Gregory Ciccarelli
Maximum-Entropy Adversarial Audio Augmentation for Keyword Spotting
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:Data augmentation is a key tool for improving the performance of deep networks, particularly when there is limited labeled data. In some fields, such as computer vision, augmentation methods have been extensively studied; however, for speech and audio data, there are relatively fewer methods developed. Using adversarial learning as a starting point, we develop a simple and effective augmentation strategy based on taking the gradient of the entropy of the outputs with respect to the inputs and then creating new data points by moving in the direction of the gradient to maximize the entropy. We validate its efficacy on several keyword spotting tasks as well as standard audio benchmarks. Our method is straightforward to implement, offering greater computational efficiency than more complex adversarial schemes like GANs. Despite its simplicity, it proves robust and effective, especially when combined with the established SpecAugment technique, leading to enhanced performance.
Longitudinal Acoustic Speech Tracking Following Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Sep 09, 2022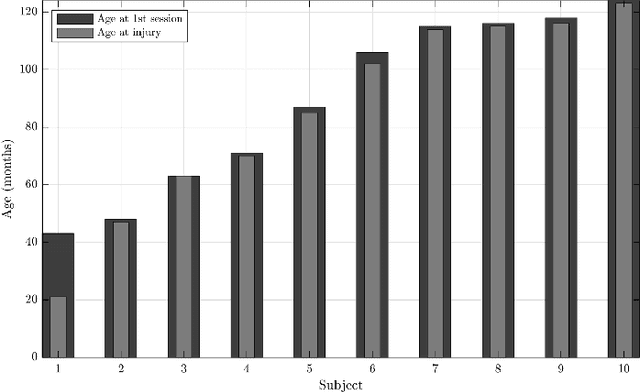
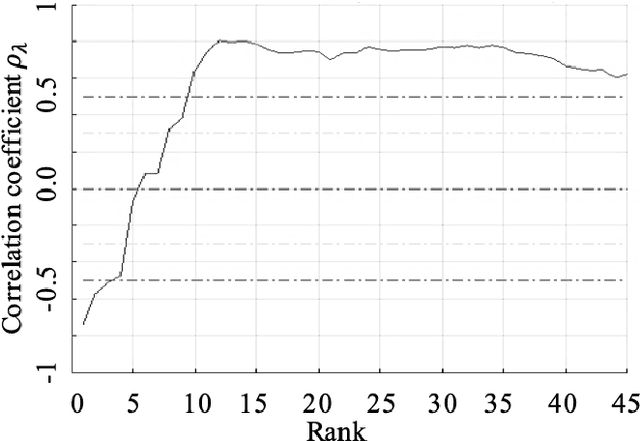
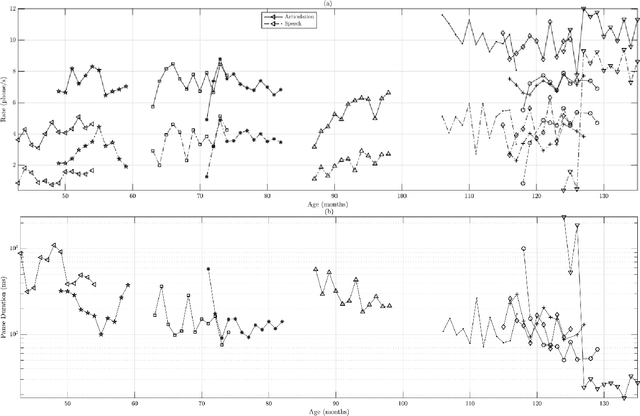
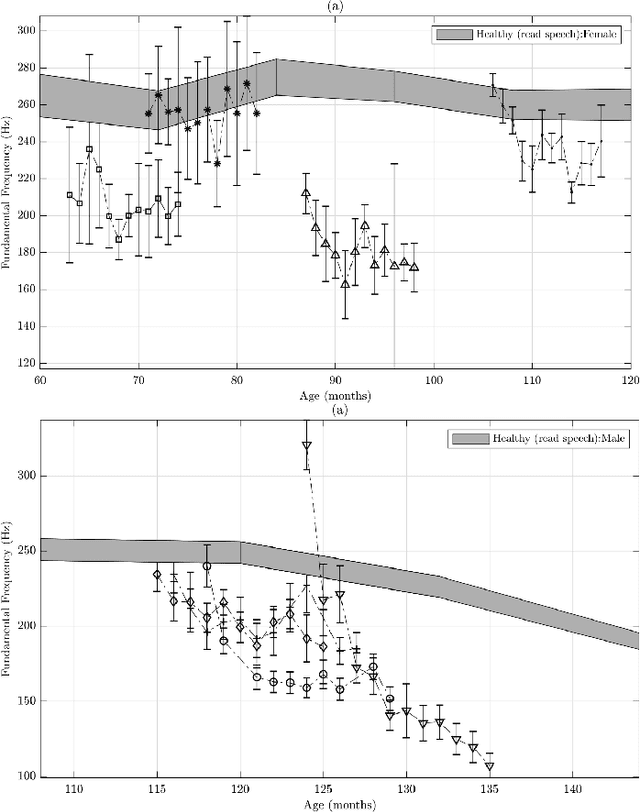
Abstract:Recommendations for common outcome measures following pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI) support the integration of instrumental measurements alongside perceptual assessment in recovery and treatment plans. A comprehensive set of sensitive, robust and non-invasive measurements is therefore essential in assessing variations in speech characteristics over time following pediatric TBI. In this article, we study the changes in the acoustic speech patterns of a pediatric cohort of ten subjects diagnosed with severe TBI. We extract a diverse set of both well-known and novel acoustic features from child speech recorded throughout the year after the child produced intelligible words. These features are analyzed individually and by speech subsystem, within-subject and across the cohort. As a group, older children exhibit highly significant (p<0.01) increases in pitch variation and phoneme diversity, shortened pause length, and steadying articulation rate variability. Younger children exhibit similar steadied rate variability alongside an increase in formant-based articulation complexity. Correlation analysis of the feature set with age and comparisons to normative developmental data confirm that age at injury plays a significant role in framing the recovery trajectory. Nearly all speech features significantly change (p<0.05) for the cohort as a whole, confirming that acoustic measures supplementing perceptual assessment are needed to identify efficacious treatment targets for speech therapy following TBI.
Challenges and Opportunities in Multi-device Speech Processing
Jun 27, 2022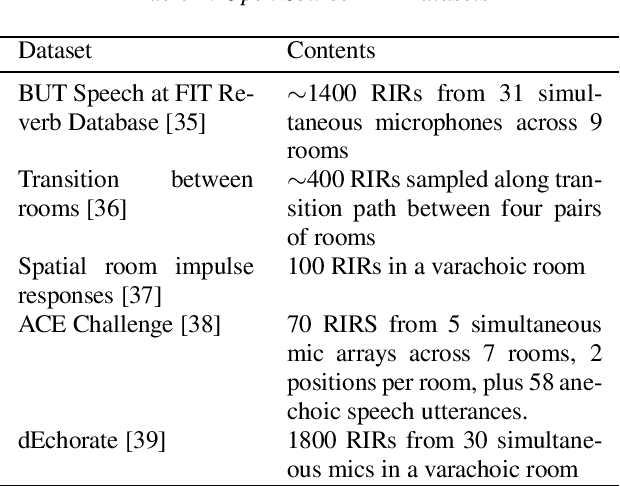
Abstract:We review current solutions and technical challenges for automatic speech recognition, keyword spotting, device arbitration, speech enhancement, and source localization in multidevice home environments to provide context for the INTERSPEECH 2022 special session, "Challenges and opportunities for signal processing and machine learning for multiple smart devices". We also identify the datasets needed to support these research areas. Based on the review and our research experience in the multi-device domain, we conclude with an outlook on the future evolution
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge