Guangyu Zhou
Zhongjing: Enhancing the Chinese Medical Capabilities of Large Language Model through Expert Feedback and Real-world Multi-turn Dialogue
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable breakthroughs in understanding and responding to user intents. However, their performance lag behind general use cases in some expertise domains, such as Chinese medicine. Existing efforts to incorporate Chinese medicine into LLMs rely on Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with single-turn and distilled dialogue data. These models lack the ability for doctor-like proactive inquiry and multi-turn comprehension and cannot always align responses with safety and professionalism experts. In this work, we introduce Zhongjing, the first Chinese medical LLaMA-based LLM that implements an entire training pipeline from pre-training to reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF). Additionally, we introduce a Chinese multi-turn medical dialogue dataset of 70,000 authentic doctor-patient dialogues, CMtMedQA, which significantly enhances the model's capability for complex dialogue and proactive inquiry initiation. We define a refined annotation rule and evaluation criteria given the biomedical domain's unique characteristics. Results show that our model outperforms baselines in various capacities and matches the performance of ChatGPT in a few abilities, despite having 50x training data with previous best model and 100x parameters with ChatGPT. RLHF further improves the model's instruction-following ability and safety.We also release our code, datasets and model for further research.
Drug-Target Interaction Prediction with Graph Attention networks
Jul 10, 2021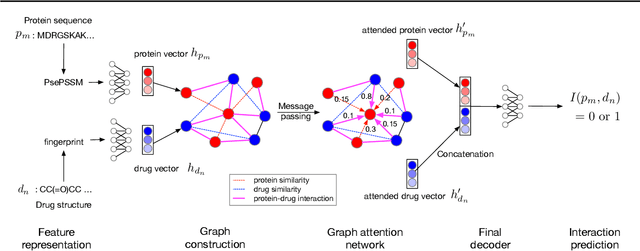
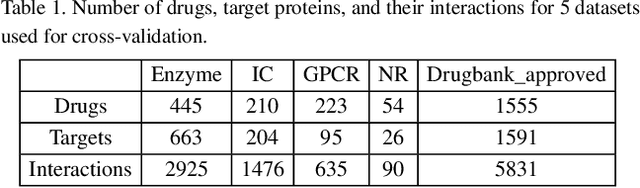
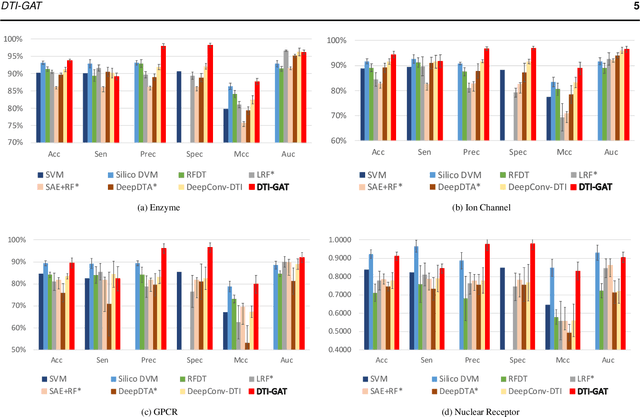
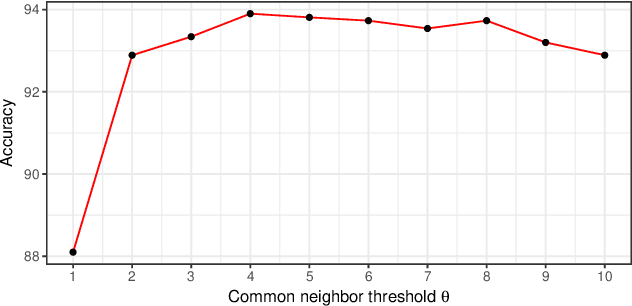
Abstract:Motivation: Predicting Drug-Target Interaction (DTI) is a well-studied topic in bioinformatics due to its relevance in the fields of proteomics and pharmaceutical research. Although many machine learning methods have been successfully applied in this task, few of them aim at leveraging the inherent heterogeneous graph structure in the DTI network to address the challenge. For better learning and interpreting the DTI topological structure and the similarity, it is desirable to have methods specifically for predicting interactions from the graph structure. Results: We present an end-to-end framework, DTI-GAT (Drug-Target Interaction prediction with Graph Attention networks) for DTI predictions. DTI-GAT incorporates a deep neural network architecture that operates on graph-structured data with the attention mechanism, which leverages both the interaction patterns and the features of drug and protein sequences. DTI-GAT facilitates the interpretation of the DTI topological structure by assigning different attention weights to each node with the self-attention mechanism. Experimental evaluations show that DTI-GAT outperforms various state-of-the-art systems on the binary DTI prediction problem. Moreover, the independent study results further demonstrate that our model can be generalized better than other conventional methods. Availability: The source code and all datasets are available at https://github.com/Haiyang-W/DTI-GRAPH
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge