James R. Williamson
Estimating Visceral Adiposity from Wrist-Worn Accelerometry
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) is a key marker of both metabolic health and habitual physical activity (PA). Excess VAT is highly correlated with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. The mechanistic basis for this pathophysiology relates to overloading the liver with fatty acids. VAT is also a highly labile fat depot, with increased turnover stimulated by catecholamines during exercise. VAT can be measured with sophisticated imaging technologies, but can also be inferred directly from PA. We tested this relationship using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 2011-2014, for individuals aged 20-60 years with 7 days of accelerometry data (n=2,456 men; 2,427 women) [1]. Two approaches were used for estimating VAT from activity. The first used engineered features based on movements during gait and sleep, and then ridge regression to map summary statistics of these features into a VAT estimate. The second approach used deep neural networks trained on 24 hours of continuous accelerometry. A foundation model first mapped each 10s frame into a high-dimensional feature vector. A transformer model then mapped each day's feature vector time series into a VAT estimate, which were averaged over multiple days. For both approaches, the most accurate estimates were obtained with the addition of covariate information about subject demographics and body measurements. The best performance was obtained by combining the two approaches, resulting in VAT estimates with correlations of r=0.86. These findings demonstrate a strong relationship between PA and VAT and, by extension, between PA and metabolic health risks.
Wearable Tracking of Eye and Body Movements During Breaching Training: Towards Real-Time Blast Injury Monitoring
May 14, 2025Abstract:Repeated exposure to blast overpressure in occupational settings has been associated with changes in cognitive and psychological health, as well as deficits in neurosensory subsystems. In this work, we describe a wearable system to simultaneously monitor physiology and blast exposure levels and demonstrate how this system can identify individualized exposure levels corresponding to acute physiological response to blast exposure. Machine learning was used to develop a dose-response model that fused multiple physiological measures (electrooculuography, gait, and balance) into a single risk score by predicting the level of blast exposure on held-out subjects (Fused model, R = 0.60). We found that blast events with peak pressure levels as low as 0.25 psi could be related to physiological changes and hence may contribute to blast injury. We also identified an individual subject with deteriorating reaction time scores that consistently showed a rapid and anomalous change in physiology-based risk scores after exposure to low-level blast events. Our results suggest that the wearable approach to blast monitoring is viable in weapons training environments as a complement to more direct but sparsely administered brain health assessments, potentially viable in austere environments, and that fusing multiple physiological signals can improve sensitivity.
Longitudinal Acoustic Speech Tracking Following Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Sep 09, 2022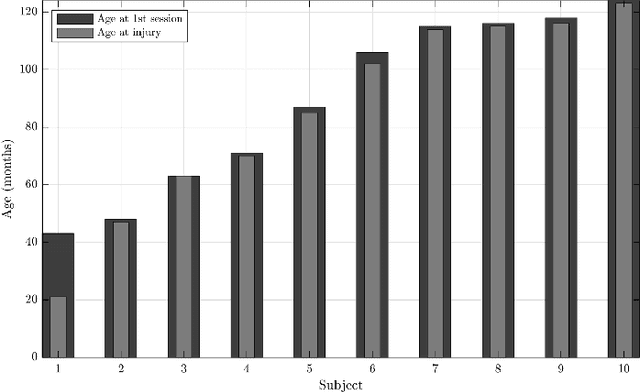
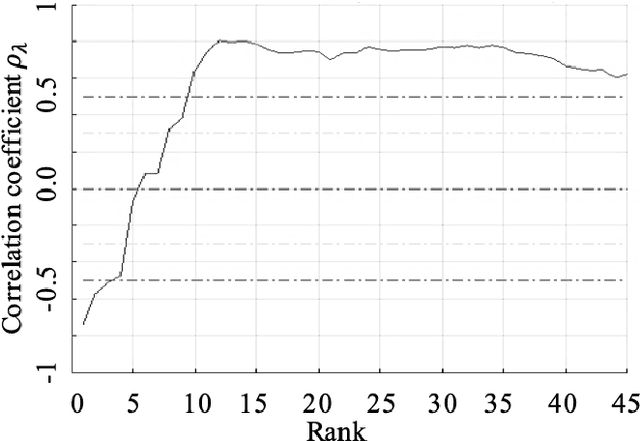
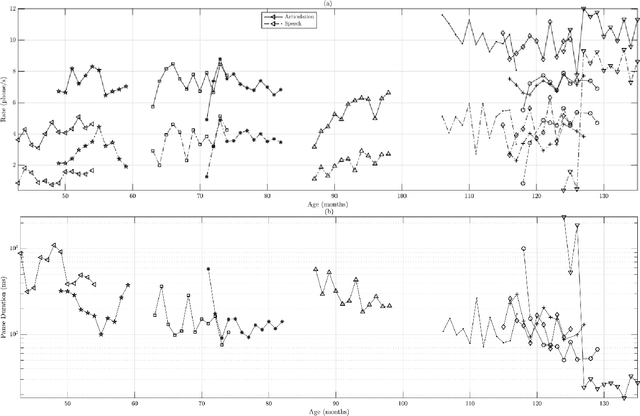
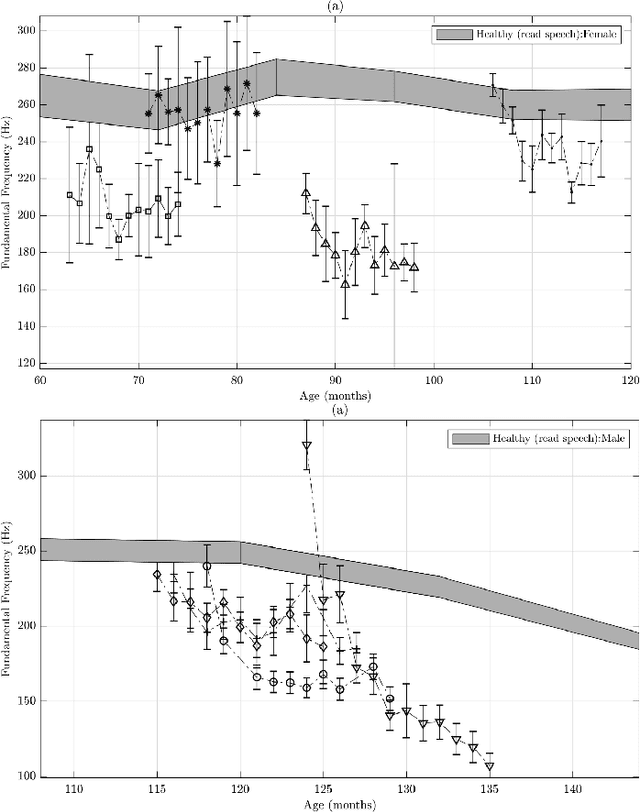
Abstract:Recommendations for common outcome measures following pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI) support the integration of instrumental measurements alongside perceptual assessment in recovery and treatment plans. A comprehensive set of sensitive, robust and non-invasive measurements is therefore essential in assessing variations in speech characteristics over time following pediatric TBI. In this article, we study the changes in the acoustic speech patterns of a pediatric cohort of ten subjects diagnosed with severe TBI. We extract a diverse set of both well-known and novel acoustic features from child speech recorded throughout the year after the child produced intelligible words. These features are analyzed individually and by speech subsystem, within-subject and across the cohort. As a group, older children exhibit highly significant (p<0.01) increases in pitch variation and phoneme diversity, shortened pause length, and steadying articulation rate variability. Younger children exhibit similar steadied rate variability alongside an increase in formant-based articulation complexity. Correlation analysis of the feature set with age and comparisons to normative developmental data confirm that age at injury plays a significant role in framing the recovery trajectory. Nearly all speech features significantly change (p<0.05) for the cohort as a whole, confirming that acoustic measures supplementing perceptual assessment are needed to identify efficacious treatment targets for speech therapy following TBI.
Assessing Functional Neural Connectivity as an Indicator of Cognitive Performance
Jul 29, 2016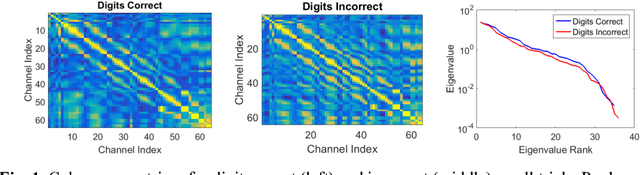
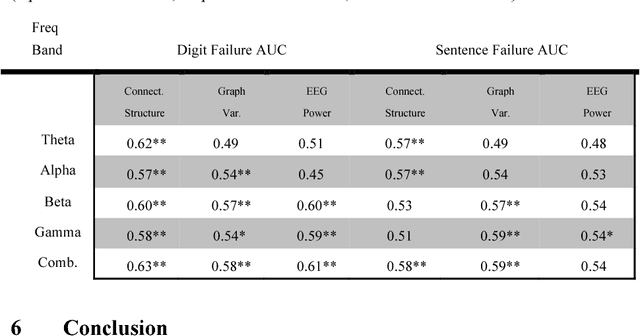
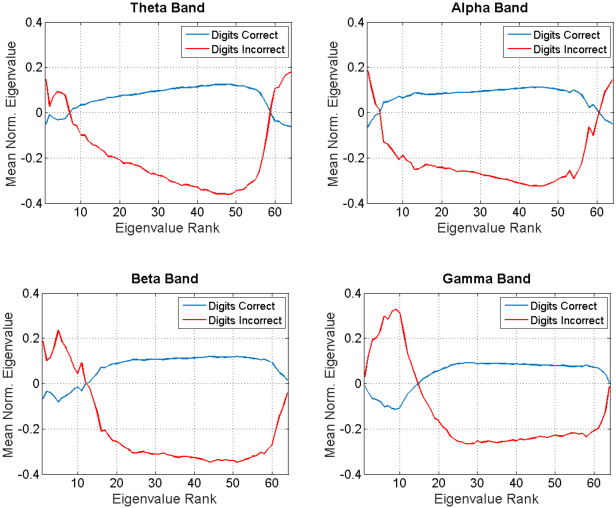
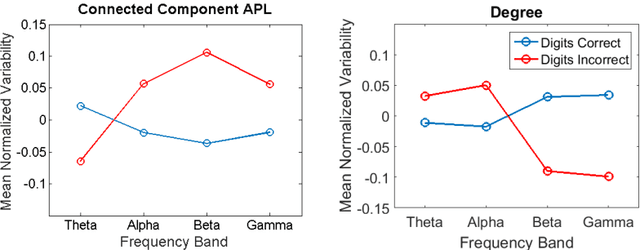
Abstract:Studies in recent years have demonstrated that neural organization and structure impact an individual's ability to perform a given task. Specifically, individuals with greater neural efficiency have been shown to outperform those with less organized functional structure. In this work, we compare the predictive ability of properties of neural connectivity on a working memory task. We provide two novel approaches for characterizing functional network connectivity from electroencephalography (EEG), and compare these features to the average power across frequency bands in EEG channels. Our first novel approach represents functional connectivity structure through the distribution of eigenvalues making up channel coherence matrices in multiple frequency bands. Our second approach creates a connectivity network at each frequency band, and assesses variability in average path lengths of connected components and degree across the network. Failures in digit and sentence recall on single trials are detected using a Gaussian classifier for each feature set, at each frequency band. The classifier results are then fused across frequency bands, with the resulting detection performance summarized using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) statistic. Fused AUC results of 0.63/0.58/0.61 for digit recall failure and 0.58/0.59/0.54 for sentence recall failure are obtained from the connectivity structure, graph variability, and channel power features respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge