G. M. Dilshan Godaliyadda
Quanta Video Restoration
Oct 19, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of single-photon image sensors has opened the door to a plethora of high-speed and low-light imaging applications. However, data collected by these sensors are often 1-bit or few-bit, and corrupted by noise and strong motion. Conventional video restoration methods are not designed to handle this situation, while specialized quanta burst algorithms have limited performance when the number of input frames is low. In this paper, we introduce Quanta Video Restoration (QUIVER), an end-to-end trainable network built on the core ideas of classical quanta restoration methods, i.e., pre-filtering, flow estimation, fusion, and refinement. We also collect and publish I2-2000FPS, a high-speed video dataset with the highest temporal resolution of 2000 frames-per-second, for training and testing. On simulated and real data, QUIVER outperforms existing quanta restoration methods by a significant margin. Code and dataset available at https://github.com/chennuriprateek/Quanta_Video_Restoration-QUIVER-
Reduced Electron Exposure for Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy using Dynamic Sampling
Jun 27, 2017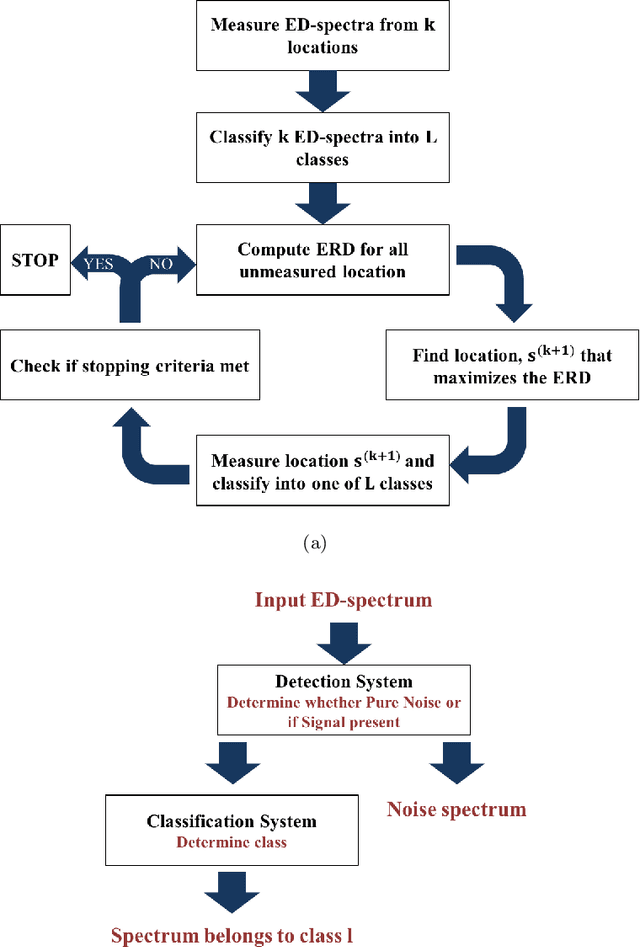
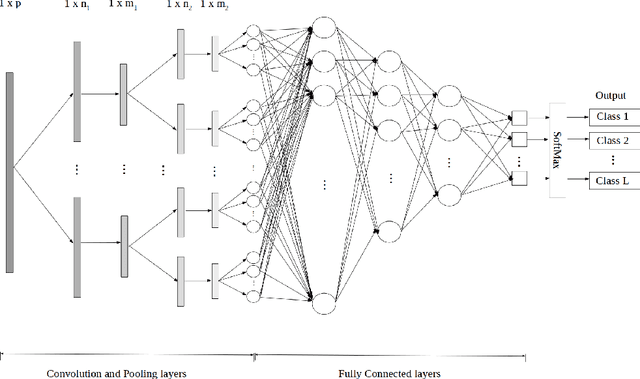
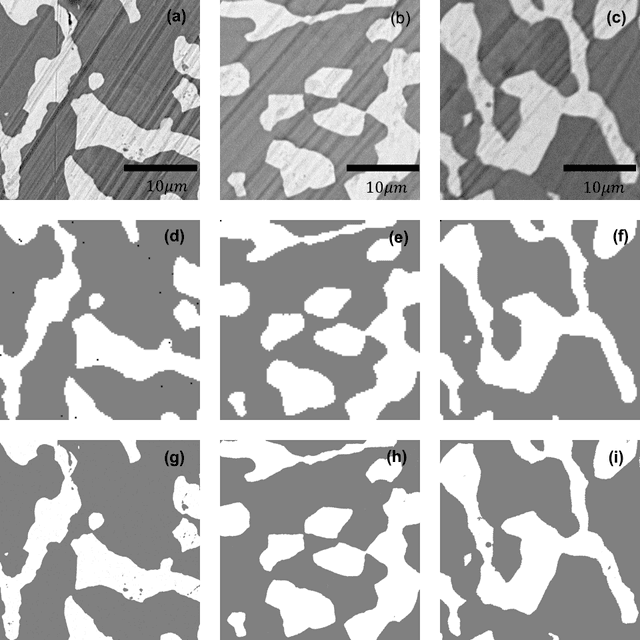
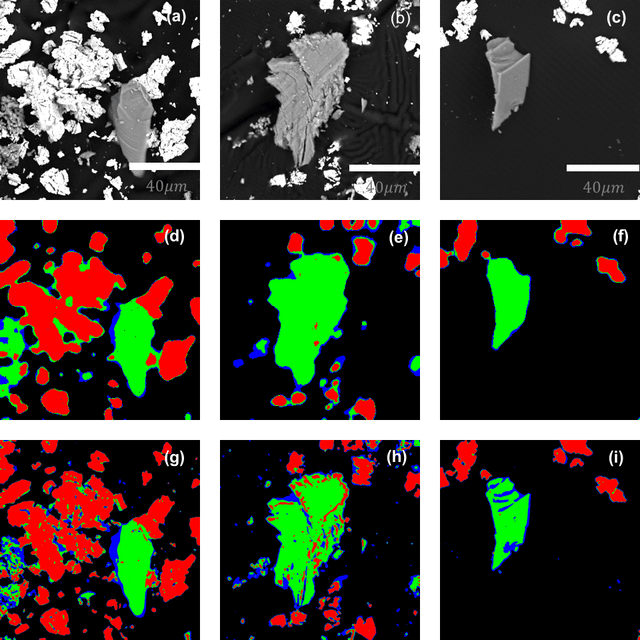
Abstract:Analytical electron microscopy and spectroscopy of biological specimens, polymers, and other beam sensitive materials has been a challenging area due to irradiation damage. There is a pressing need to develop novel imaging and spectroscopic imaging methods that will minimize such sample damage as well as reduce the data acquisition time. The latter is useful for high-throughput analysis of materials structure and chemistry. In this work, we present a novel machine learning based method for dynamic sparse sampling of EDS data using a scanning electron microscope. Our method, based on the supervised learning approach for dynamic sampling algorithm and neural networks based classification of EDS data, allows a dramatic reduction in the total sampling of up to 90%, while maintaining the fidelity of the reconstructed elemental maps and spectroscopic data. We believe this approach will enable imaging and elemental mapping of materials that would otherwise be inaccessible to these analysis techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge