Galina Zubkova
MADD: Multi-Agent Drug Discovery Orchestra
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Hit identification is a central challenge in early drug discovery, traditionally requiring substantial experimental resources. Recent advances in artificial intelligence, particularly large language models (LLMs), have enabled virtual screening methods that reduce costs and improve efficiency. However, the growing complexity of these tools has limited their accessibility to wet-lab researchers. Multi-agent systems offer a promising solution by combining the interpretability of LLMs with the precision of specialized models and tools. In this work, we present MADD, a multi-agent system that builds and executes customized hit identification pipelines from natural language queries. MADD employs four coordinated agents to handle key subtasks in de novo compound generation and screening. We evaluate MADD across seven drug discovery cases and demonstrate its superior performance compared to existing LLM-based solutions. Using MADD, we pioneer the application of AI-first drug design to five biological targets and release the identified hit molecules. Finally, we introduce a new benchmark of query-molecule pairs and docking scores for over three million compounds to contribute to the agentic future of drug design.
Gaze into the Heart: A Multi-View Video Dataset for rPPG and Health Biomarkers Estimation
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Progress in remote PhotoPlethysmoGraphy (rPPG) is limited by the critical issues of existing publicly available datasets: small size, privacy concerns with facial videos, and lack of diversity in conditions. The paper introduces a novel comprehensive large-scale multi-view video dataset for rPPG and health biomarkers estimation. Our dataset comprises 3600 synchronized video recordings from 600 subjects, captured under varied conditions (resting and post-exercise) using multiple consumer-grade cameras at different angles. To enable multimodal analysis of physiological states, each recording is paired with a 100 Hz PPG signal and extended health metrics, such as electrocardiogram, arterial blood pressure, biomarkers, temperature, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and stress level. Using this data, we train an efficient rPPG model and compare its quality with existing approaches in cross-dataset scenarios. The public release of our dataset and model should significantly speed up the progress in the development of AI medical assistants.
RuCCoD: Towards Automated ICD Coding in Russian
Feb 28, 2025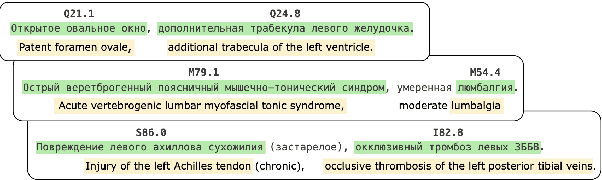
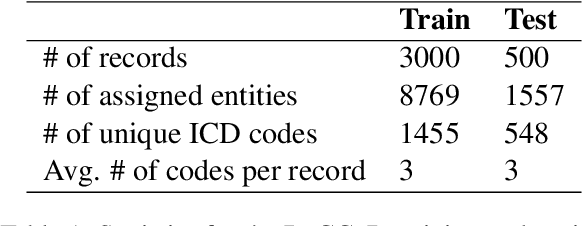
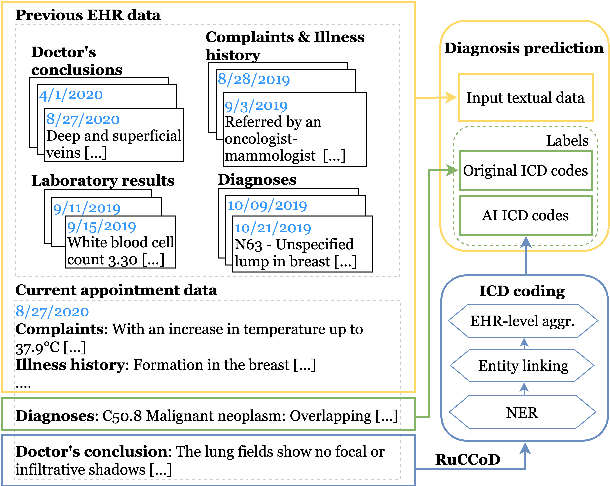
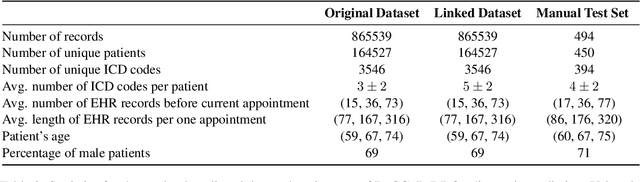
Abstract:This study investigates the feasibility of automating clinical coding in Russian, a language with limited biomedical resources. We present a new dataset for ICD coding, which includes diagnosis fields from electronic health records (EHRs) annotated with over 10,000 entities and more than 1,500 unique ICD codes. This dataset serves as a benchmark for several state-of-the-art models, including BERT, LLaMA with LoRA, and RAG, with additional experiments examining transfer learning across domains (from PubMed abstracts to medical diagnosis) and terminologies (from UMLS concepts to ICD codes). We then apply the best-performing model to label an in-house EHR dataset containing patient histories from 2017 to 2021. Our experiments, conducted on a carefully curated test set, demonstrate that training with the automated predicted codes leads to a significant improvement in accuracy compared to manually annotated data from physicians. We believe our findings offer valuable insights into the potential for automating clinical coding in resource-limited languages like Russian, which could enhance clinical efficiency and data accuracy in these contexts.
MedSyn: LLM-based Synthetic Medical Text Generation Framework
Aug 04, 2024Abstract:Generating synthetic text addresses the challenge of data availability in privacy-sensitive domains such as healthcare. This study explores the applicability of synthetic data in real-world medical settings. We introduce MedSyn, a novel medical text generation framework that integrates large language models with a Medical Knowledge Graph (MKG). We use MKG to sample prior medical information for the prompt and generate synthetic clinical notes with GPT-4 and fine-tuned LLaMA models. We assess the benefit of synthetic data through application in the ICD code prediction task. Our research indicates that synthetic data can increase the classification accuracy of vital and challenging codes by up to 17.8% compared to settings without synthetic data. Furthermore, to provide new data for further research in the healthcare domain, we present the largest open-source synthetic dataset of clinical notes for the Russian language, comprising over 41k samples covering 219 ICD-10 codes.
End-to-end SYNTAX score prediction: benchmark and methods
Jul 29, 2024
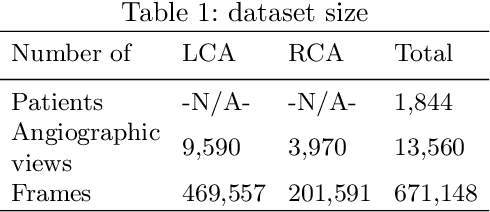
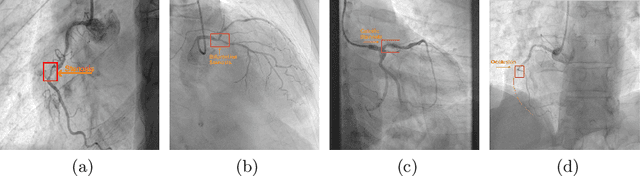
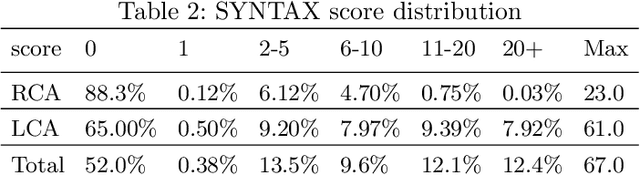
Abstract:The SYNTAX score has become a widely used measure of coronary disease severity , crucial in selecting the optimal mode of revascularization. This paper introduces a new medical regression and classification problem - automatically estimating SYNTAX score from coronary angiography. Our study presents a comprehensive dataset of 1,844 patients, featuring a balanced distribution of individuals with zero and non-zero scores. This dataset includes a first-of-its-kind, complete coronary angiography samples captured through a multi-view X-ray video, allowing one to observe coronary arteries from multiple perspectives. Furthermore, we present a novel, fully automatic end-to-end method for estimating the SYNTAX. For such a difficult task, we have achieved a solid coefficient of determination R2 of 0.51 in score predictions.
GigaPevt: Multimodal Medical Assistant
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:Building an intelligent and efficient medical assistant is still a challenging AI problem. The major limitation comes from the data modality scarceness, which reduces comprehensive patient perception. This demo paper presents the GigaPevt, the first multimodal medical assistant that combines the dialog capabilities of large language models with specialized medical models. Such an approach shows immediate advantages in dialog quality and metric performance, with a 1.18\% accuracy improvement in the question-answering task.
Neural network-based coronary dominance classification of RCA angiograms
Sep 13, 2023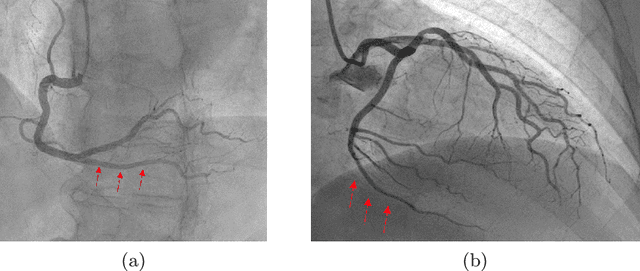
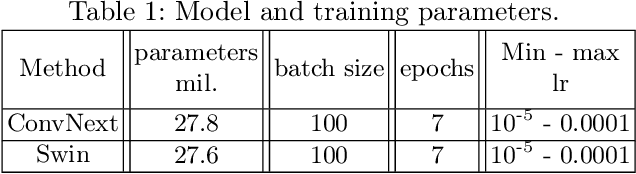
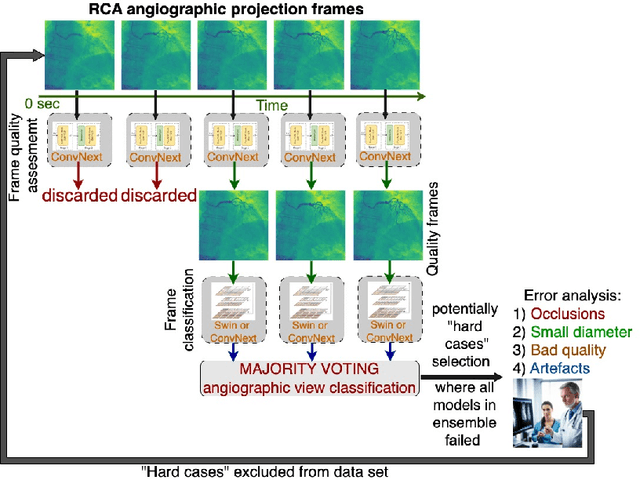
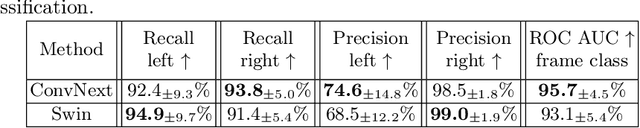
Abstract:Background. Cardiac dominance classification is essential for SYNTAX score estimation, which is a tool used to determine the complexity of coronary artery disease and guide patient selection toward optimal revascularization strategy. Objectives. Cardiac dominance classification algorithm based on the analysis of right coronary artery (RCA) angiograms using neural network Method. We employed convolutional neural network ConvNext and Swin transformer for 2D image (frames) classification, along with a majority vote for cardio angiographic view classification. An auxiliary network was also used to detect irrelevant images which were then excluded from the data set. Our data set consisted of 828 angiographic studies, 192 of them being patients with left dominance. Results. 5-fold cross validation gave the following dominance classification metrics (p=95%): macro recall=93.1%, accuracy=93.5%, macro F1=89.2%. The most common case in which the model regularly failed was RCA occlusion, as it requires utilization of LCA information. Another cause for false prediction is a small diameter combined with poor quality cardio angiographic view. In such cases, cardiac dominance classification can be complex and may require discussion among specialists to reach an accurate conclusion. Conclusion. The use of machine learning approaches to classify cardiac dominance based on RCA alone has been shown to be successful with satisfactory accuracy. However, for higher accuracy, it is necessary to utilize LCA information in the case of an occluded RCA and detect cases where there is high uncertainty.
NeuralSympCheck: A Symptom Checking and Disease Diagnostic Neural Model with Logic Regularization
Jun 02, 2022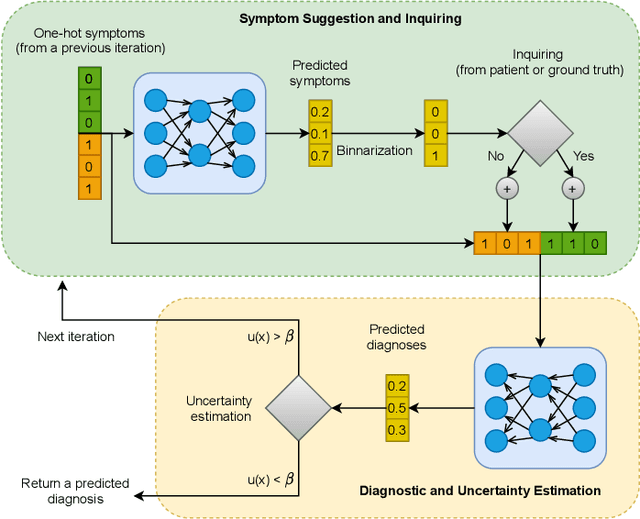
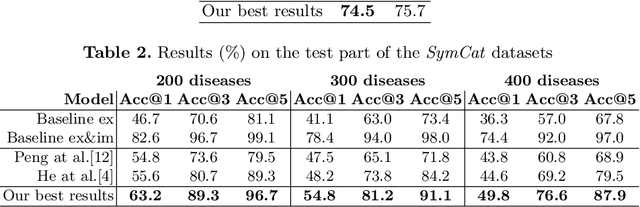
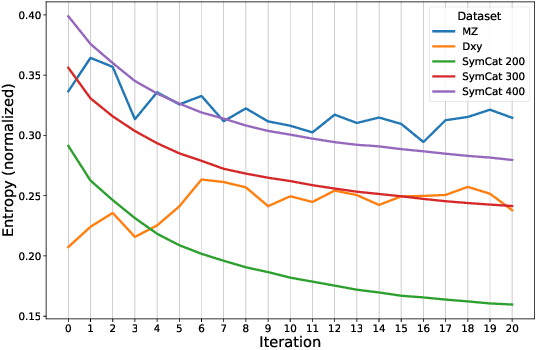
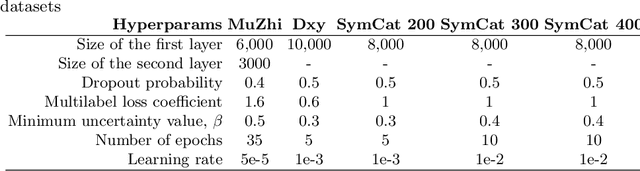
Abstract:The symptom checking systems inquire users for their symptoms and perform a rapid and affordable medical assessment of their condition. The basic symptom checking systems based on Bayesian methods, decision trees, or information gain methods are easy to train and do not require significant computational resources. However, their drawbacks are low relevance of proposed symptoms and insufficient quality of diagnostics. The best results on these tasks are achieved by reinforcement learning models. Their weaknesses are the difficulty of developing and training such systems and limited applicability to cases with large and sparse decision spaces. We propose a new approach based on the supervised learning of neural models with logic regularization that combines the advantages of the different methods. Our experiments on real and synthetic data show that the proposed approach outperforms the best existing methods in the accuracy of diagnosis when the number of diagnoses and symptoms is large.
RuMedBench: A Russian Medical Language Understanding Benchmark
Jan 17, 2022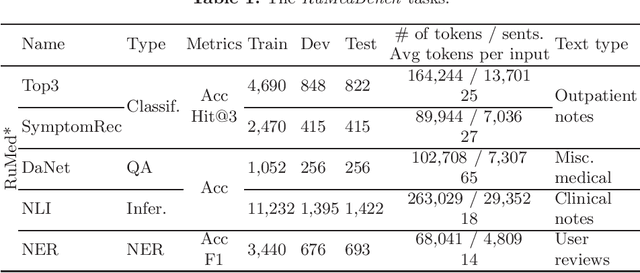
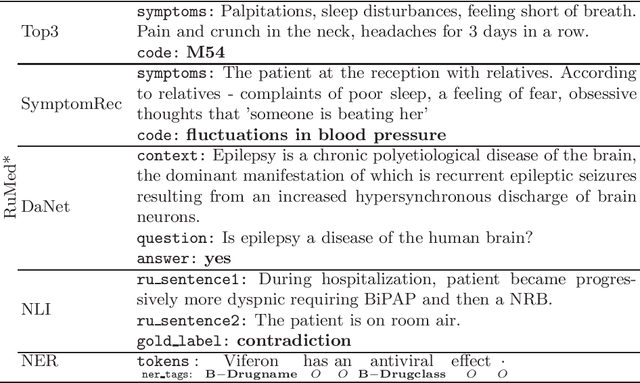
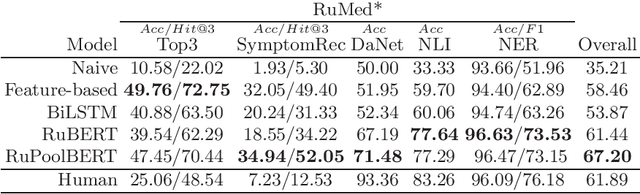
Abstract:The paper describes the open Russian medical language understanding benchmark covering several task types (classification, question answering, natural language inference, named entity recognition) on a number of novel text sets. Given the sensitive nature of the data in healthcare, such a benchmark partially closes the problem of Russian medical dataset absence. We prepare the unified format labeling, data split, and evaluation metrics for new tasks. The remaining tasks are from existing datasets with a few modifications. A single-number metric expresses a model's ability to cope with the benchmark. Moreover, we implement several baseline models, from simple ones to neural networks with transformer architecture, and release the code. Expectedly, the more advanced models yield better performance, but even a simple model is enough for a decent result in some tasks. Furthermore, for all tasks, we provide a human evaluation. Interestingly the models outperform humans in the large-scale classification tasks. However, the advantage of natural intelligence remains in the tasks requiring more knowledge and reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge