Gloria Haro
Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain
ShinyNeRF: Digitizing Anisotropic Appearance in Neural Radiance Fields
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in digitization technologies have transformed the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage. In this vein, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a leading technology for 3D digitization, delivering representations with exceptional realism. However, existing methods struggle to accurately model anisotropic specular surfaces, typically observed, for example, on brushed metals. In this work, we introduce ShinyNeRF, a novel framework capable of handling both isotropic and anisotropic reflections. Our method is capable of jointly estimating surface normals, tangents, specular concentration, and anisotropy magnitudes of an Anisotropic Spherical Gaussian (ASG) distribution, by learning an approximation of the outgoing radiance as an encoded mixture of isotropic von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distributions. Experimental results show that ShinyNeRF not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on digitizing anisotropic specular reflections, but also offers plausible physical interpretations and editing of material properties compared to existing methods.
Learning from Silence and Noise for Visual Sound Source Localization
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Visual sound source localization is a fundamental perception task that aims to detect the location of sounding sources in a video given its audio. Despite recent progress, we identify two shortcomings in current methods: 1) most approaches perform poorly in cases with low audio-visual semantic correspondence such as silence, noise, and offscreen sounds, i.e. in the presence of negative audio; and 2) most prior evaluations are limited to positive cases, where both datasets and metrics convey scenarios with a single visible sound source in the scene. To address this, we introduce three key contributions. First, we propose a new training strategy that incorporates silence and noise, which improves performance in positive cases, while being more robust against negative sounds. Our resulting self-supervised model, SSL-SaN, achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to other self-supervised models, both in sound localization and cross-modal retrieval. Second, we propose a new metric that quantifies the trade-off between alignment and separability of auditory and visual features across positive and negative audio-visual pairs. Third, we present IS3+, an extended and improved version of the IS3 synthetic dataset with negative audio. Our data, metrics and code are available on the https://xavijuanola.github.io/SSL-SaN/.
Visual Motif Identification: Elaboration of a Curated Comparative Dataset and Classification Methods
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:In cinema, visual motifs are recurrent iconographic compositions that carry artistic or aesthetic significance. Their use throughout the history of visual arts and media is interesting to researchers and filmmakers alike. Our goal in this work is to recognise and classify these motifs by proposing a new machine learning model that uses a custom dataset to that end. We show how features extracted from a CLIP model can be leveraged by using a shallow network and an appropriate loss to classify images into 20 different motifs, with surprisingly good results: an $F_1$-score of 0.91 on our test set. We also present several ablation studies justifying the input features, architecture and hyperparameters used.
A Critical Assessment of Visual Sound Source Localization Models Including Negative Audio
Oct 01, 2024Abstract:The task of Visual Sound Source Localization (VSSL) involves identifying the location of sound sources in visual scenes, integrating audio-visual data for enhanced scene understanding. Despite advancements in state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, we observe three critical flaws: i) The evaluation of the models is mainly focused in sounds produced by objects that are visible in the image, ii) The evaluation often assumes a prior knowledge of the size of the sounding object, and iii) No universal threshold for localization in real-world scenarios is established, as previous approaches only consider positive examples without accounting for both positive and negative cases. In this paper, we introduce a novel test set and metrics designed to complete the current standard evaluation of VSSL models by testing them in scenarios where none of the objects in the image corresponds to the audio input, i.e. a negative audio. We consider three types of negative audio: silence, noise and offscreen. Our analysis reveals that numerous SOTA models fail to appropriately adjust their predictions based on audio input, suggesting that these models may not be leveraging audio information as intended. Additionally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the range of maximum values in the estimated audio-visual similarity maps, in both positive and negative audio cases, and show that most of the models are not discriminative enough, making them unfit to choose a universal threshold appropriate to perform sound localization without any a priori information of the sounding object, that is, object size and visibility.
Speech inpainting: Context-based speech synthesis guided by video
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:Audio and visual modalities are inherently connected in speech signals: lip movements and facial expressions are correlated with speech sounds. This motivates studies that incorporate the visual modality to enhance an acoustic speech signal or even restore missing audio information. Specifically, this paper focuses on the problem of audio-visual speech inpainting, which is the task of synthesizing the speech in a corrupted audio segment in a way that it is consistent with the corresponding visual content and the uncorrupted audio context. We present an audio-visual transformer-based deep learning model that leverages visual cues that provide information about the content of the corrupted audio. It outperforms the previous state-of-the-art audio-visual model and audio-only baselines. We also show how visual features extracted with AV-HuBERT, a large audio-visual transformer for speech recognition, are suitable for synthesizing speech.
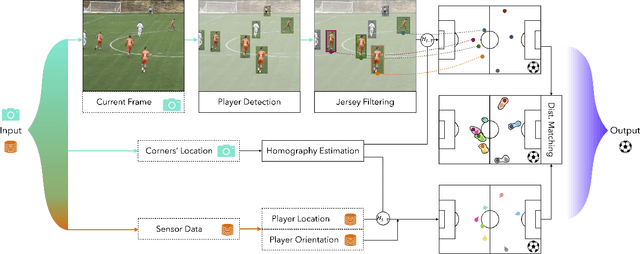
A Graph-Based Method for Soccer Action Spotting Using Unsupervised Player Classification
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Action spotting in soccer videos is the task of identifying the specific time when a certain key action of the game occurs. Lately, it has received a large amount of attention and powerful methods have been introduced. Action spotting involves understanding the dynamics of the game, the complexity of events, and the variation of video sequences. Most approaches have focused on the latter, given that their models exploit the global visual features of the sequences. In this work, we focus on the former by (a) identifying and representing the players, referees, and goalkeepers as nodes in a graph, and by (b) modeling their temporal interactions as sequences of graphs. For the player identification, or player classification task, we obtain an accuracy of 97.72% in our annotated benchmark. For the action spotting task, our method obtains an overall performance of 57.83% average-mAP by combining it with other audiovisual modalities. This performance surpasses similar graph-based methods and has competitive results with heavy computing methods. Code and data are available at https://github.com/IPCV/soccer_action_spotting.
VocaLiST: An Audio-Visual Synchronisation Model for Lips and Voices
Apr 05, 2022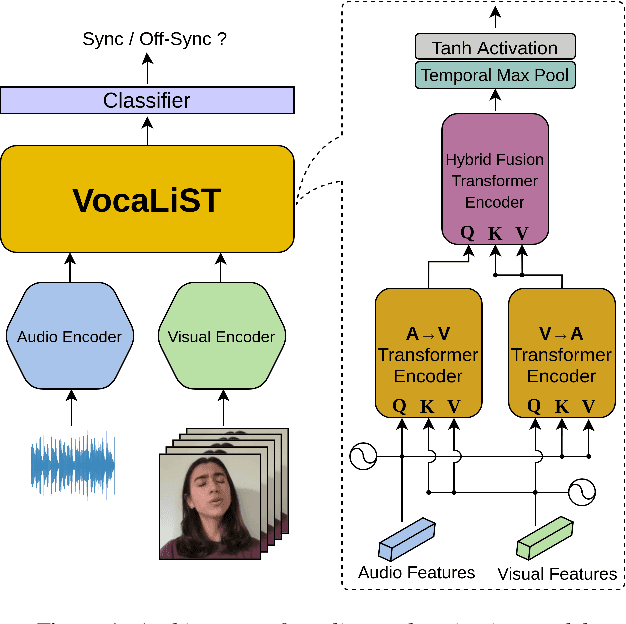

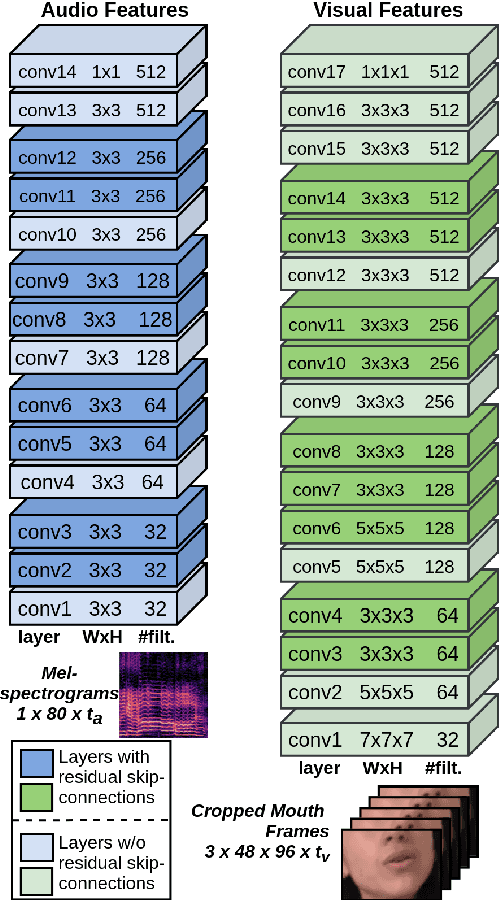

Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of lip-voice synchronisation in videos containing human face and voice. Our approach is based on determining if the lips motion and the voice in a video are synchronised or not, depending on their audio-visual correspondence score. We propose an audio-visual cross-modal transformer-based model that outperforms several baseline models in the audio-visual synchronisation task on the standard lip-reading speech benchmark dataset LRS2. While the existing methods focus mainly on the lip synchronisation in speech videos, we also consider the special case of singing voice. Singing voice is a more challenging use case for synchronisation due to sustained vowel sounds. We also investigate the relevance of lip synchronisation models trained on speech datasets in the context of singing voice. Finally, we use the frozen visual features learned by our lip synchronisation model in the singing voice separation task to outperform a baseline audio-visual model which was trained end-to-end. The demos, source code, and the pre-trained model will be made available on https://ipcv.github.io/VocaLiST/
VoViT: Low Latency Graph-based Audio-Visual Voice Separation Transformer
Mar 08, 2022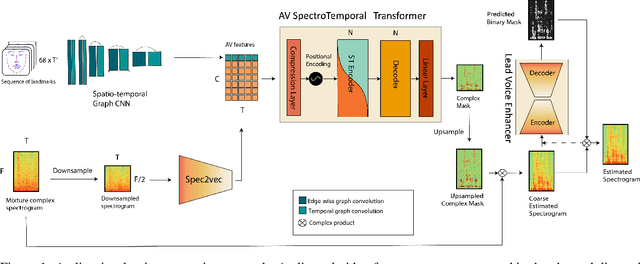
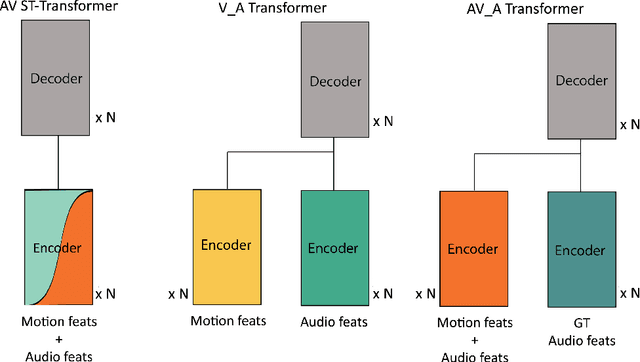
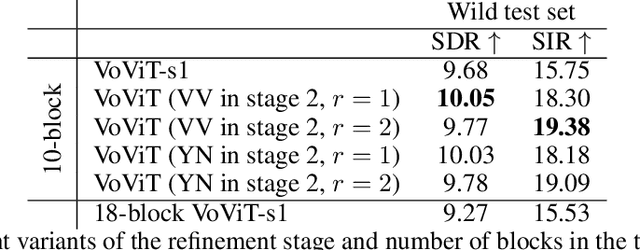
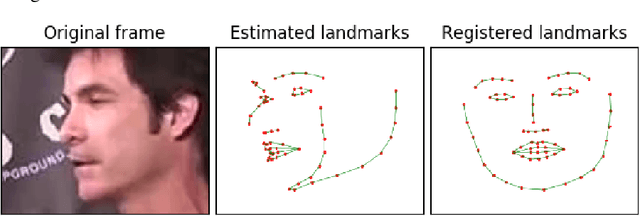
Abstract:This paper presents an audio-visual approach for voice separation which outperforms state-of-the-art methods at a low latency in two scenarios: speech and singing voice. The model is based on a two-stage network. Motion cues are obtained with a lightweight graph convolutional network that processes face landmarks. Then, both audio and motion features are fed to an audio-visual transformer which produces a fairly good estimation of the isolated target source. In a second stage, the predominant voice is enhanced with an audio-only network. We present different ablation studies and comparison to state-of-the-art methods. Finally, we explore the transferability of models trained for speech separation in the task of singing voice separation. The demos, code, and weights will be made publicly available at https://ipcv.github.io/VoViT/
Learning Football Body-Orientation as a Matter of Classification
Jun 01, 2021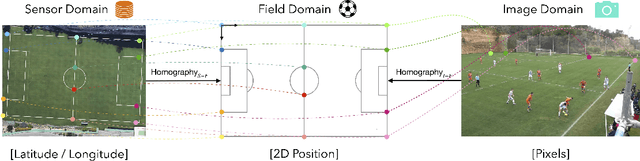
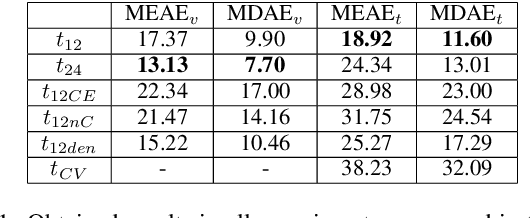
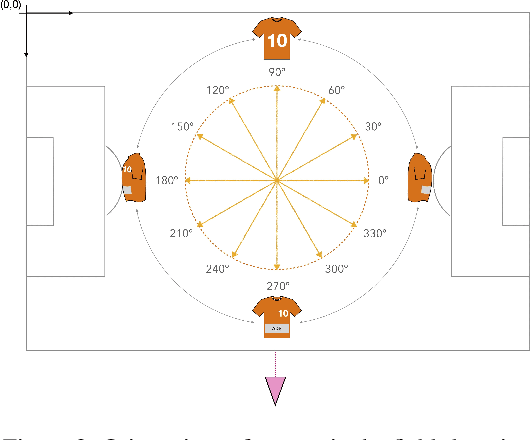
Abstract:Orientation is a crucial skill for football players that becomes a differential factor in a large set of events, especially the ones involving passes. However, existing orientation estimation methods, which are based on computer-vision techniques, still have a lot of room for improvement. To the best of our knowledge, this article presents the first deep learning model for estimating orientation directly from video footage. By approaching this challenge as a classification problem where classes correspond to orientation bins, and by introducing a cyclic loss function, a well-known convolutional network is refined to provide player orientation data. The model is trained by using ground-truth orientation data obtained from wearable EPTS devices, which are individually compensated with respect to the perceived orientation in the current frame. The obtained results outperform previous methods; in particular, the absolute median error is less than 12 degrees per player. An ablation study is included in order to show the potential generalization to any kind of football video footage.
A cappella: Audio-visual Singing Voice Separation
Apr 20, 2021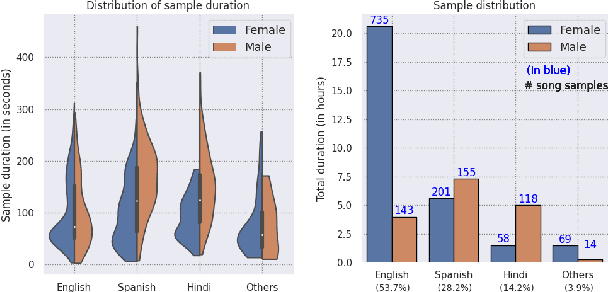

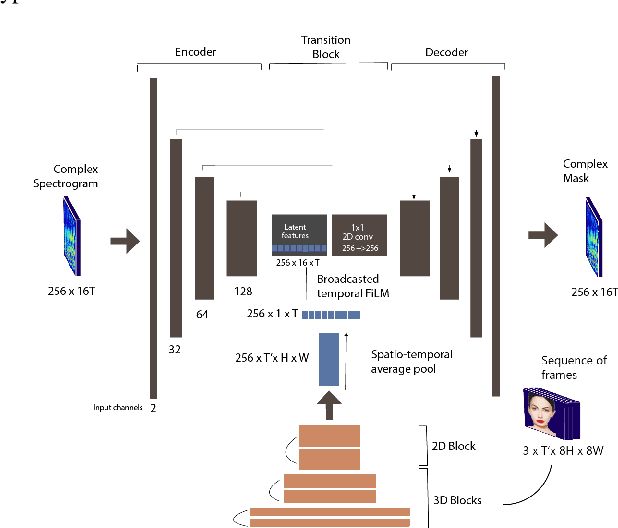
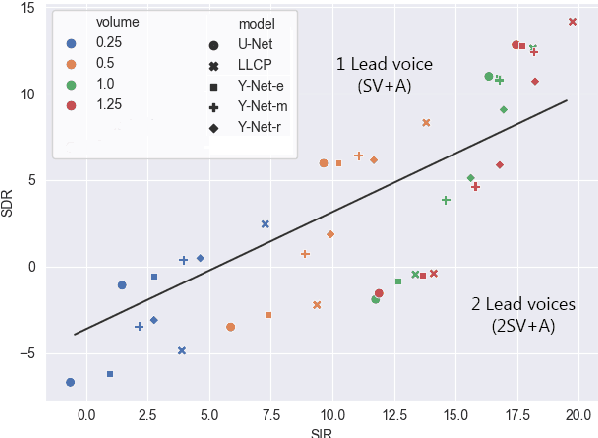
Abstract:Music source separation can be interpreted as the estimation of the constituent music sources that a music clip is composed of. In this work, we explore the single-channel singing voice separation problem from a multimodal perspective, by jointly learning from audio and visual modalities. To do so, we present Acappella, a dataset spanning around 46 hours of a cappella solo singing videos sourced from YouTube. We propose Y-Net, an audio-visual convolutional neural network which achieves state-of-the-art singing voice separation results on the Acappella dataset and compare it against its audio-only counterpart, U-Net, and a state-of-the-art audio-visual speech separation model. Singing voice separation can be particularly challenging when the audio mixture also comprises of other accompaniment voices and background sounds along with the target voice of interest. We demonstrate that our model can outperform the baseline models in the singing voice separation task in such challenging scenarios. The code, the pre-trained models and the dataset will be publicly available at https://ipcv.github.io/Acappella/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge