Giorgos Sfikas
REGLUE Your Latents with Global and Local Semantics for Entangled Diffusion
Dec 18, 2025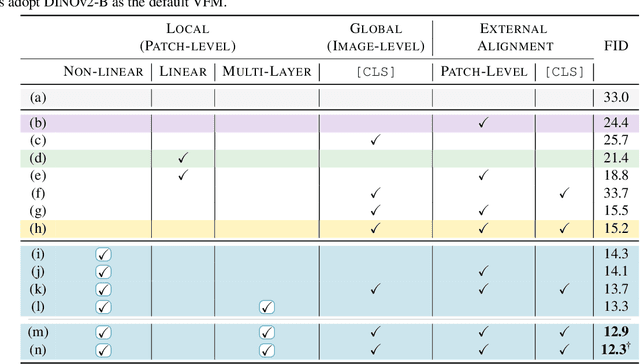
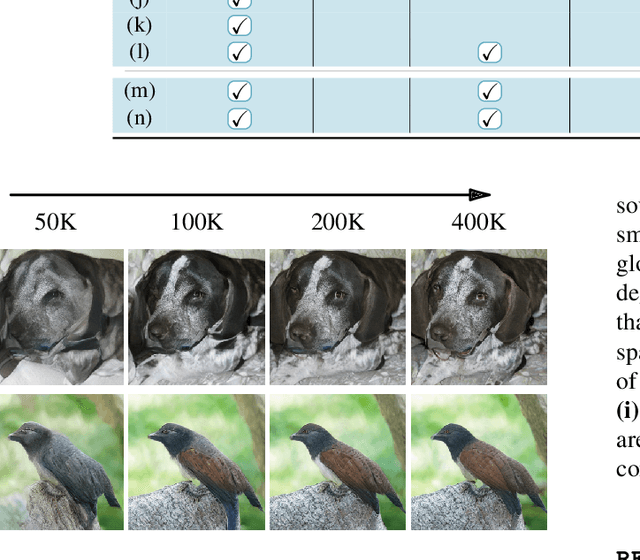
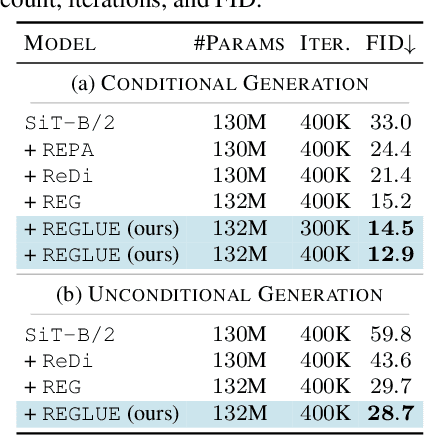
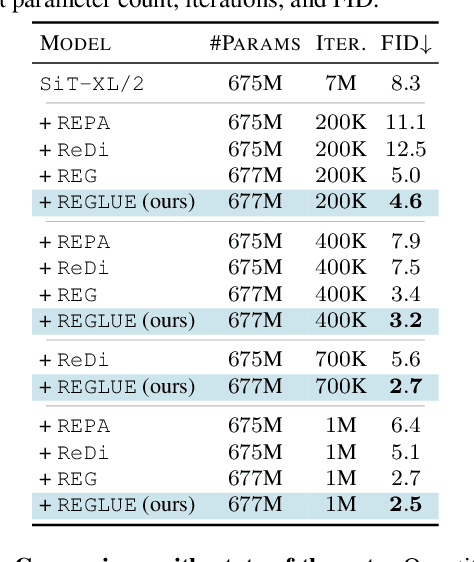
Abstract:Latent diffusion models (LDMs) achieve state-of-the-art image synthesis, yet their reconstruction-style denoising objective provides only indirect semantic supervision: high-level semantics emerge slowly, requiring longer training and limiting sample quality. Recent works inject semantics from Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) either externally via representation alignment or internally by jointly modeling only a narrow slice of VFM features inside the diffusion process, under-utilizing the rich, nonlinear, multi-layer spatial semantics available. We introduce REGLUE (Representation Entanglement with Global-Local Unified Encoding), a unified latent diffusion framework that jointly models (i) VAE image latents, (ii) compact local (patch-level) VFM semantics, and (iii) a global (image-level) [CLS] token within a single SiT backbone. A lightweight convolutional semantic compressor nonlinearly aggregates multi-layer VFM features into a low-dimensional, spatially structured representation, which is entangled with the VAE latents in the diffusion process. An external alignment loss further regularizes internal representations toward frozen VFM targets. On ImageNet 256x256, REGLUE consistently improves FID and accelerates convergence over SiT-B/2 and SiT-XL/2 baselines, as well as over REPA, ReDi, and REG. Extensive experiments show that (a) spatial VFM semantics are crucial, (b) non-linear compression is key to unlocking their full benefit, and (c) global tokens and external alignment act as complementary, lightweight enhancements within our global-local-latent joint modeling framework. The code is available at https://github.com/giorgospets/reglue .
Designing Practical Models for Isolated Word Visual Speech Recognition
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Visual speech recognition (VSR) systems decode spoken words from an input sequence using only the video data. Practical applications of such systems include medical assistance as well as human-machine interactions. A VSR system is typically employed in a complementary role in cases where the audio is corrupt or not available. In order to accurately predict the spoken words, these architectures often rely on deep neural networks in order to extract meaningful representations from the input sequence. While deep architectures achieve impressive recognition performance, relying on such models incurs significant computation costs which translates into increased resource demands in terms of hardware requirements and results in limited applicability in real-world scenarios where resources might be constrained. This factor prevents wider adoption and deployment of speech recognition systems in more practical applications. In this work, we aim to alleviate this issue by developing architectures for VSR that have low hardware costs. Following the standard two-network design paradigm, where one network handles visual feature extraction and another one utilizes the extracted features to classify the entire sequence, we develop lightweight end-to-end architectures by first benchmarking efficient models from the image classification literature, and then adopting lightweight block designs in a temporal convolution network backbone. We create several unified models with low resource requirements but strong recognition performance. Experiments on the largest public database for English words demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of our developed models. Code and trained models will be made publicly available.
Dual Orthogonal Guidance for Robust Diffusion-based Handwritten Text Generation
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-based Handwritten Text Generation (HTG) approaches achieve impressive results on frequent, in-vocabulary words observed at training time and on regular styles. However, they are prone to memorizing training samples and often struggle with style variability and generation clarity. In particular, standard diffusion models tend to produce artifacts or distortions that negatively affect the readability of the generated text, especially when the style is hard to produce. To tackle these issues, we propose a novel sampling guidance strategy, Dual Orthogonal Guidance (DOG), that leverages an orthogonal projection of a negatively perturbed prompt onto the original positive prompt. This approach helps steer the generation away from artifacts while maintaining the intended content, and encourages more diverse, yet plausible, outputs. Unlike standard Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG), which relies on unconditional predictions and produces noise at high guidance scales, DOG introduces a more stable, disentangled direction in the latent space. To control the strength of the guidance across the denoising process, we apply a triangular schedule: weak at the start and end of denoising, when the process is most sensitive, and strongest in the middle steps. Experimental results on the state-of-the-art DiffusionPen and One-DM demonstrate that DOG improves both content clarity and style variability, even for out-of-vocabulary words and challenging writing styles.
Quo Vadis Handwritten Text Generation for Handwritten Text Recognition?
Aug 13, 2025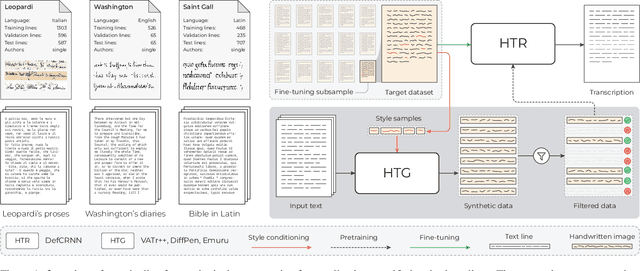
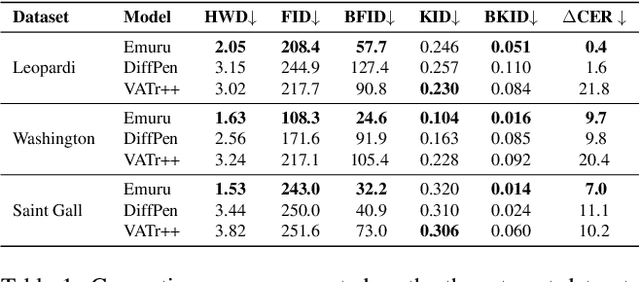

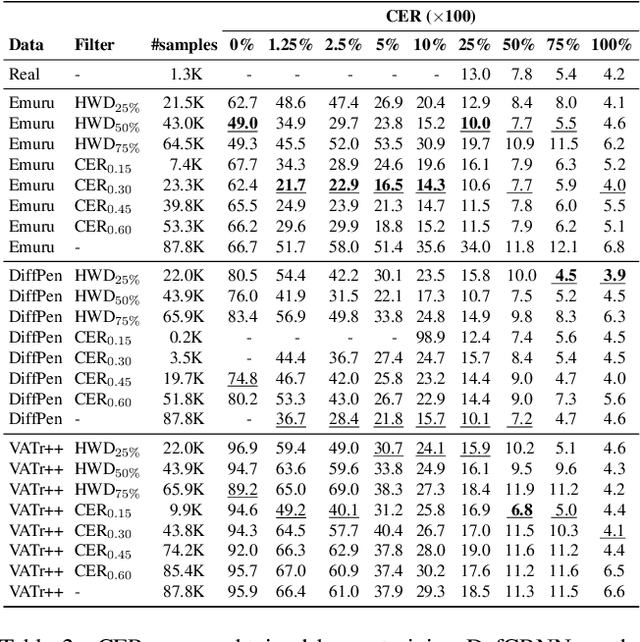
Abstract:The digitization of historical manuscripts presents significant challenges for Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) systems, particularly when dealing with small, author-specific collections that diverge from the training data distributions. Handwritten Text Generation (HTG) techniques, which generate synthetic data tailored to specific handwriting styles, offer a promising solution to address these challenges. However, the effectiveness of various HTG models in enhancing HTR performance, especially in low-resource transcription settings, has not been thoroughly evaluated. In this work, we systematically compare three state-of-the-art styled HTG models (representing the generative adversarial, diffusion, and autoregressive paradigms for HTG) to assess their impact on HTR fine-tuning. We analyze how visual and linguistic characteristics of synthetic data influence fine-tuning outcomes and provide quantitative guidelines for selecting the most effective HTG model. The results of our analysis provide insights into the current capabilities of HTG methods and highlight key areas for further improvement in their application to low-resource HTR.
Lightweight Operations for Visual Speech Recognition
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Visual speech recognition (VSR), which decodes spoken words from video data, offers significant benefits, particularly when audio is unavailable. However, the high dimensionality of video data leads to prohibitive computational costs that demand powerful hardware, limiting VSR deployment on resource-constrained devices. This work addresses this limitation by developing lightweight VSR architectures. Leveraging efficient operation design paradigms, we create compact yet powerful models with reduced resource requirements and minimal accuracy loss. We train and evaluate our models on a large-scale public dataset for recognition of words from video sequences, demonstrating their effectiveness for practical applications. We also conduct an extensive array of ablative experiments to thoroughly analyze the size and complexity of each model. Code and trained models will be made publicly available.
DiffusionPen: Towards Controlling the Style of Handwritten Text Generation
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:Handwritten Text Generation (HTG) conditioned on text and style is a challenging task due to the variability of inter-user characteristics and the unlimited combinations of characters that form new words unseen during training. Diffusion Models have recently shown promising results in HTG but still remain under-explored. We present DiffusionPen (DiffPen), a 5-shot style handwritten text generation approach based on Latent Diffusion Models. By utilizing a hybrid style extractor that combines metric learning and classification, our approach manages to capture both textual and stylistic characteristics of seen and unseen words and styles, generating realistic handwritten samples. Moreover, we explore several variation strategies of the data with multi-style mixtures and noisy embeddings, enhancing the robustness and diversity of the generated data. Extensive experiments using IAM offline handwriting database show that our method outperforms existing methods qualitatively and quantitatively, and its additional generated data can improve the performance of Handwriting Text Recognition (HTR) systems. The code is available at: https://github.com/koninik/DiffusionPen.
Rethinking HTG Evaluation: Bridging Generation and Recognition
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:The evaluation of generative models for natural image tasks has been extensively studied. Similar protocols and metrics are used in cases with unique particularities, such as Handwriting Generation, even if they might not be completely appropriate. In this work, we introduce three measures tailored for HTG evaluation, $ \text{HTG}_{\text{HTR}} $, $ \text{HTG}_{\text{style}} $, and $ \text{HTG}_{\text{OOV}} $, and argue that they are more expedient to evaluate the quality of generated handwritten images. The metrics rely on the recognition error/accuracy of Handwriting Text Recognition and Writer Identification models and emphasize writing style, textual content, and diversity as the main aspects that adhere to the content of handwritten images. We conduct comprehensive experiments on the IAM handwriting database, showcasing that widely used metrics such as FID fail to properly quantify the diversity and the practical utility of generated handwriting samples. Our findings show that our metrics are richer in information and underscore the necessity of standardized evaluation protocols in HTG. The proposed metrics provide a more robust and informative protocol for assessing HTG quality, contributing to improved performance in HTR. Code for the evaluation protocol is available at: https://github.com/koninik/HTG_evaluation.
Best Practices for a Handwritten Text Recognition System
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:Handwritten text recognition has been developed rapidly in the recent years, following the rise of deep learning and its applications. Though deep learning methods provide notable boost in performance concerning text recognition, non-trivial deviation in performance can be detected even when small pre-processing or architectural/optimization elements are changed. This work follows a ``best practice'' rationale; highlight simple yet effective empirical practices that can further help training and provide well-performing handwritten text recognition systems. Specifically, we considered three basic aspects of a deep HTR system and we proposed simple yet effective solutions: 1) retain the aspect ratio of the images in the preprocessing step, 2) use max-pooling for converting the 3D feature map of CNN output into a sequence of features and 3) assist the training procedure via an additional CTC loss which acts as a shortcut on the max-pooled sequential features. Using these proposed simple modifications, one can attain close to state-of-the-art results, while considering a basic convolutional-recurrent (CNN+LSTM) architecture, for both IAM and RIMES datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/georgeretsi/HTR-best-practices/.
Keyword Spotting Simplified: A Segmentation-Free Approach using Character Counting and CTC re-scoring
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in segmentation-free keyword spotting treat this problem w.r.t. an object detection paradigm and borrow from state-of-the-art detection systems to simultaneously propose a word bounding box proposal mechanism and compute a corresponding representation. Contrary to the norm of such methods that rely on complex and large DNN models, we propose a novel segmentation-free system that efficiently scans a document image to find rectangular areas that include the query information. The underlying model is simple and compact, predicting character occurrences over rectangular areas through an implicitly learned scale map, trained on word-level annotated images. The proposed document scanning is then performed using this character counting in a cost-effective manner via integral images and binary search. Finally, the retrieval similarity by character counting is refined by a pyramidal representation and a CTC-based re-scoring algorithm, fully utilizing the trained CNN model. Experimental validation on two widely-used datasets shows that our method achieves state-of-the-art results outperforming the more complex alternatives, despite the simplicity of the underlying model.
On the Matrix Form of the Quaternion Fourier Transform and Quaternion Convolution
Jul 04, 2023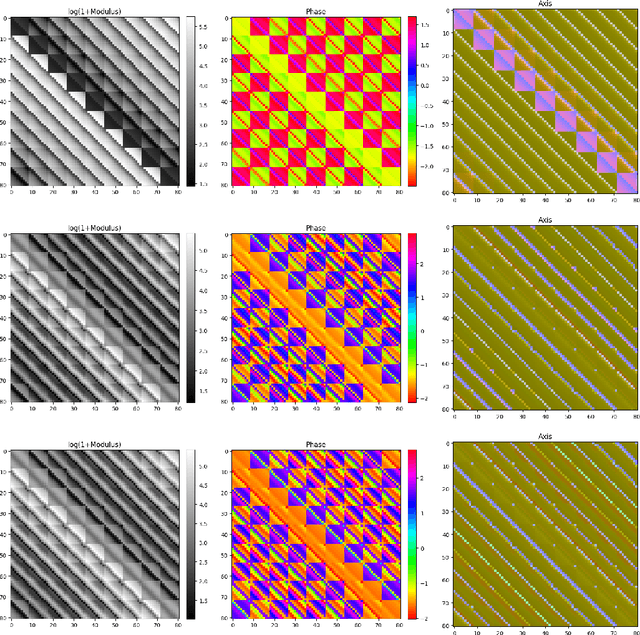
Abstract:We study matrix forms of quaternionic versions of the Fourier Transform and Convolution operations. Quaternions offer a powerful representation unit, however they are related to difficulties in their use that stem foremost from non-commutativity of quaternion multiplication, and due to that $\mu^2 = -1$ posseses infinite solutions in the quaternion domain. Handling of quaternionic matrices is consequently complicated in several aspects (definition of eigenstructure, determinant, etc.). Our research findings clarify the relation of the Quaternion Fourier Transform matrix to the standard (complex) Discrete Fourier Transform matrix, and the extend on which well-known complex-domain theorems extend to quaternions. We focus especially on the relation of Quaternion Fourier Transform matrices to Quaternion Circulant matrices (representing quaternionic convolution), and the eigenstructure of the latter. A proof-of-concept application that makes direct use of our theoretical results is presented, where we produce a method to bound the spectral norm of a Quaternionic Convolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge