Gary W. Delaney
Emergence of Computational Structure in a Neural Network Physics Simulator
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Neural networks often have identifiable computational structures - components of the network which perform an interpretable algorithm or task - but the mechanisms by which these emerge and the best methods for detecting these structures are not well understood. In this paper we investigate the emergence of computational structure in a transformer-like model trained to simulate the physics of a particle system, where the transformer's attention mechanism is used to transfer information between particles. We show that (a) structures emerge in the attention heads of the transformer which learn to detect particle collisions, (b) the emergence of these structures is associated to degenerate geometry in the loss landscape, and (c) the dynamics of this emergence follows a power law. This suggests that these components are governed by a degenerate "effective potential". These results have implications for the convergence time of computational structure within neural networks and suggest that the emergence of computational structure can be detected by studying the dynamics of network components.
Active Vibration Fluidization for Granular Jamming Grippers
Dec 13, 2022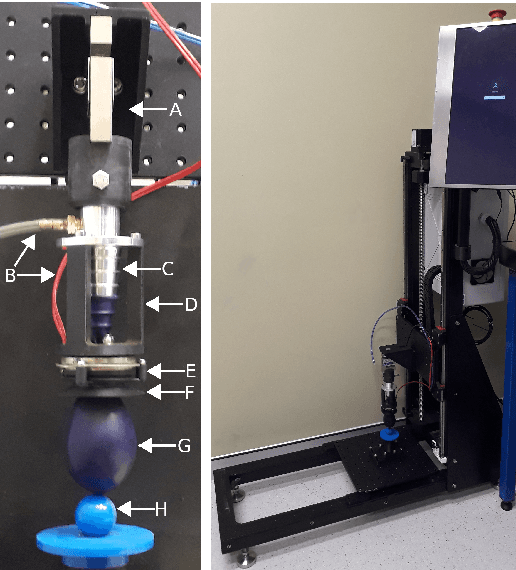
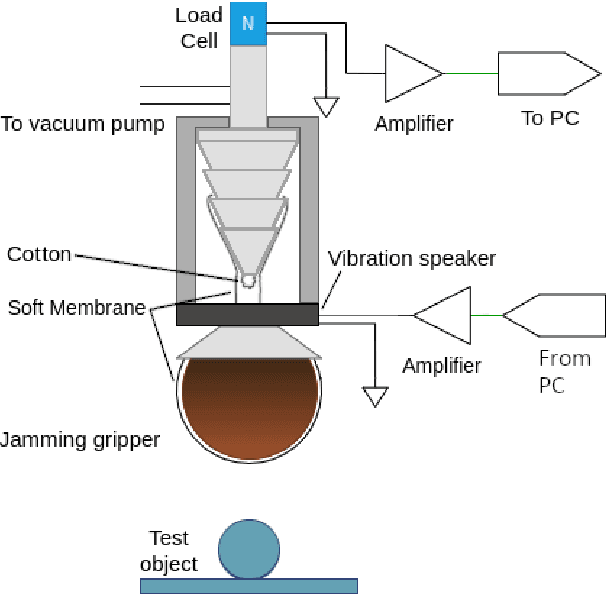
Abstract:Granular jamming has recently become popular in soft robotics with widespread applications including industrial gripping, surgical robotics and haptics. Previous work has investigated the use of various techniques that exploit the nature of granular physics to improve jamming performance, however this is generally underrepresented in the literature compared to its potential impact. We present the first research that exploits vibration-based fluidisation actively (e.g., during a grip) to elicit bespoke performance from granular jamming grippers. We augment a conventional universal gripper with a computer-controllled audio exciter, which is attached to the gripper via a 3D printed mount, and build an automated test rig to allow large-scale data collection to explore the effects of active vibration. We show that vibration in soft jamming grippers can improve holding strength. In a series of studies, we show that frequency and amplitude of the waveforms are key determinants to performance, and that jamming performance is also dependent on temporal properties of the induced waveform. We hope to encourage further study focused on active vibrational control of jamming in soft robotics to improve performance and increase diversity of potential applications.
Getting a Grip: in Materio Evolution of Membrane Morphology for Soft Robotic Jamming Grippers
Nov 02, 2021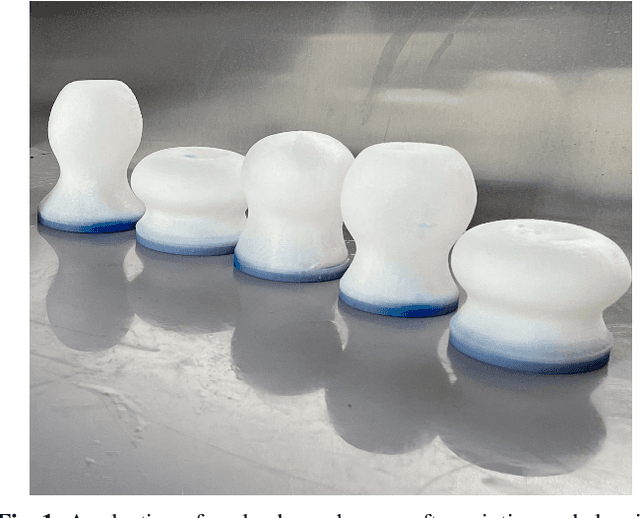
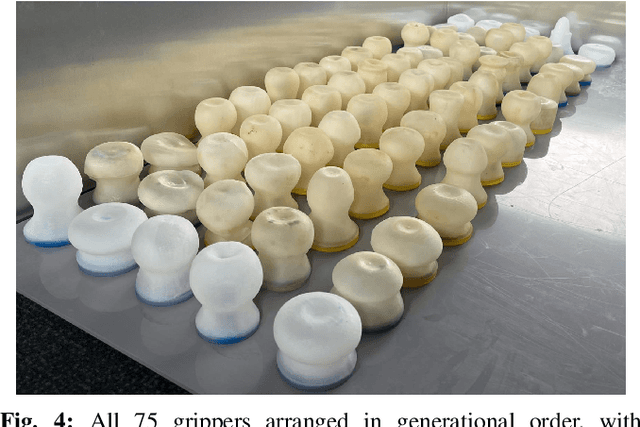
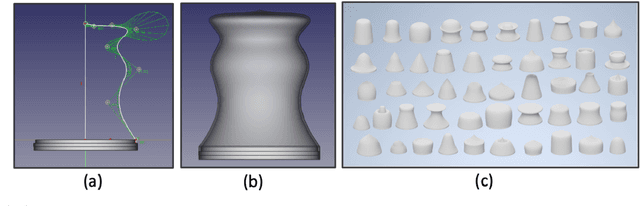

Abstract:The application of granular jamming in soft robotics is a recent and promising new technology offer exciting possibilities for creating higher performance robotic devices. Granular jamming is achieved via the application of a vacuum pressure inside a membrane containing particulate matter, and is particularly interesting from a design perspective, as a myriad of design parameters can potentially be exploited to induce a diverse variety of useful behaviours. To date, the effect of variables such as grain shape and size, as well as membrane material, have been studied as a means of inducing bespoke gripping performance, however the other main contributing factor, membrane morphology, has not been studied due to its particular complexities in both accurate modelling and fabrication. This research presents the first study that optimises membrane morphology for granular jamming grippers, combining multi-material 3D printing and an evolutionary algorithm to search through a varied morphology design space in materio. Entire generations are printed in a single run and gripper retention force is tested and used as a fitness measure. Our approach is relatively scalable, circumvents the need for modelling, and guarantees the real-world performance of the grippers considered. Results show that membrane morphology is a key determinant of gripper performance. Common high performance designs are seen to optimise all three of the main identified mechanisms by which granular grippers generate grip force, are significantly different from a standard gripper morphology, and generalise well across a range of test objects.
Vibration Improves Performance in Granular Jamming Grippers
Sep 22, 2021



Abstract:Granular jamming is a popular soft robotics technology that has seen recent widespread applications including industrial gripping, surgical robotics and haptics. However, to date the field has not fully exploited the fundamental science of the jamming phase transition, which has been rigorously studied in the field of statistical and condensed matter physics. This work introduces vibration as a means to improve the properties of granular jamming grippers through vibratory fluidisation and the exploitation of resonant modes within the granular material. We show that vibration in soft jamming grippers can improve holding strength, reduce the downwards force needed for the gripping action, and lead to a simplified setup where the second air pump, generally used for unjamming, could be removed. In a series of studies, we show that frequency and amplitude of the waveforms are key determinants to performance, and that jamming performance is also dependent on temporal properties of the induced waveform. We hope to encourage further study in transitioning fundamental jamming mechanisms into a soft robotics context to improve performance and increase diversity of applications for granular jamming grippers.
Shape, Size, and Fabrication Effects in 3D Printed Granular Jamming Grippers
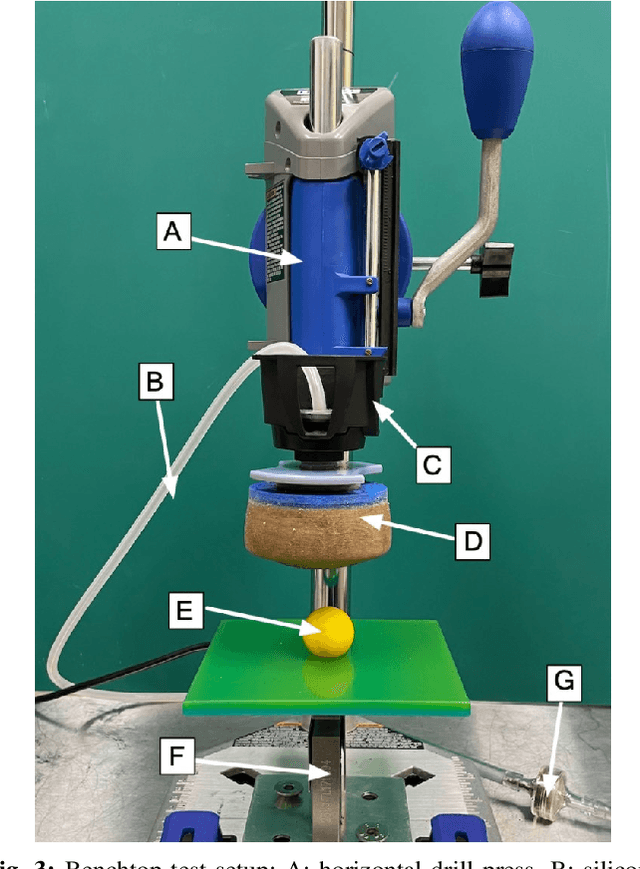
Apr 09, 2021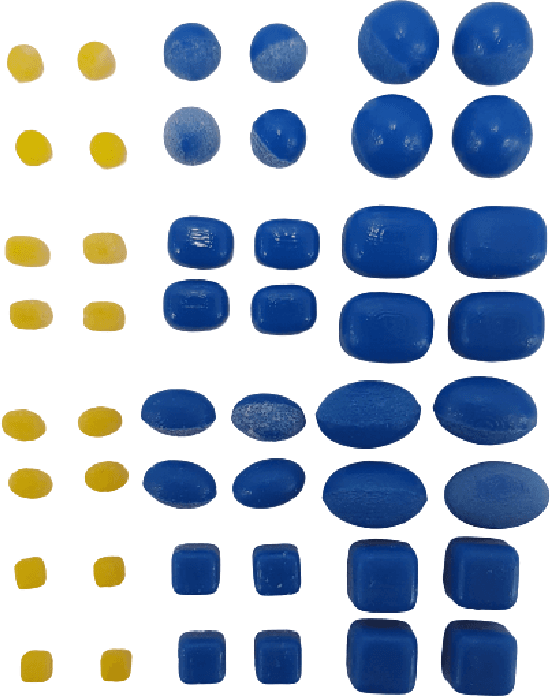
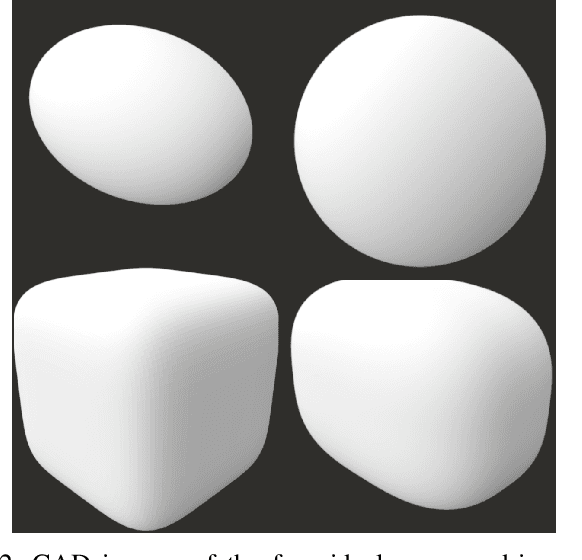

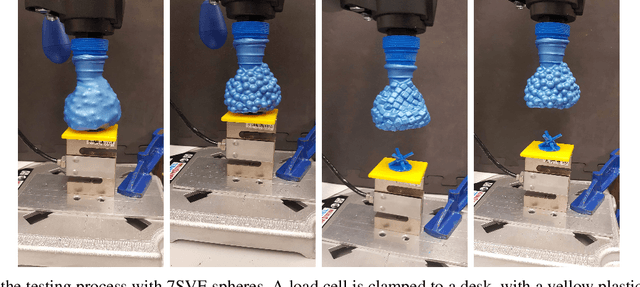
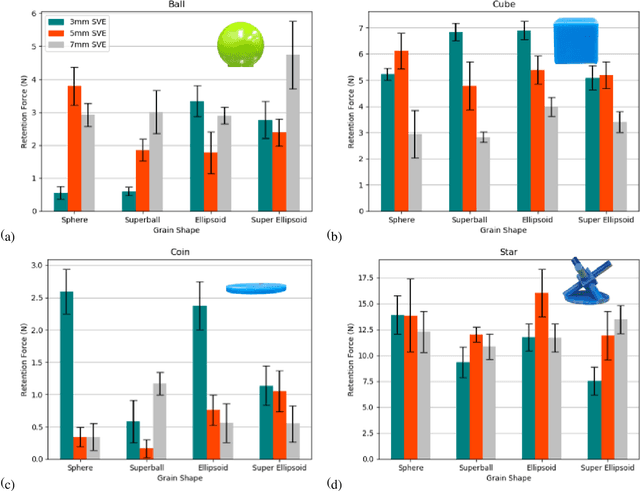
Abstract:Granular jamming is a popular soft actuation mechanism that provides high stiffness variability with minimum volume variation. Jamming is particularly interesting from a design perspective, as a myriad of design parameters can potentially be exploited to induce a diverse variety of useful behaviours. To date, grain shape has been largely ignored. Here, we focus on the use of 3D printing to expose design variables related to grain shape and size. Grains are represented by parameterised superquadrics (superellipsoids); four diverse shapes are investigated along with three size variations. Grains are 3D printed at high resolution and performance is assessed in experimental pull-off testing on a variety of benchmark test objects. We show that grain shape and size are key determinants in granular gripping performance. Moreover, there is no universally-optimal grain shape for gripping. Optical imaging assesses the accuracy of printed shapes compared to their ideal models. Results suggest that optimisation of grain shape is a key enabler for high-performance, bespoke, actuation behaviour and can be exploited to expand the range and performance of granular grippers across a range of diverse usage scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge