-world cold start similar artists ranking problem on a global music streaming service. Along with this paper, we also publicly release our source code as well as the industrial graph data from our experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge