Flavio Ponzina
QMC: Efficient SLM Edge Inference via Outlier-Aware Quantization and Emergent Memories Co-Design
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Deploying Small Language Models (SLMs) on edge platforms is critical for real-time, privacy-sensitive generative AI, yet constrained by memory, latency, and energy budgets. Quantization reduces model size and cost but suffers from device noise in emerging non-volatile memories, while conventional memory hierarchies further limit efficiency. SRAM provides fast access but has low density, DRAM must simultaneously accommodate static weights and dynamic KV caches, which creates bandwidth contention, and Flash, although dense, is primarily used for initialization and remains inactive during inference. These limitations highlight the need for hybrid memory organizations tailored to LLM inference. We propose Outlier-aware Quantization with Memory Co-design (QMC), a retraining-free quantization with a novel heterogeneous memory architecture. QMC identifies inlier and outlier weights in SLMs, storing inlier weights in compact multi-level Resistive-RAM (ReRAM) while preserving critical outliers in high-precision on-chip Magnetoresistive-RAM (MRAM), mitigating noise-induced degradation. On language modeling and reasoning benchmarks, QMC outperforms and matches state-of-the-art quantization methods using advanced algorithms and hybrid data formats, while achieving greater compression under both algorithm-only evaluation and realistic deployment settings. Specifically, compared against SoTA quantization methods on the latest edge AI platform, QMC reduces memory usage by 6.3x-7.3x, external data transfers by 7.6x, energy by 11.7x, and latency by 12.5x when compared to FP16, establishing QMC as a scalable, deployment-ready co-design for efficient on-device inference.
FaTRQ: Tiered Residual Quantization for LLM Vector Search in Far-Memory-Aware ANNS Systems
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Approximate Nearest-Neighbor Search (ANNS) is a key technique in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), enabling rapid identification of the most relevant high-dimensional embeddings from massive vector databases. Modern ANNS engines accelerate this process using prebuilt indexes and store compressed vector-quantized representations in fast memory. However, they still rely on a costly second-pass refinement stage that reads full-precision vectors from slower storage like SSDs. For modern text and multimodal embeddings, these reads now dominate the latency of the entire query. We propose FaTRQ, a far-memory-aware refinement system using tiered memory that eliminates the need to fetch full vectors from storage. It introduces a progressive distance estimator that refines coarse scores using compact residuals streamed from far memory. Refinement stops early once a candidate is provably outside the top-k. To support this, we propose tiered residual quantization, which encodes residuals as ternary values stored efficiently in far memory. A custom accelerator is deployed in a CXL Type-2 device to perform low-latency refinement locally. Together, FaTRQ improves the storage efficiency by 2.4$\times$ and improves the throughput by up to 9$ \times$ than SOTA GPU ANNS system.
DPQ-HD: Post-Training Compression for Ultra-Low Power Hyperdimensional Computing
May 08, 2025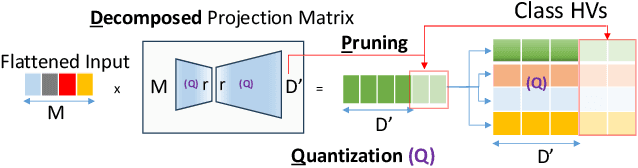
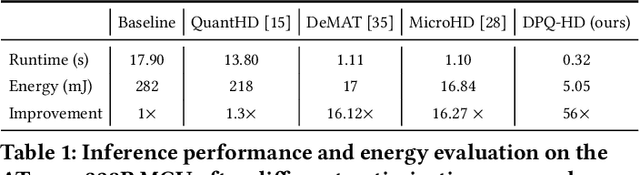
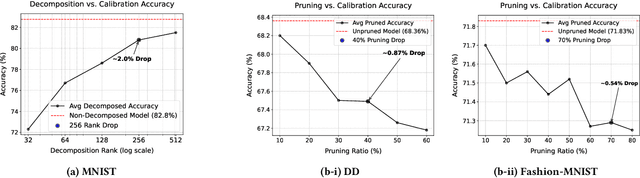
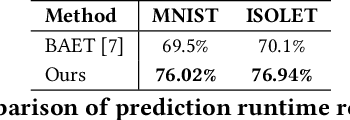
Abstract:Hyperdimensional Computing (HDC) is emerging as a promising approach for edge AI, offering a balance between accuracy and efficiency. However, current HDC-based applications often rely on high-precision models and/or encoding matrices to achieve competitive performance, which imposes significant computational and memory demands, especially for ultra-low power devices. While recent efforts use techniques like precision reduction and pruning to increase the efficiency, most require retraining to maintain performance, making them expensive and impractical. To address this issue, we propose a novel Post Training Compression algorithm, Decomposition-Pruning-Quantization (DPQ-HD), which aims at compressing the end-to-end HDC system, achieving near floating point performance without the need of retraining. DPQ-HD reduces computational and memory overhead by uniquely combining the above three compression techniques and efficiently adapts to hardware constraints. Additionally, we introduce an energy-efficient inference approach that progressively evaluates similarity scores such as cosine similarity and performs early exit to reduce the computation, accelerating prediction inference while maintaining accuracy. We demonstrate that DPQ-HD achieves up to 20-100x reduction in memory for image and graph classification tasks with only a 1-2% drop in accuracy compared to uncompressed workloads. Lastly, we show that DPQ-HD outperforms the existing post-training compression methods and performs better or at par with retraining-based state-of-the-art techniques, requiring significantly less overall optimization time (up to 100x) and faster inference (up to 56x) on a microcontroller
Offload Rethinking by Cloud Assistance for Efficient Environmental Sound Recognition on LPWANs
Feb 21, 2025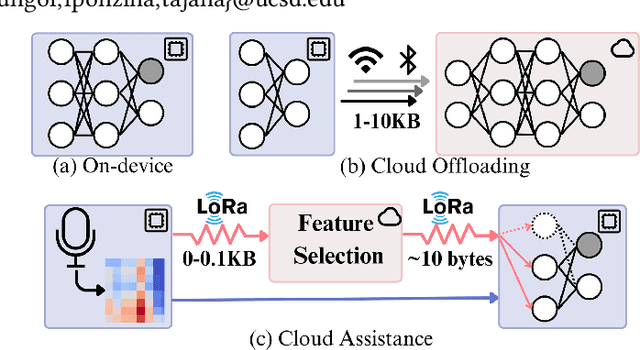
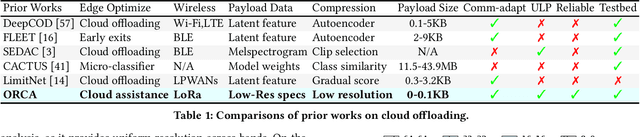

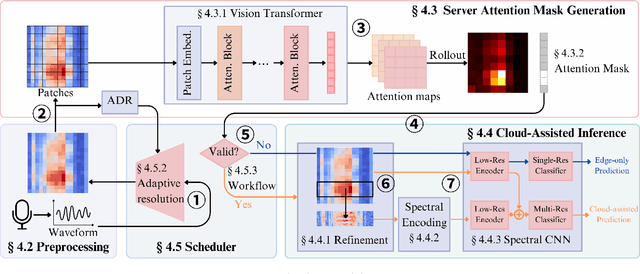
Abstract:Learning-based environmental sound recognition has emerged as a crucial method for ultra-low-power environmental monitoring in biological research and city-scale sensing systems. These systems usually operate under limited resources and are often powered by harvested energy in remote areas. Recent efforts in on-device sound recognition suffer from low accuracy due to resource constraints, whereas cloud offloading strategies are hindered by high communication costs. In this work, we introduce ORCA, a novel resource-efficient cloud-assisted environmental sound recognition system on batteryless devices operating over the Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs), targeting wide-area audio sensing applications. We propose a cloud assistance strategy that remedies the low accuracy of on-device inference while minimizing the communication costs for cloud offloading. By leveraging a self-attention-based cloud sub-spectral feature selection method to facilitate efficient on-device inference, ORCA resolves three key challenges for resource-constrained cloud offloading over LPWANs: 1) high communication costs and low data rates, 2) dynamic wireless channel conditions, and 3) unreliable offloading. We implement ORCA on an energy-harvesting batteryless microcontroller and evaluate it in a real world urban sound testbed. Our results show that ORCA outperforms state-of-the-art methods by up to $80 \times$ in energy savings and $220 \times$ in latency reduction while maintaining comparable accuracy.
SpecPCM: A Low-power PCM-based In-Memory Computing Accelerator for Full-stack Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Mass spectrometry (MS) is essential for proteomics and metabolomics but faces impending challenges in efficiently processing the vast volumes of data. This paper introduces SpecPCM, an in-memory computing (IMC) accelerator designed to achieve substantial improvements in energy and delay efficiency for both MS spectral clustering and database (DB) search. SpecPCM employs analog processing with low-voltage swing and utilizes recently introduced phase change memory (PCM) devices based on superlattice materials, optimized for low-voltage and low-power programming. Our approach integrates contributions across multiple levels: application, algorithm, circuit, device, and instruction sets. We leverage a robust hyperdimensional computing (HD) algorithm with a novel dimension-packing method and develop specialized hardware for the end-to-end MS pipeline to overcome the non-ideal behavior of PCM devices. We further optimize multi-level PCM devices for different tasks by using different materials. We also perform a comprehensive design exploration to improve energy and delay efficiency while maintaining accuracy, exploring various combinations of hardware and software parameters controlled by the instruction set architecture (ISA). SpecPCM, with up to three bits per cell, achieves speedups of up to 82x and 143x for MS clustering and DB search tasks, respectively, along with a four-orders-of-magnitude improvement in energy efficiency compared with state-of-the-art CPU/GPU tools.
E-QUARTIC: Energy Efficient Edge Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks for Resource-Optimized Learning
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Ensemble learning is a meta-learning approach that combines the predictions of multiple learners, demonstrating improved accuracy and robustness. Nevertheless, ensembling models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) result in high memory and computing overhead, preventing their deployment in embedded systems. These devices are usually equipped with small batteries that provide power supply and might include energy-harvesting modules that extract energy from the environment. In this work, we propose E-QUARTIC, a novel Energy Efficient Edge Ensembling framework to build ensembles of CNNs targeting Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based embedded systems. Our design outperforms single-instance CNN baselines and state-of-the-art edge AI solutions, improving accuracy and adapting to varying energy conditions while maintaining similar memory requirements. Then, we leverage the multi-CNN structure of the designed ensemble to implement an energy-aware model selection policy in energy-harvesting AI systems. We show that our solution outperforms the state-of-the-art by reducing system failure rate by up to 40% while ensuring higher average output qualities. Ultimately, we show that the proposed design enables concurrent on-device training and high-quality inference execution at the edge, limiting the performance and energy overheads to less than 0.04%.
MicroHD: An Accuracy-Driven Optimization of Hyperdimensional Computing Algorithms for TinyML systems
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:Hyperdimensional computing (HDC) is emerging as a promising AI approach that can effectively target TinyML applications thanks to its lightweight computing and memory requirements. Previous works on HDC showed that limiting the standard 10k dimensions of the hyperdimensional space to much lower values is possible, reducing even more HDC resource requirements. Similarly, other studies demonstrated that binary values can be used as elements of the generated hypervectors, leading to significant efficiency gains at the cost of some degree of accuracy degradation. Nevertheless, current optimization attempts do not concurrently co-optimize HDC hyper-parameters, and accuracy degradation is not directly controlled, resulting in sub-optimal HDC models providing several applications with unacceptable output qualities. In this work, we propose MicroHD, a novel accuracy-driven HDC optimization approach that iteratively tunes HDC hyper-parameters, reducing memory and computing requirements while ensuring user-defined accuracy levels. The proposed method can be applied to HDC implementations using different encoding functions, demonstrates good scalability for larger HDC workloads, and achieves compression and efficiency gains up to 200x when compared to baseline implementations for accuracy degradations lower than 1%.
Bit-Line Computing for CNN Accelerators Co-Design in Edge AI Inference
Sep 12, 2022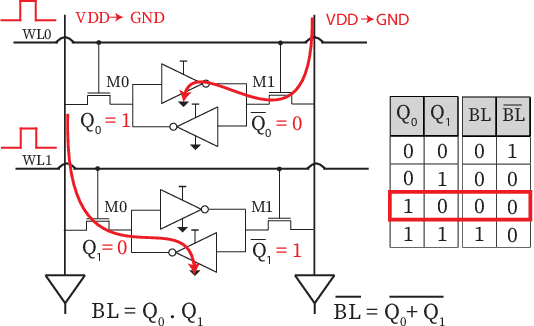

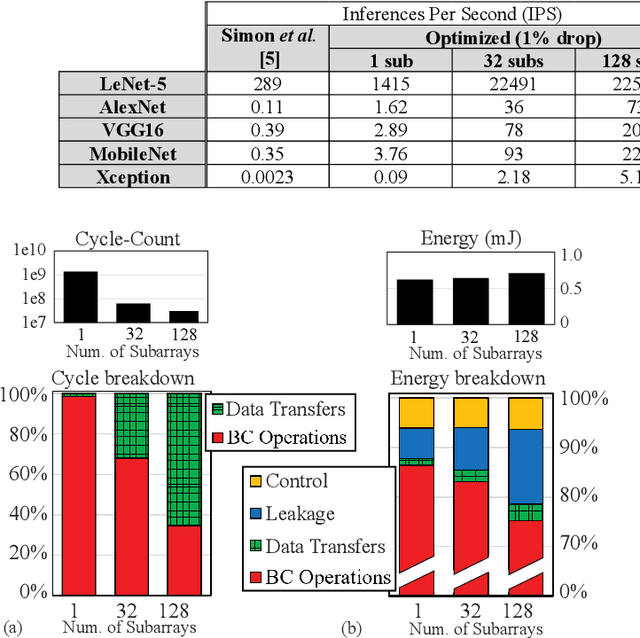
Abstract:By supporting the access of multiple memory words at the same time, Bit-line Computing (BC) architectures allow the parallel execution of bit-wise operations in-memory. At the array periphery, arithmetic operations are then derived with little additional overhead. Such a paradigm opens novel opportunities for Artificial Intelligence (AI) at the edge, thanks to the massive parallelism inherent in memory arrays and the extreme energy efficiency of computing in-situ, hence avoiding data transfers. Previous works have shown that BC brings disruptive efficiency gains when targeting AI workloads, a key metric in the context of emerging edge AI scenarios. This manuscript builds on these findings by proposing an end-to-end framework that leverages BC-specific optimizations to enable high parallelism and aggressive compression of AI models. Our approach is supported by a novel hardware module performing real-time decoding, as well as new algorithms to enable BC-friendly model compression. Our hardware/software approach results in a 91% energy savings (for a 1% accuracy degradation constraint) regarding state-of-the-art BC computing approaches.
An Error-Based Approximation Sensing Circuit for Event-Triggered, Low Power Wearable Sensors
Jun 25, 2021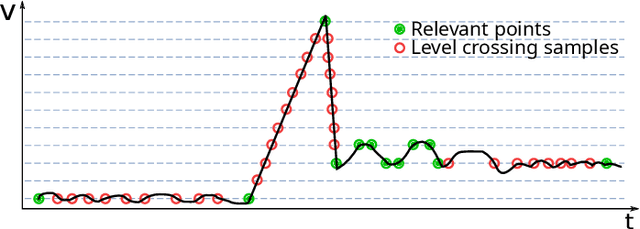
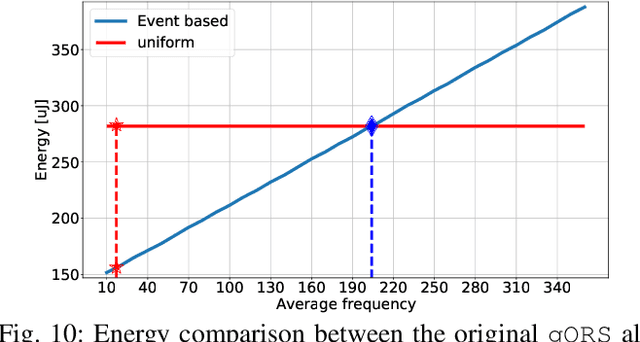
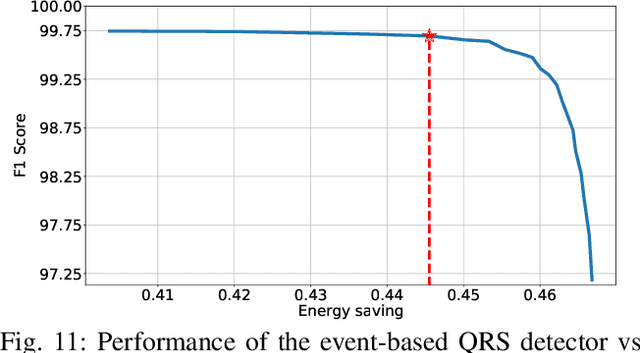
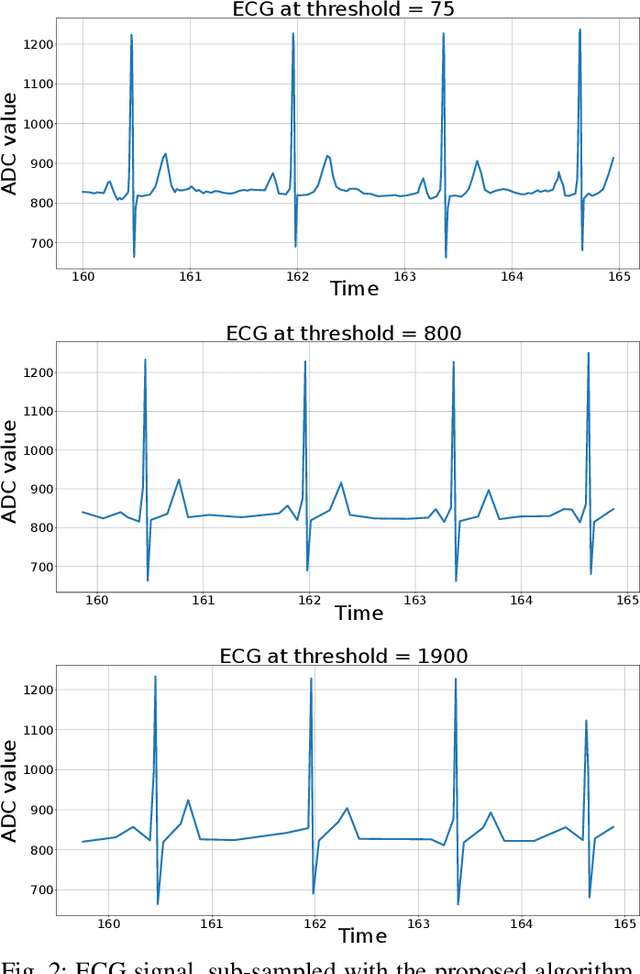
Abstract:Event-based sensors have the potential to optimize energy consumption at every stage in the signal processing pipeline, including data acquisition, transmission, processing and storage. However, almost all state-of-the-art systems are still built upon the classical Nyquist-based periodic signal acquisition. In this work, we design and validate the Polygonal Approximation Sampler (PAS), a novel circuit to implement a general-purpose event-based sampler using a polygonal approximation algorithm as the underlying sampling trigger. The circuit can be dynamically reconfigured to produce a coarse or a detailed reconstruction of the analog input, by adjusting the error threshold of the approximation. The proposed circuit is designed at the Register Transfer Level and processes each input sample received from the ADC in a single clock cycle. The PAS has been tested with three different types of archetypal signals captured by wearable devices (electrocardiogram, accelerometer and respiration data) and compared with a standard periodic ADC. These tests show that single-channel signals, with slow variations and constant segments (like the used single-lead ECG and the respiration signals) take great advantage from the used sampling technique, reducing the amount of data used up to 99% without significant performance degradation. At the same time, multi-channel signals (like the six-dimensional accelerometer signal) can still benefit from the designed circuit, achieving a reduction factor up to 80% with minor performance degradation. These results open the door to new types of wearable sensors with reduced size and higher battery lifetime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge